Ritalin
Evidence Based Answers
4 Studies: The Long Term Effects of Methylphenidate (Ritalin) in Adults
Published: August 17, 2024
Studies Summary
💊
Effectiveness of Methylphenidate in Reducing ADHD Symptoms
Studies consistently show that methylphenidate is effective in reducing ADHD symptoms in adults, with significant improvements noted in both short-term and long-term trials. However, the extent of improvement varies among individuals.
⚠️
Common Adverse Effects Over Long-Term Use
Long-term use of methylphenidate in adults is associated with mild but common side effects like decreased appetite, dry mouth, and heart palpitations. These side effects need to be monitored to ensure they don’t impact long-term health.
🧠
Cognitive Function Improvement in Adults
Methylphenidate has been shown to improve cognitive functions such as memory and attention in adults with ADHD, which can significantly help with daily challenges. However, the extent of these cognitive benefits may differ between individuals.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults

Peer Reviewed Study 1
Long-Term Effects of Methylphenidate on ADHD Symptoms and Social Adjustment in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Overview of Methylphenidate's Long-Term Effects in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Evidence of Methylphenidate's Efficacy in Treating Adult ADHD
Peer Reviewed Study 4
Short-Term Efficacy of Methylphenidate in Adults with ADHD
Background: Effectiveness of Methylphenidate in Adults: A Closer Look at the Data
Methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin, is used to treat ADHD in adults. Over time, its effectiveness varies. Some studies show significant improvement in symptoms like concentration and calmness, while others report more moderate outcomes. For example, early studies found that 8 out of 11 adults showed noticeable improvements, but later studies indicated that only 25% to 57% of adults responded positively.
In contrast, a more recent controlled trial with stricter diagnostic criteria reported a 78% positive response rate. This shows that the effectiveness of methylphenidate may depend on individual factors and the specific criteria used in studies.
In contrast, a more recent controlled trial with stricter diagnostic criteria reported a 78% positive response rate. This shows that the effectiveness of methylphenidate may depend on individual factors and the specific criteria used in studies.

“
Later studies indicated therapeutic response rates to methylphenidate in 25% to 57% of adults with ADHD-like symptoms. This response rate is less than that typically seen in children with ADHD.
“
The authors of the recently published COMPAS trial found that after 1 year of treatment, MPH 'maintained' the advantage over placebo in a number of efficacy outcomes.
Background: Understanding the Long-Term Safety and Common Side Effects of Methylphenidate
Common side effects of methylphenidate in adults include decreased appetite, dry mouth, and heart palpitations. These effects are usually mild and temporary but can be bothersome. For instance, about 20% of adults experience decreased appetite, while 15% report dry mouth. Heart palpitations are less common, affecting around 13% of users.
Although these side effects are generally mild, they may still impact day-to-day activities. In some cases, they might lead to treatment discontinuation, especially if the side effects persist or become severe.
Although these side effects are generally mild, they may still impact day-to-day activities. In some cases, they might lead to treatment discontinuation, especially if the side effects persist or become severe.

“
The most common adverse events related to long-term treatment with MPH are decreased appetite (~ 20%), dry mouth (15%), heart palpitations (13%), gastrointestinal infections (~ 10%), and agitation/feeling restless (~ 10%).
“
Consistent elevations in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (3 to 5 mmHg) and heart rate (five beats per minute) have been reported to result from stimulant treatment of ADHD in adults.
Background: Exploring the Cognitive Benefits of Methylphenidate in Adults with ADHD
Methylphenidate can improve certain cognitive functions in adults with ADHD, such as memory, learning, and attention. For example, studies have shown positive results in tests of memory and learning skills, both verbal and non-verbal. These cognitive benefits, however, can vary among individuals, and the exact mechanisms by which methylphenidate enhances these functions are still not fully understood.
It's also worth noting that the drug may have different effects depending on individual brain chemistry and the severity of ADHD symptoms.
It's also worth noting that the drug may have different effects depending on individual brain chemistry and the severity of ADHD symptoms.

“
Methylphenidate has been found to improve certain aspects of cognitive functioning in those who have suffered TBI... Significant positive results have been found in tests of memory and learning skills, both verbal and non-verbal fluency and attention.
Background: Managing the Addiction Risks of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate has the potential for abuse and addiction, particularly at higher doses. While therapeutic doses for ADHD are generally safe and do not activate the brain's reward system, excessive doses can lead to addiction.
This occurs because high doses trigger changes in specific neurons that contribute to addictive behaviors. It's important to manage the dosage carefully and be aware of the signs of misuse to prevent dependency.
This occurs because high doses trigger changes in specific neurons that contribute to addictive behaviors. It's important to manage the dosage carefully and be aware of the signs of misuse to prevent dependency.

“
The abuse potential of methylphenidate is another issue that has received considerable attention. Methylphenidate and cocaine both bind to the dopamine transporter and compete for the same binding sites in the striatum.
“
The therapeutic dosages for ADHD or narcolepsy that physicians prescribe are not harmful enough to activate the reward system within the CNS, known as the nucleus accumbens. However, excessively higher dosages taken by those who intentionally abuse the drug lead to an overexpression of deltaFosB, a transcriptional activator, in specific neurons within the striatum.
Background: Cardiovascular Considerations with Long-Term Use of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate may cause increases in heart rate and blood pressure in some adults. These effects are typically mild, with systolic and diastolic blood pressure increasing by 3 to 5 mmHg, and heart rate rising by about five beats per minute.
However, these changes could be more concerning for those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Long-term studies suggest that these cardiovascular effects do not diminish over time, which is why regular monitoring during treatment is recommended.
However, these changes could be more concerning for those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Long-term studies suggest that these cardiovascular effects do not diminish over time, which is why regular monitoring during treatment is recommended.

“
Consistent elevations in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (3 to 5 mmHg) and heart rate (five beats per minute) have been reported to result from stimulant treatment of ADHD in adults.
“
There are reports that methylphenidate may increase heart rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressure, so it must be used with caution in patients whose cardiovascular conditions may be aggravated.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Overview of Methylphenidate's Long-Term Effects in Adults
Methylphenidate (MPH) is widely used to treat ADHD in adults, primarily by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and noradrenaline. It has been shown to be moderately effective in managing ADHD symptoms and emotional regulation deficits. The most common side effects of long-term use include decreased appetite, dry mouth, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal infections, and agitation or restlessness.
This abstract provides a comprehensive overview of the pharmacology and clinical utility of MPH in adult ADHD patients.
This abstract provides a comprehensive overview of the pharmacology and clinical utility of MPH in adult ADHD patients.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Evidence of Methylphenidate's Efficacy in Treating Adult ADHD
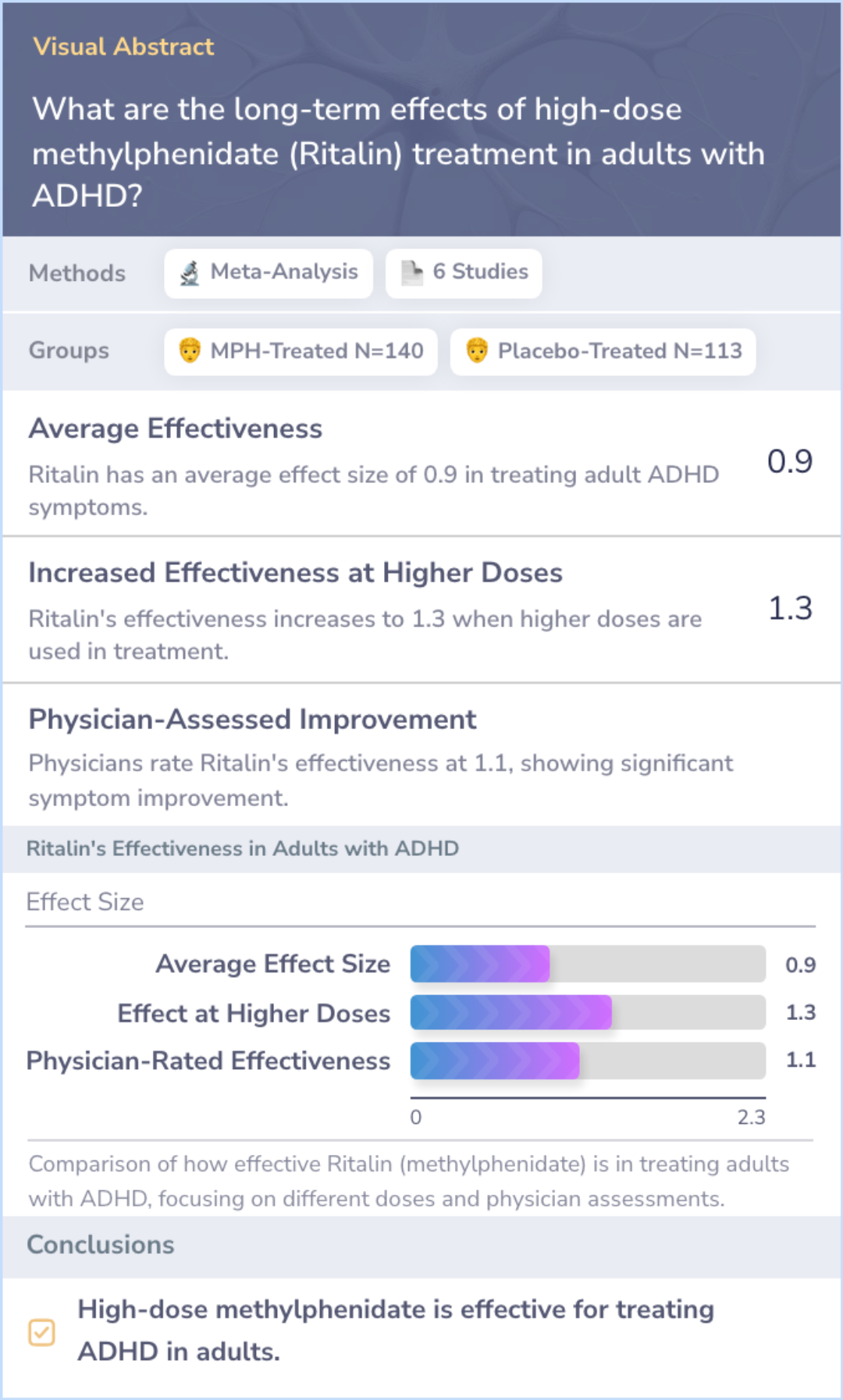
This meta-analysis reviewed six studies focusing on adults with ADHD treated with methylphenidate (MPH). The studies involved 140 adults treated with MPH and 113 given a placebo. The analysis found that higher doses of MPH led to greater improvements in symptoms. The mean effect size was 0.9, and when treatment was optimized with higher doses, the effect size increased to 1.3. These findings provide strong evidence that MPH is effective in treating ADHD in adults.
The analysis also showed that the efficacy of MPH in adults is similar to what has been observed in children and adolescents.
The analysis also showed that the efficacy of MPH in adults is similar to what has been observed in children and adolescents.

Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Short-Term Efficacy of Methylphenidate in Adults with ADHD
This study explores the short-term effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) in adults with ADHD, using a double-blind randomized cross-over trial. Results show that 38-51% of adults responded positively to the medication, compared to 7-18% on placebo, indicating significant effectiveness.
Although the study found that side effects were common, those directly related to methylphenidate were few and generally mild. These findings support the short-term efficacy and tolerability of methylphenidate in adults.
Although the study found that side effects were common, those directly related to methylphenidate were few and generally mild. These findings support the short-term efficacy and tolerability of methylphenidate in adults.

Key Takeaways
Conclusions
The long-term effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) in adults paint a nuanced picture. On one hand, the medication is effective in managing ADHD symptoms, with many adults experiencing significant improvements in their daily lives. On the other hand, there's a real need to be mindful of the potential risks, like cardiovascular issues and the possibility of addiction. The studies highlight how important it is to tailor treatment to each individual, keeping a close eye on both the benefits and any emerging side effects. Ultimately, while methylphenidate can be a valuable tool, its long-term use requires careful consideration to ensure it remains both effective and safe.

Evidence Summary
Variability in Methylphenidate’s Long-Term Effectiveness
Methylphenidate is known to treat ADHD in adults, but its long-term effectiveness shows varied results. While some patients see significant improvement in their symptoms, others experience moderate benefits. This difference suggests that methylphenidate's effectiveness isn't uniform for everyone.
Understanding individual responses can help tailor treatment plans and ensure better long-term management of ADHD symptoms in adults.
Understanding individual responses can help tailor treatment plans and ensure better long-term management of ADHD symptoms in adults.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate's Influence on Impulsive Decisions
This article investigates the impact of methylphenidate on impulsive decision-making by examining how the drug influences choices involving delay and reward. The focus is on whether methylphenidate makes individuals more or less impulsive. By understanding these effects, the study aims to shed light on how the drug might alter the level of impulsiveness in its users.
The findings may offer insights into the complex relationship between methylphenidate use and impulsive behavior, contributing to a broader understanding of its impact on decision-making processes.
The findings may offer insights into the complex relationship between methylphenidate use and impulsive behavior, contributing to a broader understanding of its impact on decision-making processes.
Evidence Summary
ADHD and Response Inhibition: Continuous Performance Test Challenges
Research into response inhibition shows that adults with ADHD struggle more than both typical adults and those with anxiety when it comes to the Continuous Performance Test, a key measure of attention and impulse control. These findings highlight specific challenges in managing ADHD symptoms, particularly in tasks requiring sustained focus.
Differences across other tests might be linked to how they assess various brain functions, suggesting that ADHD-related deficits may manifest uniquely depending on the test used.
Differences across other tests might be linked to how they assess various brain functions, suggesting that ADHD-related deficits may manifest uniquely depending on the test used.
Evidence Summary
Ritalin's Broad Cognitive Effects
Ritalin isn't just for treating ADHD; it can also sharpen focus, improve attention, and boost memory and alertness. While commonly prescribed for ADHD, its cognitive effects go beyond symptom management.
The medication's ability to enhance these mental faculties highlights its broader impacts on cognition, making it a key tool in managing these challenges in daily life.
The medication's ability to enhance these mental faculties highlights its broader impacts on cognition, making it a key tool in managing these challenges in daily life.