Strattera Paper Database
Visual Abstract
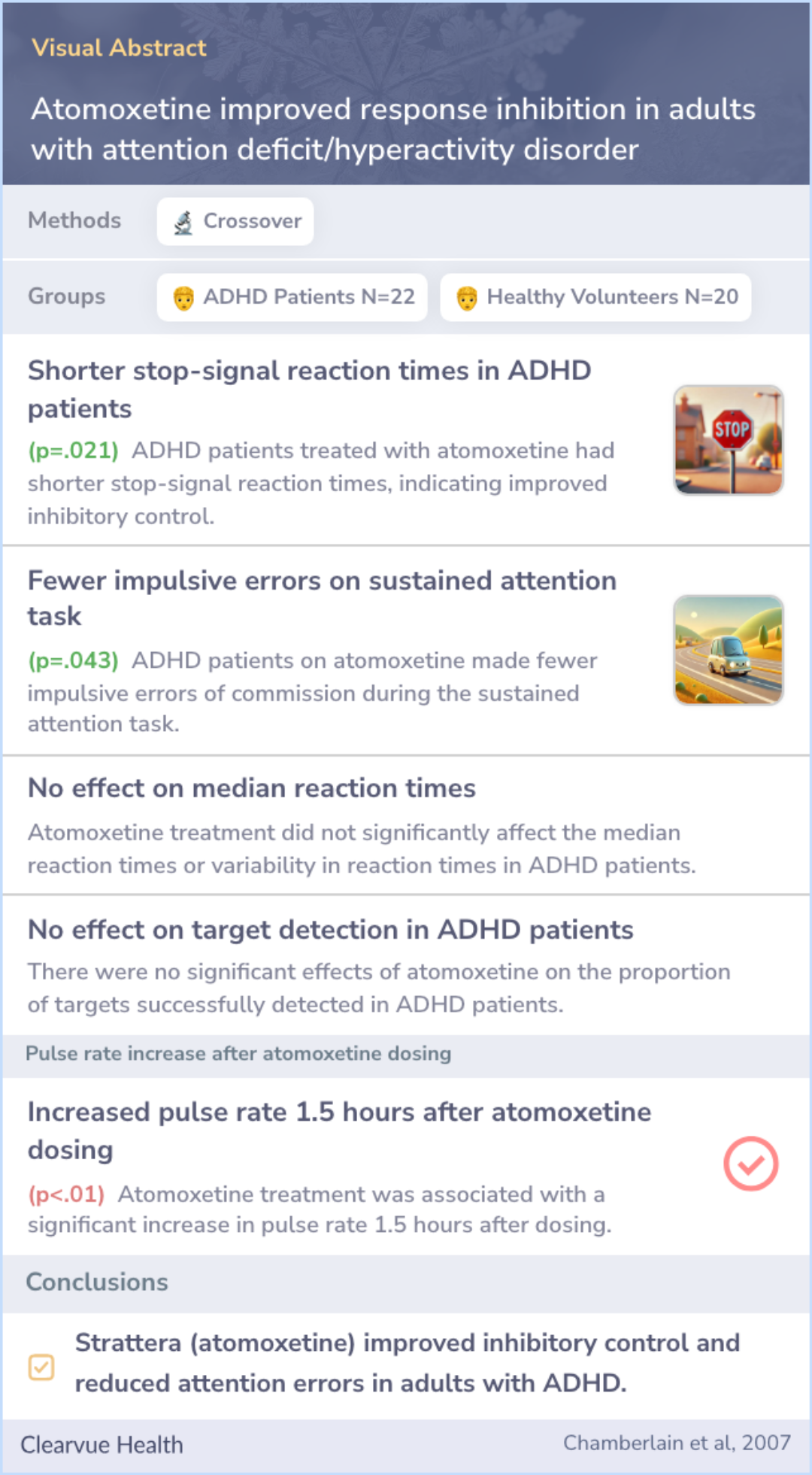
Atomoxetine improved response inhibition in adults with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Atomoxetine and ADHD
October 25, 2024
author
Chamberlain SR, Del Campo N, Dowson J, Müller U, Clark L, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ
journal
Biol Psychiatry
Date Published
2007-11-01
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers aimed to determine if a single oral dose of Strattera (atomoxetine) could improve cognitive functions in adults with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
The study found that Strattera (atomoxetine) improved response inhibition and reduced errors in sustained attention among adults with ADHD.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with existing evidence that Strattera (atomoxetine) can enhance cognitive functions in ADHD, particularly in controlling impulsive behaviors, suggesting its potential in treating other disorders involving impulsivity.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to evaluate how a single dose of atomoxetine affects cognitive function in adults with ADHD. Researchers focused on aspects like response inhibition. The findings show that atomoxetine helped improve inhibitory control in patients, while some working memory issues persisted. This suggests that while the medication can enhance certain cognitive functions, other challenges may remain for those with ADHD.
The study raises questions about how ADHD medications may enhance cognitive function even in those without ADHD, highlighting ethical concerns.
The study raises questions about how ADHD medications may enhance cognitive function even in those without ADHD, highlighting ethical concerns.
Abstract: background
Atomoxetine, a highly selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), shows efficacy in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Compared with psychostimulants, atomoxetine has a distinct mode of brain action and potential...more

Study Aim
"The aim of our study was to evaluate the cognitive effects of acute atomoxetine treatment in adults with ADHD for the first time."
Cognitive Enhancement Issues
"The possibility of cognitive enhancement in people without neuropsychiatric disorders using ADHD medications raises important ethical and legislative issues."
Performance Improvement
"When on atomoxetine, ADHD patients no longer showed deficits in stop-signal response inhibition, although the working memory deficit remained."
Study Summary
Methods
In this study, 22 adults diagnosed with ADHD received a single 60 mg dose of Strattera (atomoxetine). To compare its effects, the study used a placebo-controlled, double-blind design, meaning neither the participants nor the researchers knew who received the actual medication.
Cognitive tests measured response inhibition, attention, memory, and problem-solving. These results were then compared with data from 20 healthy volunteers who did not have ADHD.
Cognitive tests measured response inhibition, attention, memory, and problem-solving. These results were then compared with data from 20 healthy volunteers who did not have ADHD.
Abstract: methods
Twenty-two adults with DSM-IV ADHD were administered a single oral dose of atomoxetine (60 mg) in a placebo-controlled double-blind crossover design. Cognitive effects were assessed using stop-signal, sustained attention, spatial working memory, and ...more
Study Summary
Results
The study found that ADHD patients who took the placebo struggled more with self-control and memory tasks compared to healthy individuals. However, after taking Strattera (atomoxetine), these patients showed significant improvements.
Specifically, they reacted faster in tasks requiring quick decisions and made fewer mistakes in tasks that required sustained focus. This suggests that Strattera (atomoxetine) helps enhance key cognitive functions in adults with ADHD.
Specifically, they reacted faster in tasks requiring quick decisions and made fewer mistakes in tasks that required sustained focus. This suggests that Strattera (atomoxetine) helps enhance key cognitive functions in adults with ADHD.
Abstract: results
The ADHD patients under placebo conditions showed response inhibition and working memory deficits compared with healthy volunteers. Atomoxetine treatment in the ADHD patients was associated with shorter stop-signal reaction times and lower numbers of...more


Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings suggest that Strattera (atomoxetine) improves self-control by enhancing brain functions tied to attention and decision-making. This could help explain why the drug is effective in treating ADHD symptoms.
Additionally, the results hint that Strattera (atomoxetine) might have potential uses beyond ADHD, particularly in treating other conditions where impulsivity is a problem.
Additionally, the results hint that Strattera (atomoxetine) might have potential uses beyond ADHD, particularly in treating other conditions where impulsivity is a problem.
Abstract: conclusions
Atomoxetine improved inhibitory control, most likely via noradrenergically mediated augmentation of prefrontal cortex function. These results have implications for understanding the mechanisms by which atomoxetine exerts beneficial clinical effects a...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
ADHD Treatment Authorization
Atomoxetine, marketed as Strattera, is FDA-approved for ADHD in adults and children over six years old.
⚙️
Distinct Brain Mechanism
Atomoxetine acts as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, influencing select brain regions.
📉
Variable Bioavailability
Atomoxetine's effectiveness varies between individuals due to first-pass metabolism differences.
🧠
Integral Treatment Component
Formulated as part of a broader ADHD treatment program that includes various interventions.
🧬
Metabolism and Excretion
Atomoxetine metabolized mainly by CYP2D6 and excreted primarily through urine, requiring dose adjustments.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Atomoxetine and ADHD
In line with the abstract's findings that atomoxetine improves inhibitory control and cognitive function, its role as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor highlights its impact on enhancing attention and impulse control.
Monitoring for psychiatric and cardiovascular symptoms is necessary as atomoxetine can induce significant side effects, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions.
Dosage considerations are crucial for individuals with specific metabolic profiles, including those who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, to avoid heightened systemic exposure.
Given its interaction potential, atomoxetine should not be combined with MAOIs due to risk of severe adverse reactions.
Monitoring for psychiatric and cardiovascular symptoms is necessary as atomoxetine can induce significant side effects, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions.
Dosage considerations are crucial for individuals with specific metabolic profiles, including those who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, to avoid heightened systemic exposure.
Given its interaction potential, atomoxetine should not be combined with MAOIs due to risk of severe adverse reactions.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine's Impact on ADHD Symptom Management
Atomoxetine plays a crucial role in managing ADHD symptoms in young adults, specifically enhancing attention and reducing hyperactivity. It provides a comprehensive evaluation of both the advantages and potential drawbacks of the medication. The piece highlights how atomoxetine not only improves symptoms but also the cognitive functions critical for daily activities.
This highlights atomoxetine's efficacy, a detail discussed in greater depth regarding inhibitory control improvements noted in the study.
This highlights atomoxetine's efficacy, a detail discussed in greater depth regarding inhibitory control improvements noted in the study.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine's Role in ADHD Treatment: Safety and Comparisons
The article offers insight into the safety profile of atomoxetine, an ADHD medication. It outlines common side effects and provides a detailed comparison with other treatment options, presenting a comprehensive view for those considering different ADHD medications.
By exploring atomoxetine’s profile, this piece complements the findings on its cognitive effects, giving a broader perspective on its usage and safety in ADHD treatments.
By exploring atomoxetine’s profile, this piece complements the findings on its cognitive effects, giving a broader perspective on its usage and safety in ADHD treatments.
Evidence Summary
Evaluating Atomoxetine Across Ages
The article explores how atomoxetine aids children across different age groups, focusing on its success in managing ADHD symptoms and noting any unique side effects experienced by younger and older kids. It further examines how variation in age might influence the outcomes of this treatment, highlighting results from various studies.
The discussion centers on comparing the drug's effectiveness and safety profiles across distinct age demographics, providing insights into its role in pediatric ADHD care.
The discussion centers on comparing the drug's effectiveness and safety profiles across distinct age demographics, providing insights into its role in pediatric ADHD care.