Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
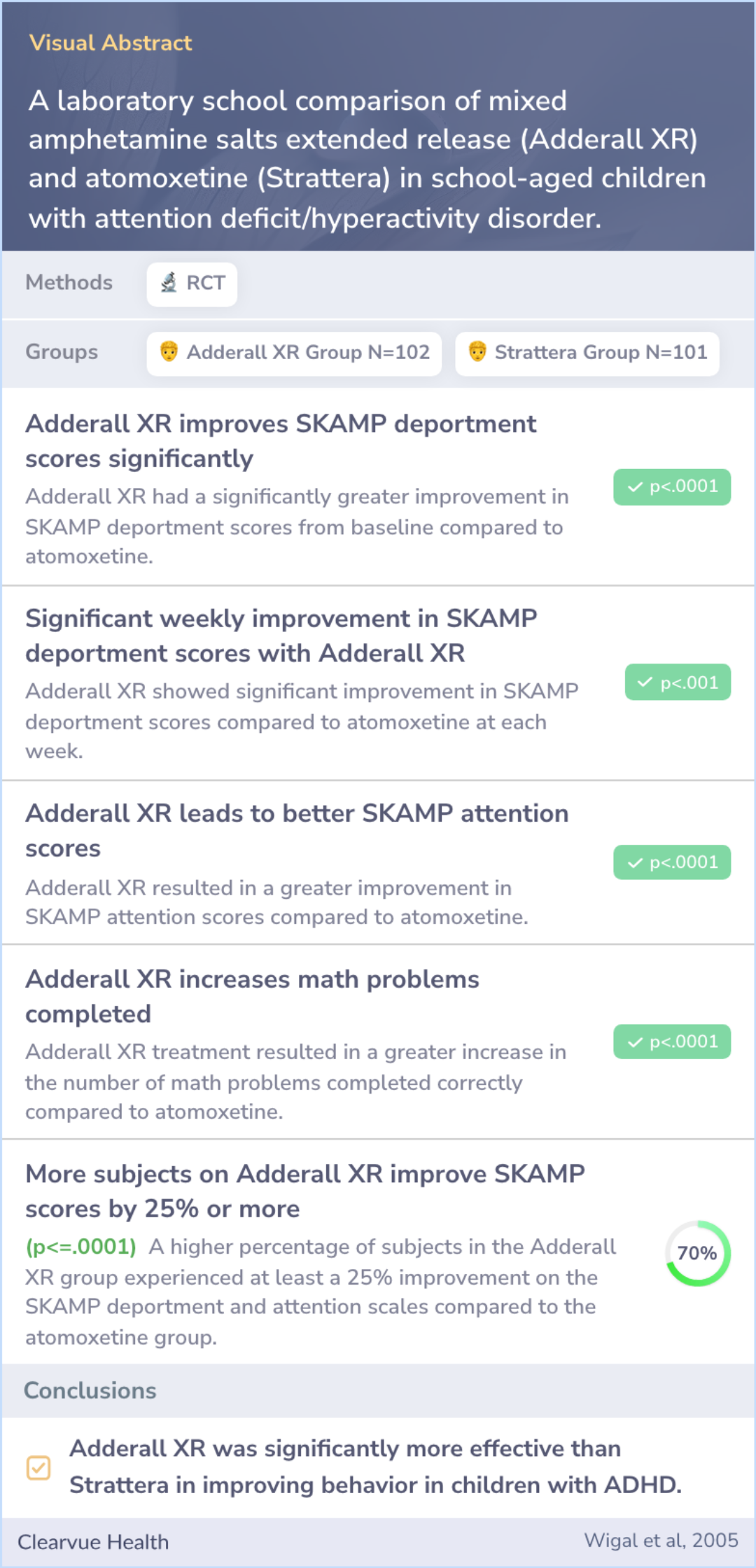
A laboratory school comparison of mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR) and atomoxetine (Strattera) in school-aged children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Comparison of Adderall XR and Strattera in school-aged children with ADHD
September 9, 2024
author
Wigal SB, McGough JJ, McCracken JT, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Posner KL, Wigal TL, Kollins SH, Clark TM, Mays DA, Zhang Y, Tulloch SJ
journal
J Atten Disord
Date Published
2005 Aug
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers wanted to know which medication, Adderall XR or Strattera, is more effective in improving behavior in children with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
They found that Adderall XR was significantly more effective than Strattera in improving behavior in children with ADHD.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that Adderall XR may be a better option than Strattera for treating ADHD in children, aligning with current guidelines that support its use for this condition.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study compared atomoxetine with an extended-release stimulant in children with ADHD. It aimed to evaluate effectiveness, tolerability, and treatment timing. MAS XR treatment showed greater symptom improvement than atomoxetine. The effects of MAS XR were consistent across the school day. Atomoxetine's effects waned over time. The study lasted three weeks to assess atomoxetine's benefit with once-daily dosing. Medication satisfaction surveys need careful interpretation as they were created for this study. The adverse events were similar to past data on these medications. Stimulants have been effective for treating ADHD over the years, providing continuous symptom control.
Abstract: background
Mixed amphetamine salts extended release (MAS XR; Adderall XR) and atomoxetine (Strattera) were compared in children 6 to 12 years old with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) combined or hyperactive/impulsive type in a randomized, double...more

First Direct Comparison
"This study was the first to directly compare atomoxetine with an extended-release stimulant (MAS XR) in children 6 to 12 years old with ADHD."
Study Goals
"The goals of this study were to evaluate the efficacy, tolerability, and time course of treatment effect."
Guiding Treatment Choices
"The results of this study and other well-controlled comparator studies may guide clinicians in the selection of optimal pharmacotherapeutic regimens for patients with ADHD."
Study Summary
Methods
The primary method used to measure the effectiveness of the treatments was the SKAMP rating scale, a tool specifically designed to assess ADHD symptoms in children during school activities. This scale evaluates different aspects of behavior, including attention and deportment, which are critical in understanding how well a child can function in a classroom setting.
The study was structured as a forced-dose-escalation trial, meaning that children began with a lower dose of the medication, which was gradually increased. This approach helps to identify the most effective dose for each child while monitoring any side effects. All participants were closely observed over the course of the trial, and data were collected at multiple points to track changes in their behavior and symptoms.
The study was structured as a forced-dose-escalation trial, meaning that children began with a lower dose of the medication, which was gradually increased. This approach helps to identify the most effective dose for each child while monitoring any side effects. All participants were closely observed over the course of the trial, and data were collected at multiple points to track changes in their behavior and symptoms.
Abstract: methods
Primary efficacy measure was the SKAMP (Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham) behavioral rating scale.
Study Summary
Results
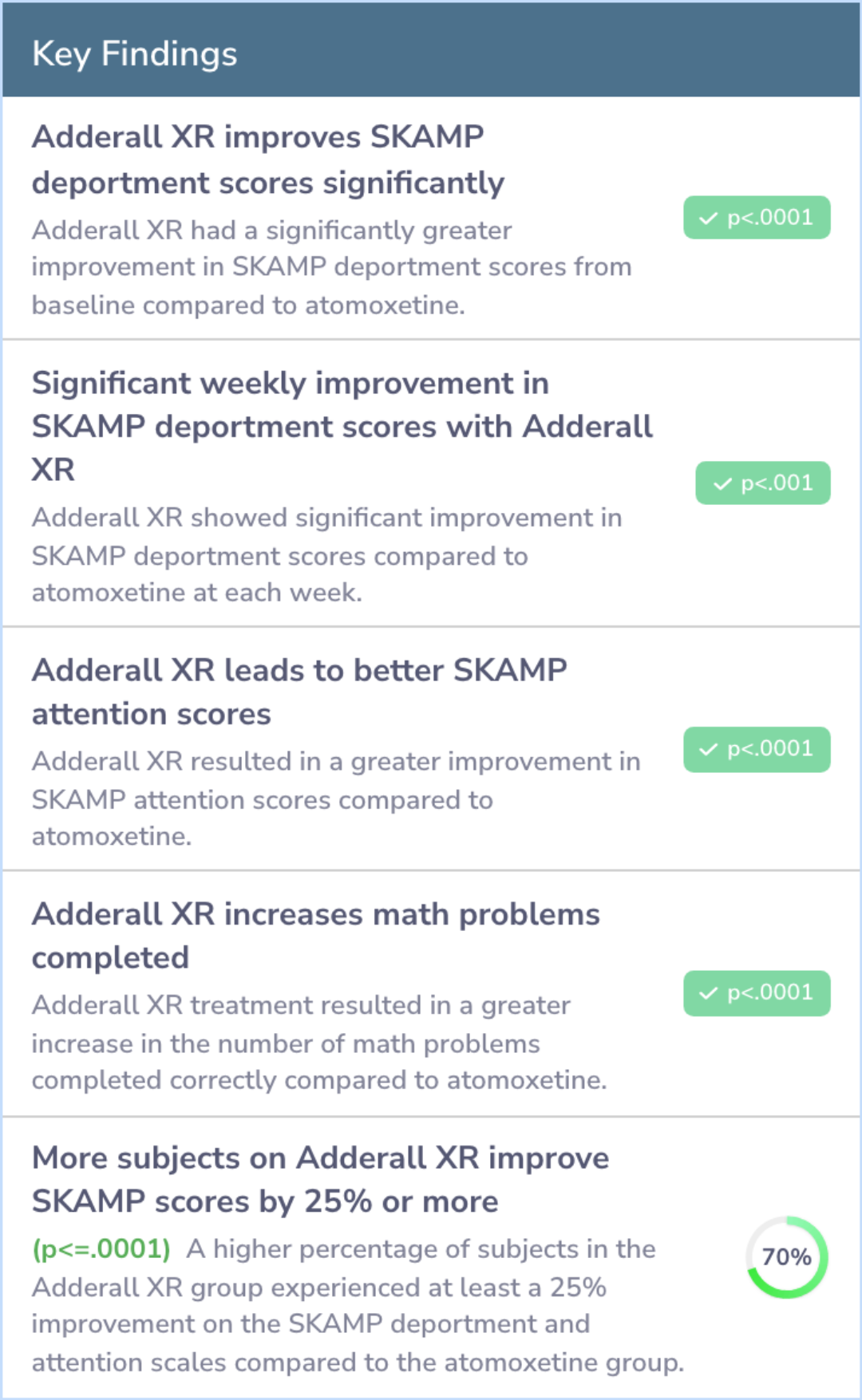
The findings showed that children who were treated with MAS XR (Adderall XR) experienced significantly greater improvements in their behavior compared to those who took atomoxetine (Strattera). This was evident from the changes in their SKAMP deportment scores, with MAS XR showing a larger reduction in symptoms overall.
These improvements were consistent across the entire duration of the study, with MAS XR outperforming atomoxetine at each weekly check-in. While both medications were generally well-tolerated, the results clearly indicated that MAS XR provided a stronger therapeutic effect in managing ADHD symptoms in children.
These improvements were consistent across the entire duration of the study, with MAS XR outperforming atomoxetine at each weekly check-in. While both medications were generally well-tolerated, the results clearly indicated that MAS XR provided a stronger therapeutic effect in managing ADHD symptoms in children.
Abstract: results
Changes in mean SKAMP deportment scores from baseline were significantly greater for MAS XR (n = 102) than for atomoxetine (n = 101) overall (-0.56 and -0.13, respectively; p < .0001) and at each week (p < .001). Adverse events were similar for both ...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study concluded that MAS XR (Adderall XR) is more effective than atomoxetine (Strattera) for treating children with ADHD, particularly in managing behavior and attention in a school setting. The extended release formula of MAS XR allowed for longer-lasting symptom control throughout the day.
Given these findings, MAS XR may be a better option for children who need consistent and sustained management of their ADHD symptoms, particularly in environments where focus and good behavior are essential, such as in school. This makes it a preferable choice over atomoxetine for many children with ADHD.
Given these findings, MAS XR may be a better option for children who need consistent and sustained management of their ADHD symptoms, particularly in environments where focus and good behavior are essential, such as in school. This makes it a preferable choice over atomoxetine for many children with ADHD.
Abstract: conclusions
The extended time course of action and greater therapeutic efficacy of MAS XR suggests that it is more effective than atomoxetine in children with ADHD.

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
FDA Approval for ADHD
Adderall is FDA-approved to treat ADHD, enhancing focus and reducing impulse behaviors in children.
🧬
Mechanism of Action
Adderall boosts dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, aiding attention and alertness.
📦
Dosing Forms
Available in immediate and extended-release formulations, Adderall allows personalized treatment.
⚠️
Potential Side Effects
Possible adverse effects include cardiovascular risks, growth suppression, and serotonin syndrome.
🔍
Monitoring Requirements
Regular monitoring of cardiac health, growth, and potential abuse is necessary for Adderall use.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Comparison of Adderall XR and Strattera in school-aged children with ADHD
In line with the comparative study of MAS XR and atomoxetine, stimulant medications like Adderall® show a mild yet clinically significant increase in heart rate and blood pressure, warranting careful monitoring. Methylphenidate remains the first-line treatment for ADHD in preschool children, aligning with the focus on optimizing therapeutic strategies. Assessing adolescents for substance use before starting stimulant therapy reflects comprehensive care, acknowledging potential risks. Combining behavioral therapy with medications enhances outcomes, suggesting an integrated approach that resonates with the study findings. Stimulant-induced psychotic symptoms, while rare, highlight the need for vigilance during treatment. Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon, linked to Adderall®, suggests cautious dosing adjustments to alleviate adverse effects.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate: A Close Look at ADHD Medications
Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate both address ADHD symptoms, yet they differ in effectiveness and side effects. Examining patient responses helps distinguish their unique impacts. This information aids in making informed choices.
Insights from the study show varied patient reactions to Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, emphasizing the importance of understanding medication differences for tailored ADHD treatment.
Insights from the study show varied patient reactions to Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, emphasizing the importance of understanding medication differences for tailored ADHD treatment.
Evidence Summary
ADHD and Challenges in Reaction Time
Children with ADHD show slower and more inconsistent reaction times when trying to stop actions, according to findings that explore core behavioral inhibition traits using a stop-signal task.
While there are clear deficits in attention and cognitive processing, the results suggest that these are more about general attention challenges than specifically about problems with inhibiting behavior.
While there are clear deficits in attention and cognitive processing, the results suggest that these are more about general attention challenges than specifically about problems with inhibiting behavior.
Evidence Summary
Virtual Reality Unveils ADHD Performance Patterns
The use of virtual reality tools for evaluating ADHD in children offers a more realistic setting, similar to a traditional classroom. This innovative method allows controlled tasks, helping to identify differences in attention and performance between ADHD children and their peers. Unlike control groups who maintain concentration, ADHD children exhibit declining performance over time, mirroring trends from Continuous Performance Tests.
Virtual environments provide reliable insights into how ADHD affects sustained attention, addressing performance decrements over time. This aligns with broader studies comparing treatment efficacy in managing ADHD symptoms in school settings.
Virtual environments provide reliable insights into how ADHD affects sustained attention, addressing performance decrements over time. This aligns with broader studies comparing treatment efficacy in managing ADHD symptoms in school settings.
Evidence Summary
Dissecting ADHD: Beyond Core Symptoms
The study explores ADHD as a diverse condition by analyzing neuropsychological deficits, including executive functions and emotional aspects. Children with ADHD, aged 7-13, displayed distinct differences in response time and emotional regulation compared to their peers.
While both groups similarly recognized disgust, executive functioning and variability in reaction times were prominent differentiators, highlighting the complex nature of ADHD.
While both groups similarly recognized disgust, executive functioning and variability in reaction times were prominent differentiators, highlighting the complex nature of ADHD.
Evidence Summary
Concerta vs. MPH: Dosing Convenience and Effectiveness in ADHD
Concerta offers the convenience of once-daily dosing, contrasting with the thrice-daily schedule required for methylphenidate (MPH). Both serve children managing ADHD but vary in administration frequency. Effectiveness remains the focal point, as the comparison highlights how these two medications fit into daily routines.
The abstract discusses different ADHD medication comparisons, mirroring this broader theme of treatment effectiveness and dosage management.
The abstract discusses different ADHD medication comparisons, mirroring this broader theme of treatment effectiveness and dosage management.