Strattera Paper Database
Visual Abstract
Comparison of the subjective, physiological, and psychomotor effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate in light drug users
Effects of Atomoxetine vs Methylphenidate
October 25, 2024
author
Heil SH, Holmes HW, Bickel WK, Higgins ST, Badger GJ, Laws HF, Faries DE
journal
Drug Alcohol Depend
Date Published
2002 Jul 1
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the subjective, physiological, and psychomotor effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate compared to a placebo in healthy volunteers.
💡
What They Found
They found that methylphenidate increased certain subjective stimulant effects and blood pressure, while atomoxetine mainly increased blood pressure without similar subjective effects.
📚
What This Means
These findings indicate that atomoxetine does not produce the same stimulant-like effects as methylphenidate and appears less likely to have abuse potential, which aligns with existing evidence on atomoxetine's profile as a non-stimulant ADHD medication.
Study Summary
Methods
The study involved 16 participants who were not dependent on drugs, having six sessions where they received different doses of atomoxetine (Strattera) and methylphenidate (Ritalin). A placebo was also tested. To ensure fairness, neither the participants nor the supervisors knew who received which drug at any session.
Throughout, their feelings, motor skills, and physical health were observed using several tests, assessing these factors both before and after the drugs were given at specific intervals.
Throughout, their feelings, motor skills, and physical health were observed using several tests, assessing these factors both before and after the drugs were given at specific intervals.
Abstract: methods
Sixteen non-dependent light drug users participated in six experimental sessions, receiving placebo, atomoxetine (20, 45 and 90 mg) and methylphenidate (20 and 40 mg) using a double-blind, Latin square design. Subjective drug effects were assessed us...more

Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore the differences between atomoxetine and methylphenidate, particularly in terms of their subjective effects. Atomoxetine is highlighted as having a different impact, with no significant similarity to methylphenidate regarding feelings of pleasure. The findings provide important insights that can inform future research and treatment strategies in ADHD management.
Understanding these differences is essential, especially considering the concerns about abuse potential in ADHD treatments.
Understanding these differences is essential, especially considering the concerns about abuse potential in ADHD treatments.
Abstract: background
This study compared the subjective, physiological, and psychomotor effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate with placebo in healthy volunteers.

Comparison with Methylphenidate
"The results suggest that atomoxetine, relative to placebo, does not produce subjective effects similar to methylphenidate in healthy volunteers with light drug use histories and that it is not likely to have abuse liability, making it a promising candidate for further development as a treatment for ADHD."
Lack of Pleasurable Effects
"Across the doses and time frame examined and with the instruments tested, atomoxetine does not engender pleasurable subjective drug effects, suggesting that it is unlikely that atomoxetine will have abuse liability."
Filling a Gap in Literature
"Despite these limitations, the present study begins to fill an important gap in the literature by allowing the comparison of findings from preclinical studies to human populations."
Study Summary
Results
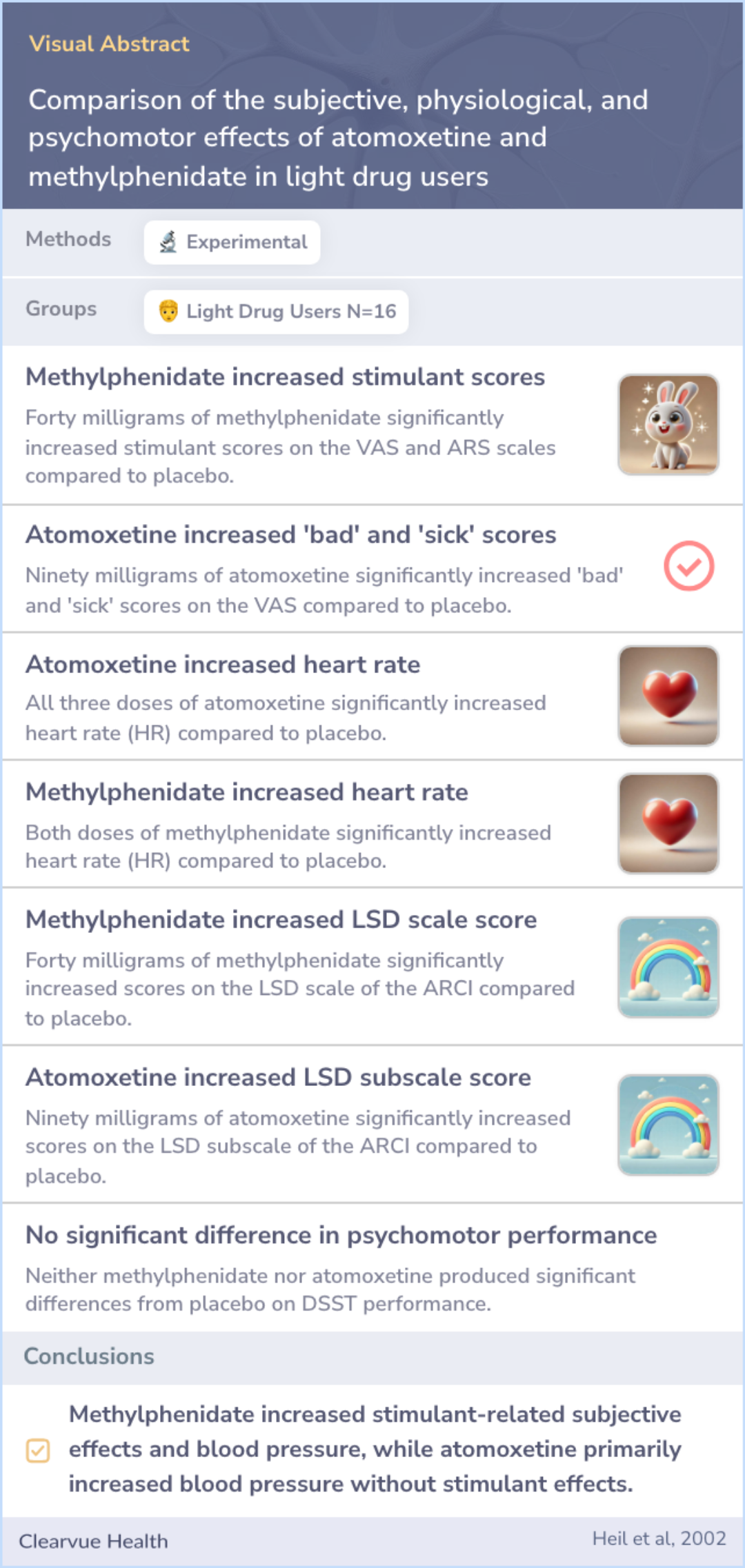
Methylphenidate, in a higher dose, appeared to increase feelings of stimulation among participants, resembling feelings associated with certain known stimulants. Meanwhile, atomoxetine at high doses was relatively unpleasant, causing some discomfort.
Both drugs raised heart rate and blood pressure, though atomoxetine notably affected diastolic and systolic pressures more variably. Neither drug showed significant impacts on motor skills compared to placebo.
Both drugs raised heart rate and blood pressure, though atomoxetine notably affected diastolic and systolic pressures more variably. Neither drug showed significant impacts on motor skills compared to placebo.
Abstract: results
Forty milligrams methylphenidate produced significant increases on the stimulant portions of the VAS and ARS and the benzedrine, amphetamine, morphine-benzedrine and lysergic acid diethylamine (LSD) subscales of the ARCI relative to placebo. Ninety m...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
From the study's results, atomoxetine doesn't create the same subjective experiences as methylphenidate. Its potential for misuse appears low when judged against methylphenidate's effects.
This might suggest atomoxetine is less likely to be used recreationally or lead to dependency compared to methylphenidate, impacting how these medications are considered for treatment in various settings.
This might suggest atomoxetine is less likely to be used recreationally or lead to dependency compared to methylphenidate, impacting how these medications are considered for treatment in various settings.
Abstract: conclusions
These results suggest that atomoxetine does not induce subjective effects similar to methylphenidate and suggest that it is unlikely that atomoxetine will have abuse liability.

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
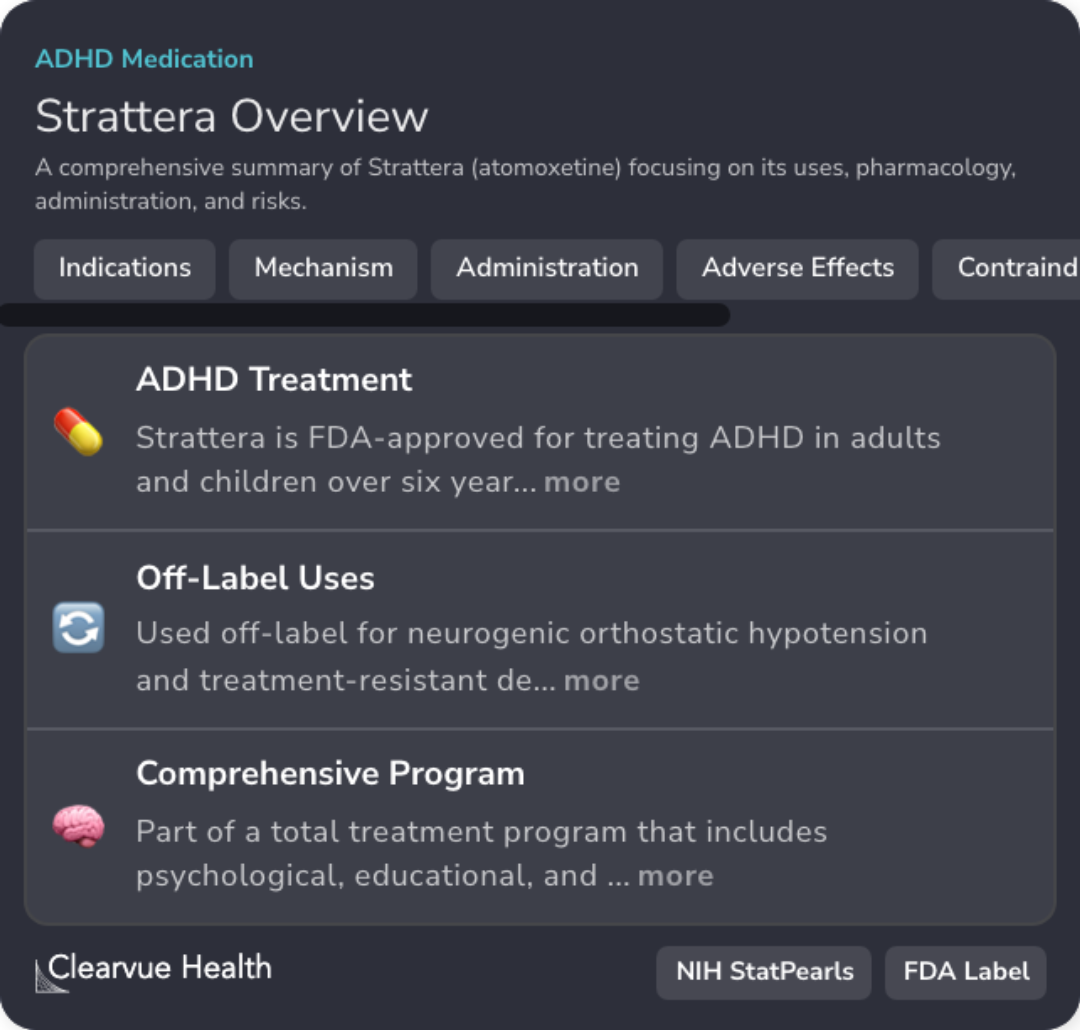
Atomoxetine as an ADHD Medication
Atomoxetine's FDA-approval as a treatment for ADHD includes use in adults and children over six.
⚙️
Mechanism of Atomoxetine
Acts as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, influencing dopamine in specific brain areas.
🤕
Adverse Effects and Monitoring
Noteworthy adverse reactions include headache and nausea; critical to monitor blood pressure closely.
🚫
Contraindications for Atomoxetine
Avoid use in individuals with cardiac problems or MAOIs use; risk of severe interactions.
🔢
Dosing Practices
Atomoxetine dosing varies, highlighting importance of adjustments for different patient profiles.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Effects of Atomoxetine vs Methylphenidate
In line with findings that emphasize atomoxetine's lower abuse potential compared to methylphenidate, healthcare professionals note its selective inhibition of norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake.
The reduced cardiovascular risks and absence of growth suppression in atomoxetine treatment present a safer profile for long-term use.
Monitoring for psychiatric symptoms remains crucial for atomoxetine, underscoring the need for caution in pediatric populations.
The reduced cardiovascular risks and absence of growth suppression in atomoxetine treatment present a safer profile for long-term use.
Monitoring for psychiatric symptoms remains crucial for atomoxetine, underscoring the need for caution in pediatric populations.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine in ADHD Treatment
The comparison between methylphenidate and atomoxetine focuses on their effectiveness in managing ADHD symptoms. Both medications play significant roles in treatment, but they work differently. While methylphenidate is a stimulant, atomoxetine is not, leading to varied outcomes in treatment efficacy.
This comparison highlights which drug might be more beneficial for individuals, guiding decisions in ADHD management based on the unique effects of each medication.
This comparison highlights which drug might be more beneficial for individuals, guiding decisions in ADHD management based on the unique effects of each medication.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate: Effectiveness and Side Effects
The comparison highlights how Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, both used to treat ADHD, differ in their effectiveness, side effects, and how patients respond to each. This side-by-side look gives a clear view of these differences, helping readers make informed decisions.
It’s not just about effectiveness; the discussion also dives into side effects and patient experiences, shedding light on how each medication might impact daily life differently.
It’s not just about effectiveness; the discussion also dives into side effects and patient experiences, shedding light on how each medication might impact daily life differently.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine: Balancing Attention Improvement with Side Effects in ADHD Treatment
Atomoxetine plays a role in managing ADHD by enhancing attention and reducing hyperactivity in young adults. This medication offers a therapeutic approach to ADHD with its unique set of benefits, but it also comes with potential side effects that should be considered. The discussion focuses on these aspects to give a comprehensive look at atomoxetine's role in treating ADHD.
A deeper dive into these factors provides insight into how atomoxetine balances efficacy with tolerability in ADHD treatment.
A deeper dive into these factors provides insight into how atomoxetine balances efficacy with tolerability in ADHD treatment.