Trending ADHD Papers
Visual Abstract
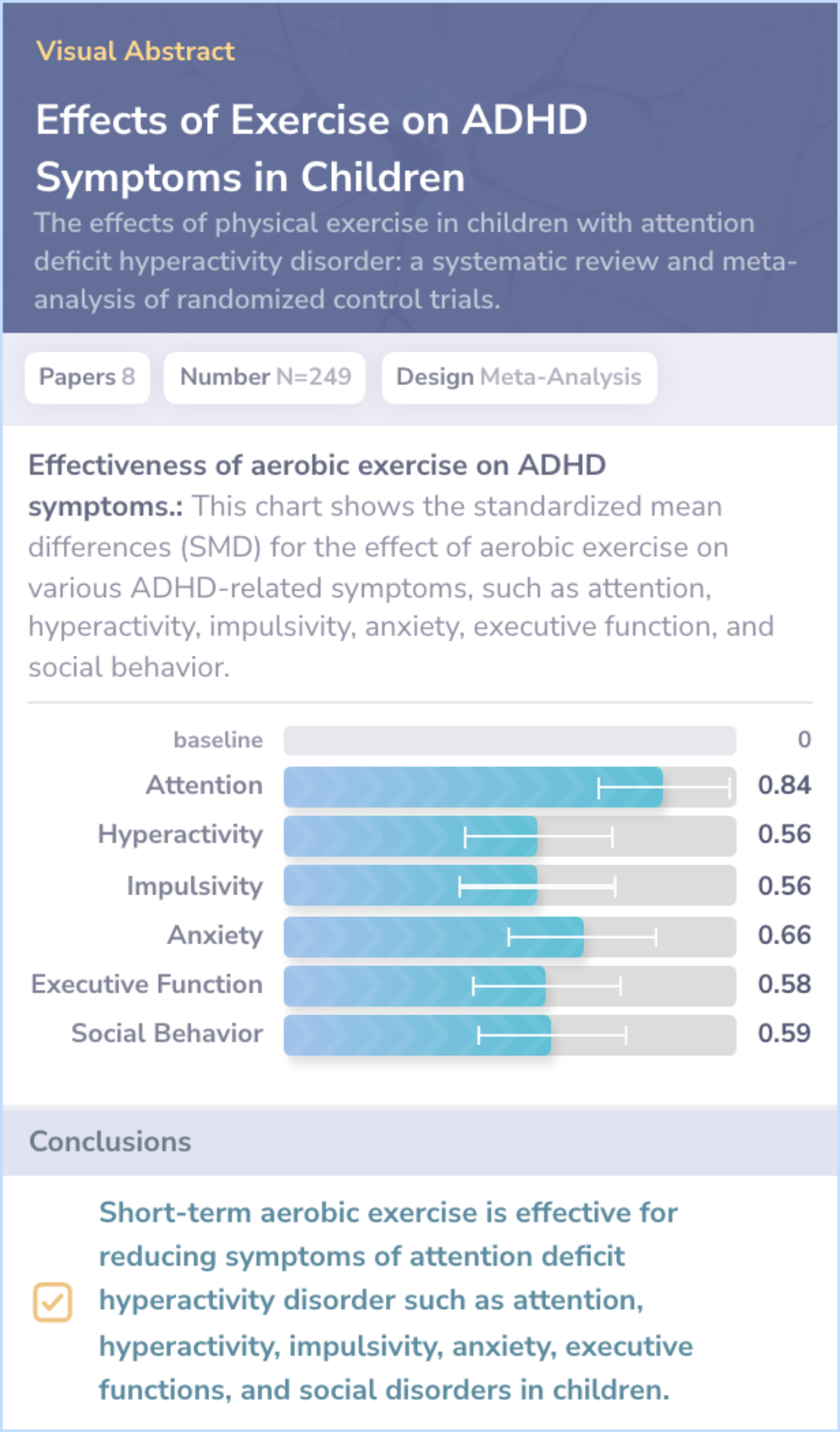
Effects of physical exercise on attention deficit and other major symptoms in children with ADHD: A meta-analysis
Impact of Exercise on ADHD Symptoms
December 9, 2024
author
Sun W, Yu M, Zhou X
journal
Psychiatry Res.
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers aimed to study the effects of physical exercise on symptoms, motor skills, and executive function in children with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
The study found that physical exercise improved attention, executive function, and motor skills in children with ADHD, but didn't significantly affect hyperactivity, depression, social problems, or aggressive behavior.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that exercise could be a beneficial addition to ADHD treatment by boosting attention, executive function, and motor skills, unlike medication options explored in similar research, which do not always address all these areas simultaneously.
Study Overview
Background & Objectives
Physical activity can be an untapped resource in managing ADHD, a disorder where traditional treatments often focus on medication like methylphenidate. This stimulant raises dopamine and norepinephrine levels, but concerns about side effects persist.
This study explores how exercise might help ADHD symptoms, aiming to understand its influence on children's attention, motor skills, and executive functions compared to medication-only interventions.
This study explores how exercise might help ADHD symptoms, aiming to understand its influence on children's attention, motor skills, and executive functions compared to medication-only interventions.
Abstract: background
To explore the effects of physical exercise intervention on the cardinal symptoms, motor skills and executive function among children w...more
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers analyzed data from randomized controlled trials—a type of study where participants are randomly assigned treatments. This study looked at findings in several research databases up until March 2021.
The studies involved were chosen based on strict criteria. Advanced software like RevMan and Stata helped in assessing data quality and examining any biases in the publication of findings.
The studies involved were chosen based on strict criteria. Advanced software like RevMan and Stata helped in assessing data quality and examining any biases in the publication of findings.
Abstract: methods
Literature searches for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were performed in PubMed, The Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, CNK...more
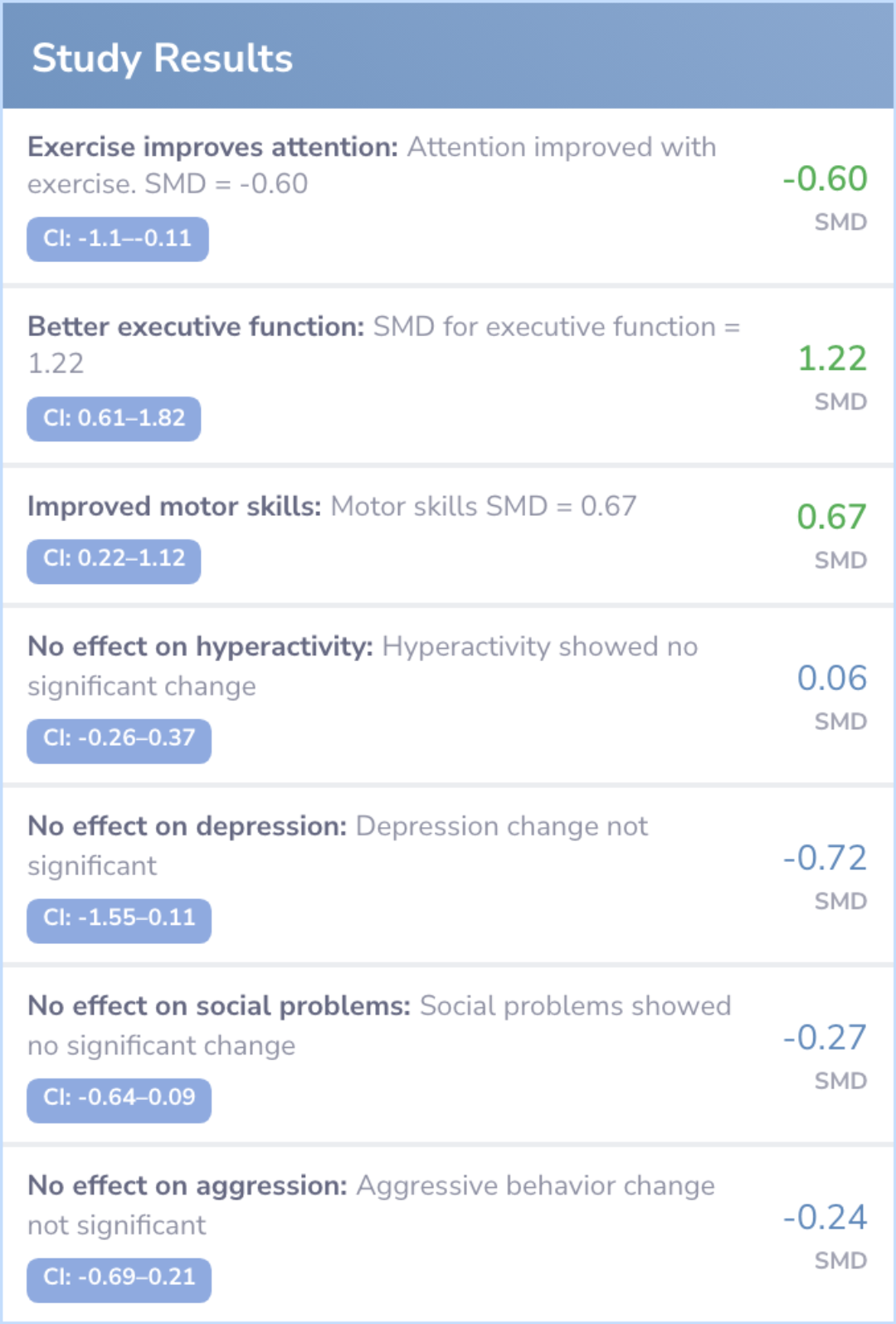
Study Results
Results
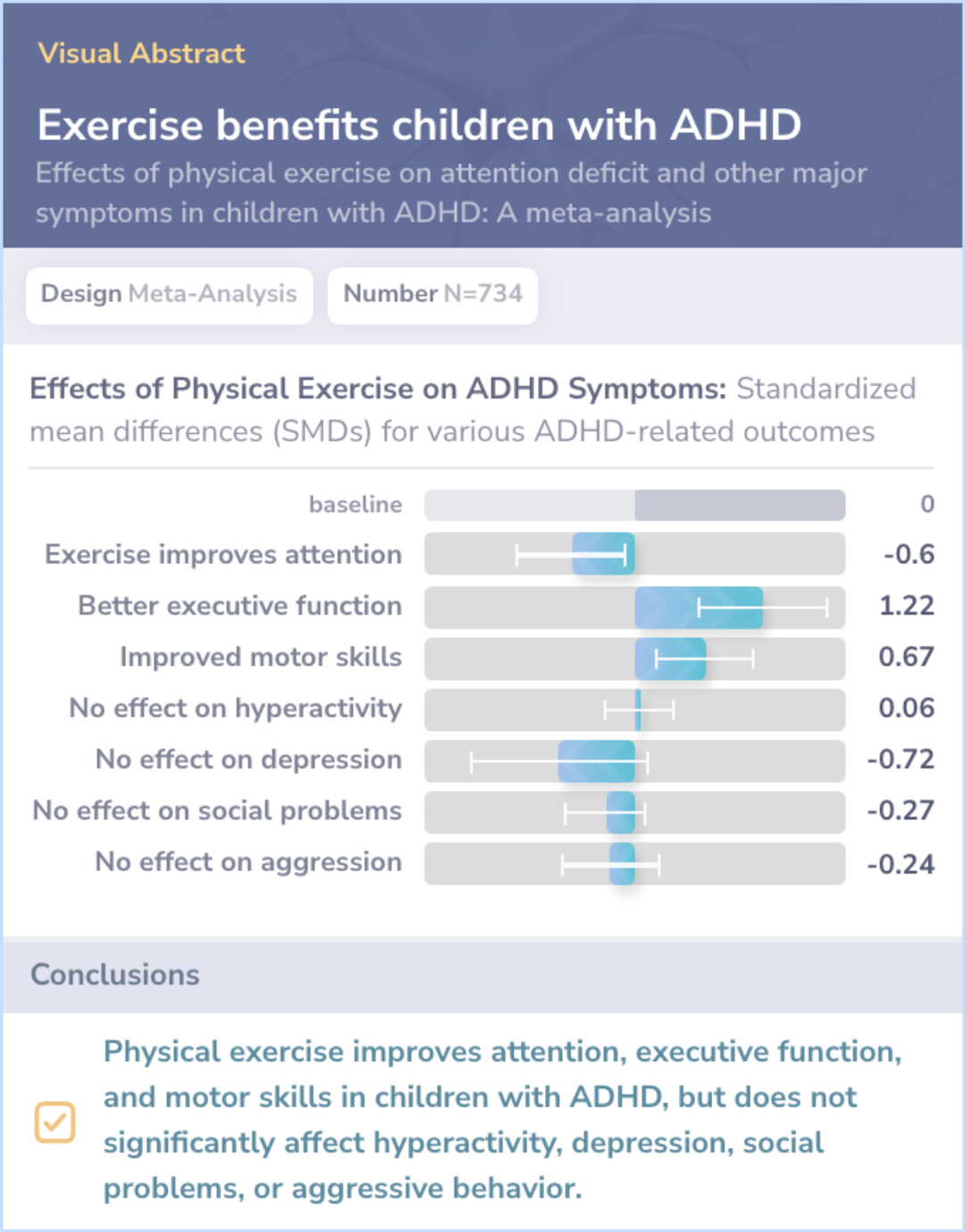
The analysis included 15 trials with 734 children. Results suggested that physical exercise led to improvements in focusing ability, decision-making skills, and motor coordination in children with ADHD.
However, exercise didn't significantly change hyperactivity, depression, social issues, or aggressive behavior. The impact of exercise might differ due to how often and how long the activities were done.
However, exercise didn't significantly change hyperactivity, depression, social issues, or aggressive behavior. The impact of exercise might differ due to how often and how long the activities were done.
Abstract: results
A total of 15 RCTs with 734 subjects were included. The meta-analysis showed that physical exercise can improve the attention of ADHD c...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
Engaging in physical activities can benefit children with ADHD by enhancing their attention and coordination skills. This suggests exercise could be a useful part of managing ADHD.
While exercise appears promising, it notably didn't change behaviors like hyperactivity or aggression, indicating that different types or schedules of interventions might be needed.
While exercise appears promising, it notably didn't change behaviors like hyperactivity or aggression, indicating that different types or schedules of interventions might be needed.
Abstract: conclusions
Physical exercise can help alleviate the symptoms of ADHD in children. Specifically, it can improve attention, executive function, and motor skills.
Clinical Guidelines
Guidelines suggest that structured exercise can significantly enhance motor coordination and improve attention through targeted cardiovascular activities in children with ADHD.
Customized plans tailored to individual needs improve executive functions like working memory. Regular, varied exercises, including aerobic and resistance, provide diverse benefits.
Parental involvement in exercise programs enhances motivation and adherence.
Customized plans tailored to individual needs improve executive functions like working memory. Regular, varied exercises, including aerobic and resistance, provide diverse benefits.
Parental involvement in exercise programs enhances motivation and adherence.
Literature Review
Cerrillo-Urbina et al
Core Insight:The comparison paper shows that both aerobic and yoga exercises have positive effects on ADHD symptoms, with aerobic exercise addressing a broader range of symptoms.
What It Adds:
Broader Symptom Impact: The comparison paper highlights effects on anxiety and social issues, not addressed in the primary paper.
Shared Themes:Both papers acknowledge the benefits of physical exercise on improving attention and executive function in children with ADHD.
Literature Review
Zhang et al, 2020
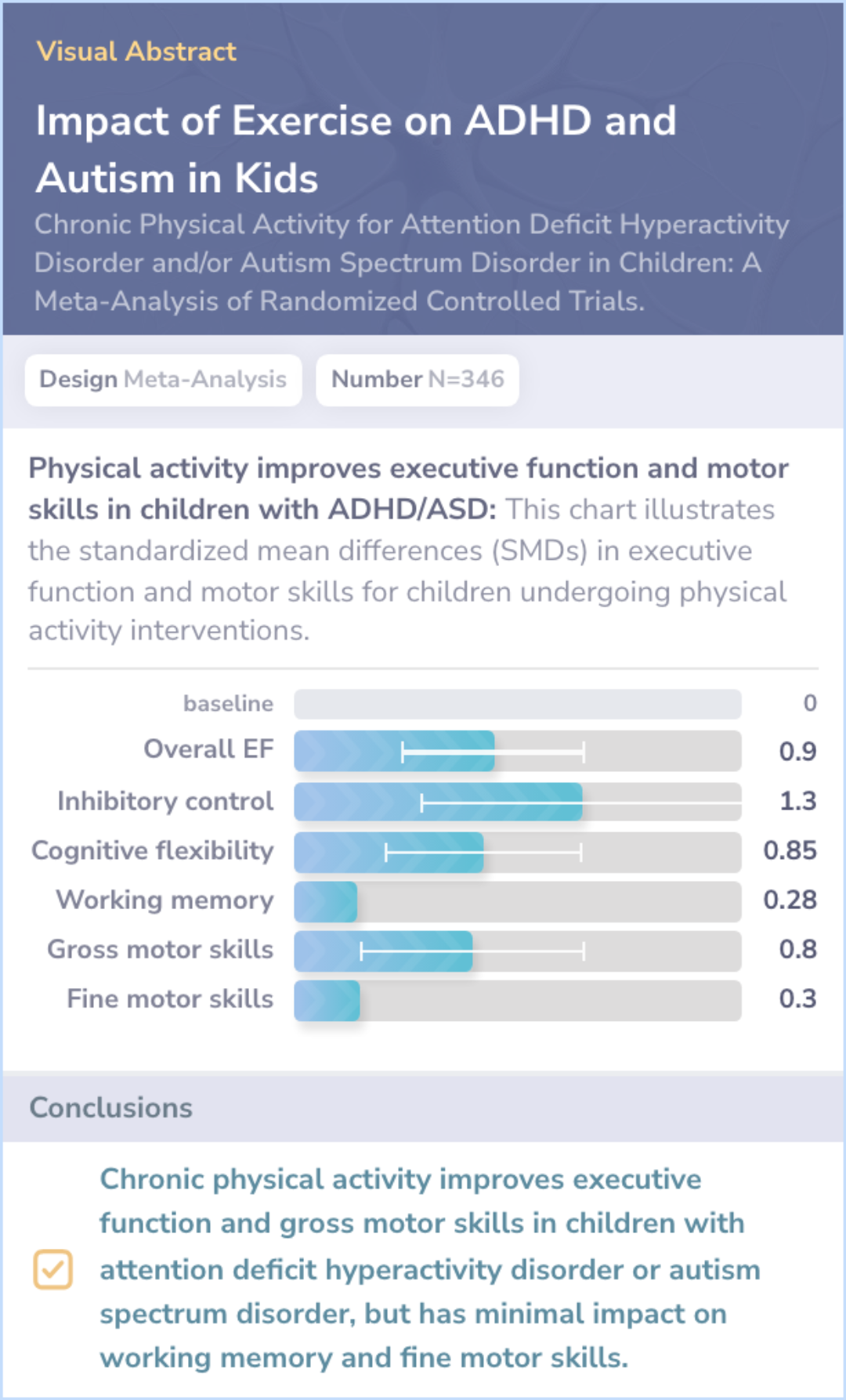
Core Insight:Both papers investigate the effects of physical activity on executive function and motor skills in children with ADHD, with the comparison paper also including children with autism.
What It Adds:
Inclusion of Autism: The comparison paper extends findings to children with autism.
Specific Function Outcomes: Highlights improvements in gross motor skills, inhibitory control.
Shared Themes:Both studies affirm that physical activity can enhance executive function and motor skills in children with ADHD.