Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Interventions for generalized anxiety disorder in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Interventions for GAD in Older Adults
November 25, 2024
author
Gonçalves DC, Byrne GJ
journal
J Anxiety Disord
Date Published
2012 Jan
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the effectiveness of treatments for generalized anxiety disorder in adults aged 55 and older.
💡
What They Found
The study found that both pharmacological and psychotherapeutic interventions were beneficial for older adults with GAD.
📚
What This Means
The findings suggest that both medication and therapy can effectively manage GAD in older adults, aligning with the multi-faceted approach in current guidelines.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study aimed to explore Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) among older adults, discovering that many do not seek mental health help, despite a willingness when offered. The findings suggest that although older adults can show some improvement over time, active interventions lead to significantly better outcomes.
Interestingly, it also revealed that older adults have positive views on mental health support, challenging previous assumptions about their attitudes towards seeking help.
Interestingly, it also revealed that older adults have positive views on mental health support, challenging previous assumptions about their attitudes towards seeking help.
Abstract: background
To perform a systematic review of the efficacy of controlled interventions for GAD in adults aged 55 years and older.

GAD Prevalence and Help-Seeking
"Despite the high prevalence of the disorder, individuals with GAD seldom seek the help of mental health professionals."
Positive Attitudes Toward Help
"Contrary to what has been previously believed, older adults display positive attitudes towards mental health professionals and would accept help if offered."
Intervention Outcomes
"Although some symptomatic improvement is possible even when waiting for treatment, potential gains are significantly higher when an intervention is used."
Study Summary
Methods
The research involved searching online databases and prominent publications about aging. This means they looked through a lot of previous studies to find relevant information on GAD treatments. They also checked references in these articles to ensure they didn't miss any important data.
The goal was to gather as much existing information as possible to understand how different treatments are performing in real-world settings.
The goal was to gather as much existing information as possible to understand how different treatments are performing in real-world settings.
Abstract: methods
Direct search of digital databases and the main publications on aging and iterative searches of the references from retrieved articles.

Study Summary
Results
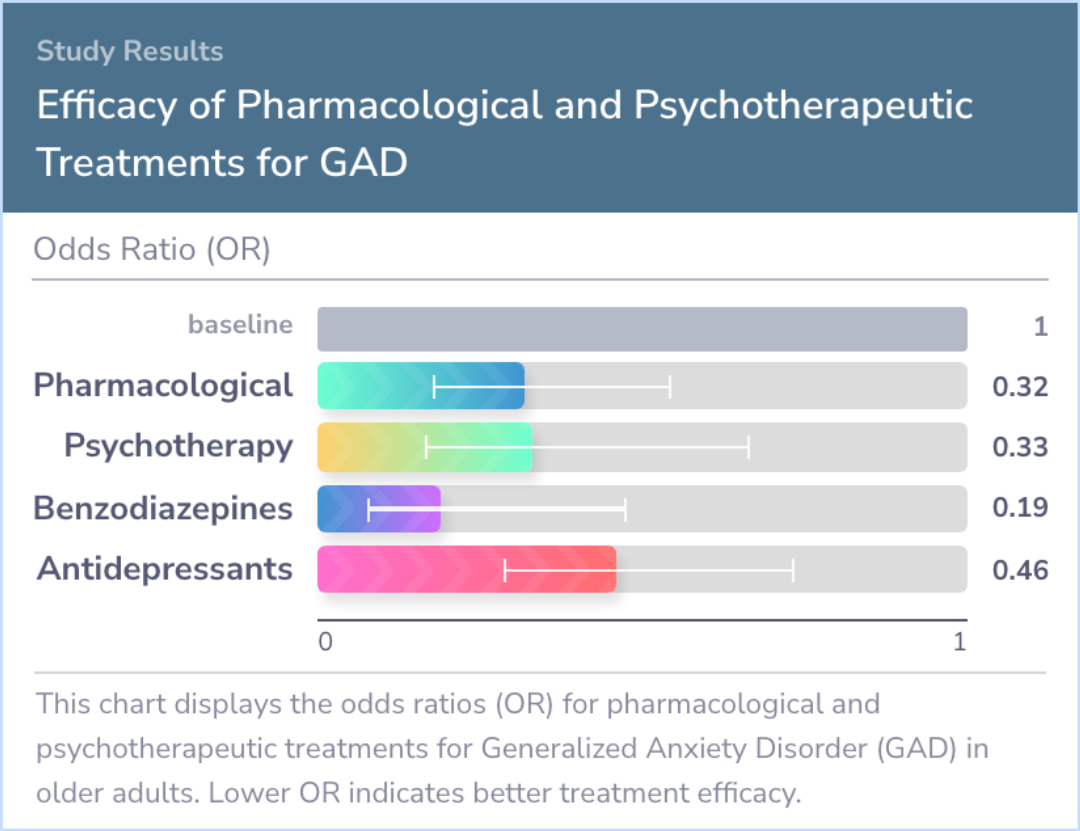
A total of 27 studies were selected, including 14 focusing on medications and 13 on therapies. In all, 2,373 participants were included from the start. Both types of treatment showed similar effectiveness, meaning they both helped reduce anxiety symptoms.
The findings indicated that treatments, whether drugs or psychotherapy, were more effective than placebo or no treatment at all, providing reassurance to patients and healthcare providers about active treatment benefits.
The findings indicated that treatments, whether drugs or psychotherapy, were more effective than placebo or no treatment at all, providing reassurance to patients and healthcare providers about active treatment benefits.
Abstract: results
Twenty-seven trials (14 pharmacological, 13 psychotherapeutic) fulfilled the inclusion criteria, reporting results from 2373 baseline participants. There were no differences between trials in their overall quality. Pooled treatment effects for pharma...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The study concluded that older adults with GAD saw improvements from both medications and therapeutic interventions. This is promising for those seeking treatment options. Moving forward, it's suggested that future research should look into combining medication and therapy.
Such combined treatments might offer even greater relief, providing a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety in older individuals.
Such combined treatments might offer even greater relief, providing a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety in older individuals.
Abstract: conclusions
Older adults with GAD benefited from both pharmacological and psychotherapeutic interventions. Future studies should investigate combined treatment with medication and psychotherapy.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
Scope of GAD in Older Adults
GAD emerges as prevalent in older ages, marked by excessive worry impacting daily life.
💊
Pharmacological Interventions
SSRIs, SNRIs, and benzodiazepines are common, yet careful management is key.
💭
Efficacy of CBT
CBT aids in altering maladaptive thought patterns, proving effective for GAD.
🔗
Complexities of Comorbidities
GAD often coexists with depression and other disorders, complicating treatment.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Interventions for GAD in Older Adults
In line with the findings, various pharmacotherapies and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) show effectiveness in treating GAD.
SSRIs and SNRIs often serve as first-line treatments, but some patients might opt for CBT due to concerns over medication side effects.
Combining both treatments may offer enhanced results.
Additionally, GAD in older adults is commonly linked to late-onset and a poorer quality of life.
SSRIs and SNRIs often serve as first-line treatments, but some patients might opt for CBT due to concerns over medication side effects.
Combining both treatments may offer enhanced results.
Additionally, GAD in older adults is commonly linked to late-onset and a poorer quality of life.
Evidence Summary
Managing Worry and Irritability in Late-Life GAD
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) affects older adults by causing constant worry, trouble sleeping, and irritability. These symptoms make everyday activities difficult and reduce quality of life.
Treating GAD with the right approach can improve daily functioning, but identifying the condition early is key to helping older adults manage their symptoms effectively.
Better diagnosis leads to improved outcomes and more tailored treatment for those with late-life GAD.
Treating GAD with the right approach can improve daily functioning, but identifying the condition early is key to helping older adults manage their symptoms effectively.
Better diagnosis leads to improved outcomes and more tailored treatment for those with late-life GAD.
Evidence Summary
Sleep Struggles and Quality of Life in Older Adults with GAD
Insomnia is a frequent challenge for older adults living with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), making it difficult for them to fall asleep or stay asleep. This sleep disruption can have a significant impact on their daily lives.
The persistent sleep issues experienced by older adults with GAD can lead to a decrease in overall quality of life, as these disruptions make restful sleep hard to achieve.
The persistent sleep issues experienced by older adults with GAD can lead to a decrease in overall quality of life, as these disruptions make restful sleep hard to achieve.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Treatments for Reducing Anxiety in Older Adults
The comparison focuses on studies that evaluate different treatments for generalized anxiety disorder in older adults. Data from various research sources is analyzed to see which methods work best in reducing anxiety. Both pharmacological and psychotherapeutic options are compared based on their effectiveness.
This offers a clear view of how these treatments stack up against each other in practical applications for managing anxiety symptoms.
This offers a clear view of how these treatments stack up against each other in practical applications for managing anxiety symptoms.



