Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Evidence Based Answers
Is GAD a lifelong condition?
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) often persists with fluctuating symptoms, is influenced by coexisting conditions, and shows gender-based differences in diagnosis and outcomes. Full recovery is rare, and comorbidities like depression reduce recovery chances.
Click to explore a section:
GAD persists long-term, with fluctuating symptoms and gender differences in outcomes.
Studies Summary
⏳
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Often Persists
GAD is a long-term condition with symptoms that can last for years. Full recovery is uncommon, but symptoms may improve temporarily.
🎭
Recovery Chances Vary by Onset and Coexisting Conditions
Shorter episodes and older onset improve recovery chances, while depression and other conditions often make recovery harder.
📉
Symptom Fluctuations Are Common in GAD
Symptom severity can change over time, with some experiencing periods of relief followed by relapses that make ongoing challenges likely.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 1
Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Lifelong Patterns
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Recovery from GAD: Insights
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Does GAD Persist Over Time?
Background: The Chronic Nature of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a condition that often persists for long periods, with symptoms that come and go. People with GAD may have times when symptoms improve or disappear, but full recovery is uncommon.
The severity of symptoms can vary throughout a person’s life, ranging from mild to more intense episodes.
The severity of symptoms can vary throughout a person’s life, ranging from mild to more intense episodes.
“
Source Quotes:
The symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder tend to be chronic and wax and wane across the lifespan, fluctuating between syndromal and subsyndromal forms of the disorder.,Rates of full remission are very low.
GAD is a chronic illness with fluctuating symptom severity. In approximately half of the cases, there are intervening symptom-free periods.
Background: How Symptoms Fluctuate Over Time
Although GAD is a long-term condition, symptom severity can change. Some people may have periods where symptoms lessen or even temporarily go away, but relapses often occur.
Studies show that while many individuals experience some level of improvement, ongoing challenges are common.
Studies show that while many individuals experience some level of improvement, ongoing challenges are common.
“
Source Quotes:
In one prospective study of 179 individuals with GAD, approximately 60 percent of patients recovered over 12 years (ie, had no more than residual symptoms for eight consecutive weeks), but approximately one-half of recovered patients subsequently relapsed during the 12-year period.,In another prospective study involving 142 subjects with GAD followed for 14 years, the severity of anxiety symptoms over time decreased only modestly.
Background: Impact of Coexisting Conditions with GAD
GAD frequently occurs with other health conditions, such as depression, chronic pain, or asthma. These additional conditions can make GAD symptoms worse and complicate treatment.
For example, individuals with both GAD and depression may experience more intense anxiety and greater difficulties in daily life.
For example, individuals with both GAD and depression may experience more intense anxiety and greater difficulties in daily life.
“
Source Quotes:
The presence of comorbid disorders such as major depression appear to be associated with more severe and prolonged course of illness and greater functional impairment.
Patients with generalized anxiety disorder have increased risks of other mental and physical health conditions (e.g., chronic pain syndromes, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and inflammatory bowel disease).
Background: When Does GAD Begin?
The age when GAD begins varies widely. Some people experience symptoms as children, while others develop the condition later in life, often triggered by health problems or stress.
Earlier onset of GAD is often linked to more significant challenges in daily functioning.
Earlier onset of GAD is often linked to more significant challenges in daily functioning.
“
Source Quotes:
The age at onset is highly variable; some cases of generalized anxiety disorder begin in childhood, most begin in early adulthood, and another peak of new-onset cases occurs in older adulthood, often in the context of chronic physical health conditions.
The median age at onset for generalized anxiety disorder is 30 years; however, age at onset is spread over a very broad range.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Lifelong Patterns
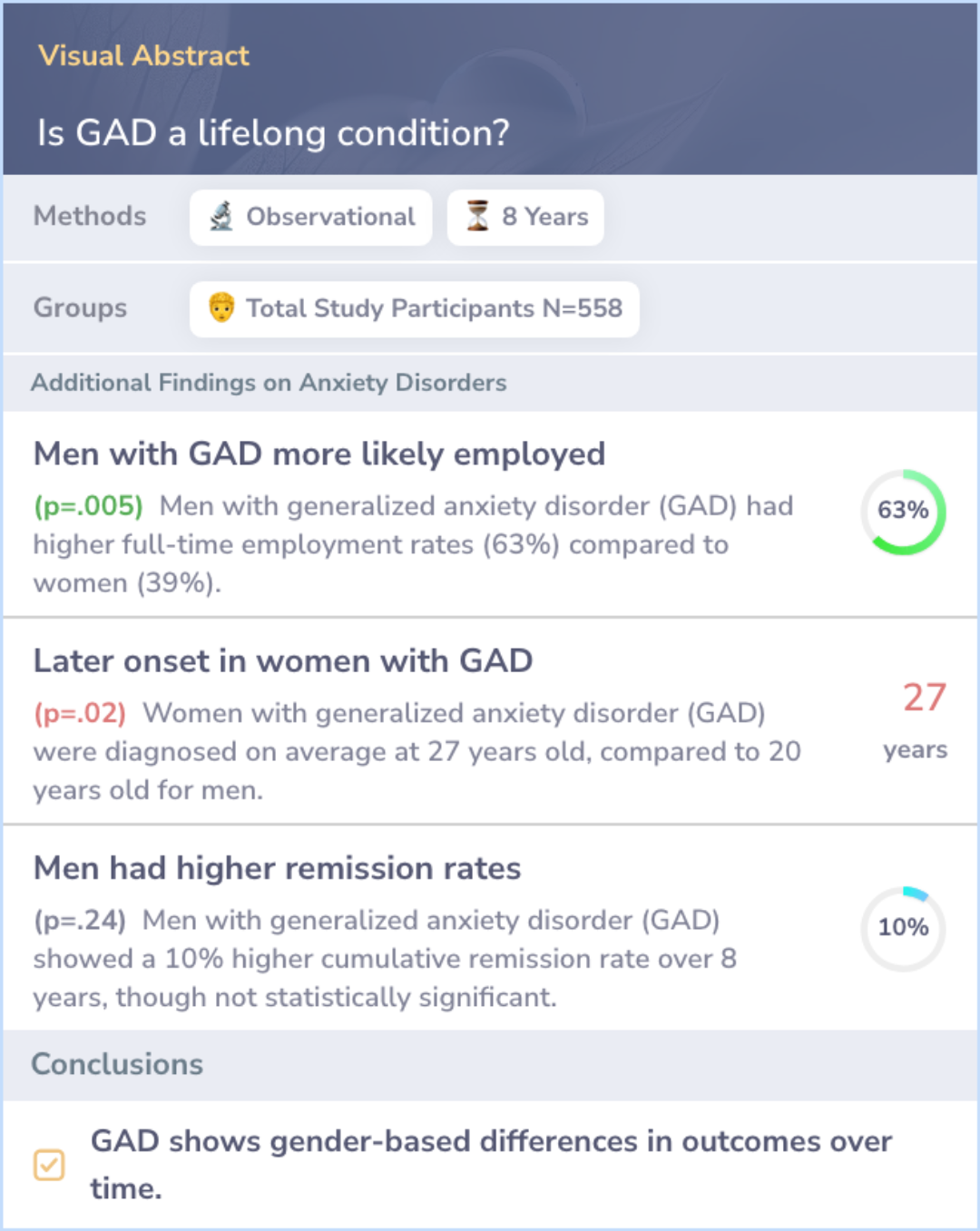
Men with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) tend to have better outcomes in full-time employment rates, with 63% compared to 39% in women.
Women with GAD are diagnosed, on average, 7 years later than men. However, men show a slightly higher remission rate over time, although this difference is not statistically significant.
Women with GAD are diagnosed, on average, 7 years later than men. However, men show a slightly higher remission rate over time, although this difference is not statistically significant.
author
Yonkers KA, Bruce SE, Dyck IR, Keller MB
journal
Depress Anxiety
Date Published
2003
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Recovery from GAD: Insights
Most patients with GAD continue to show symptoms even after 2 years, but recovery is possible, especially under certain conditions.
Patients with shorter episodes or older onset of GAD had better recovery chances, while comorbid depression decreased recovery likelihood.
Patients with shorter episodes or older onset of GAD had better recovery chances, while comorbid depression decreased recovery likelihood.
author
Rodriguez BF, Weisberg RB, Pagano ME, Bruce SE, Spencer MA, Culpepper L, Keller MB
journal
J Nerv Ment Dis
Date Published
2006 Feb

Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Does GAD Persist Over Time?
Anxiety disorders, including GAD, often have long-lasting symptoms that can persist for years.
Recovery from GAD is less likely compared to some other anxiety disorders, and there is a high chance of relapse after recovery.
Comorbid mental health conditions, such as depression, further reduce recovery chances.
Recovery from GAD is less likely compared to some other anxiety disorders, and there is a high chance of relapse after recovery.
Comorbid mental health conditions, such as depression, further reduce recovery chances.
author
Bruce SE, Yonkers KA, Otto MW, Eisen JL, Weisberg RB, Pagano M, Shea MT, Keller MB
journal
Am J Psychiatry
Date Published
2005 Jun

Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) often persists over a lifetime, with symptoms that can fluctuate and vary. While symptoms may improve at times, complete recovery is uncommon and relapses are regular.
Research indicates that GAD is typically accompanied by other health conditions such as depression and chronic pain, exacerbating symptoms and complicating management efforts.
Research indicates that GAD is typically accompanied by other health conditions such as depression and chronic pain, exacerbating symptoms and complicating management efforts.
Evidence Summary
How Anxiety Disorders Change Over Time
Anxiety disorders can follow varied paths over years, with some remaining steady while others change significantly. Factors such as personal resilience and disorder type play key roles in shaping these trajectories.
Different anxiety disorders show distinct patterns of progression, highlighting how individual experiences and circumstances influence their long-term development.
The 8-year span reveals how these conditions evolve, offering insights into their persistence and transformation.
Different anxiety disorders show distinct patterns of progression, highlighting how individual experiences and circumstances influence their long-term development.
The 8-year span reveals how these conditions evolve, offering insights into their persistence and transformation.
Evidence Summary
Personality Traits and Anxiety Over Time
Certain personality traits may play a role in shaping long-term anxiety levels. Characteristics like sensitivity or resilience could influence how some people experience anxiety over time.
The study highlights specific traits that might make individuals more vulnerable to ongoing anxiety, emphasizing the connection between personality and chronic anxiety outcomes.
This sheds light on how personal differences affect mental health trajectories.
The study highlights specific traits that might make individuals more vulnerable to ongoing anxiety, emphasizing the connection between personality and chronic anxiety outcomes.
This sheds light on how personal differences affect mental health trajectories.
Evidence Summary
How Primary Care Supports Anxiety Recovery
Primary care doctors play a key role in helping patients manage and recover from generalized anxiety disorder by offering accessible, familiar care. They apply common treatments, such as therapy and medication, tailored to individual needs.
This approach not only supports symptom management but also makes it easier for patients to stick with their treatment plan, highlighting the value of primary care in addressing anxiety effectively.
This approach not only supports symptom management but also makes it easier for patients to stick with their treatment plan, highlighting the value of primary care in addressing anxiety effectively.


