MCTD
Evidence Based Answers
MCTD Symptoms Overview
Raynaud's phenomenon and puffy hands are major early indicators of MCTD. Joint and muscle issues underline the systemic nature of the disease. Lung problems are widespread, often undetected early, yet critical to monitor.
Published: December 16, 2024
Key early signs like Raynaud's, joint and muscle issues, and lung concerns show MCTD's impact.
Raynaud's Phenomenon and Puffy Hands
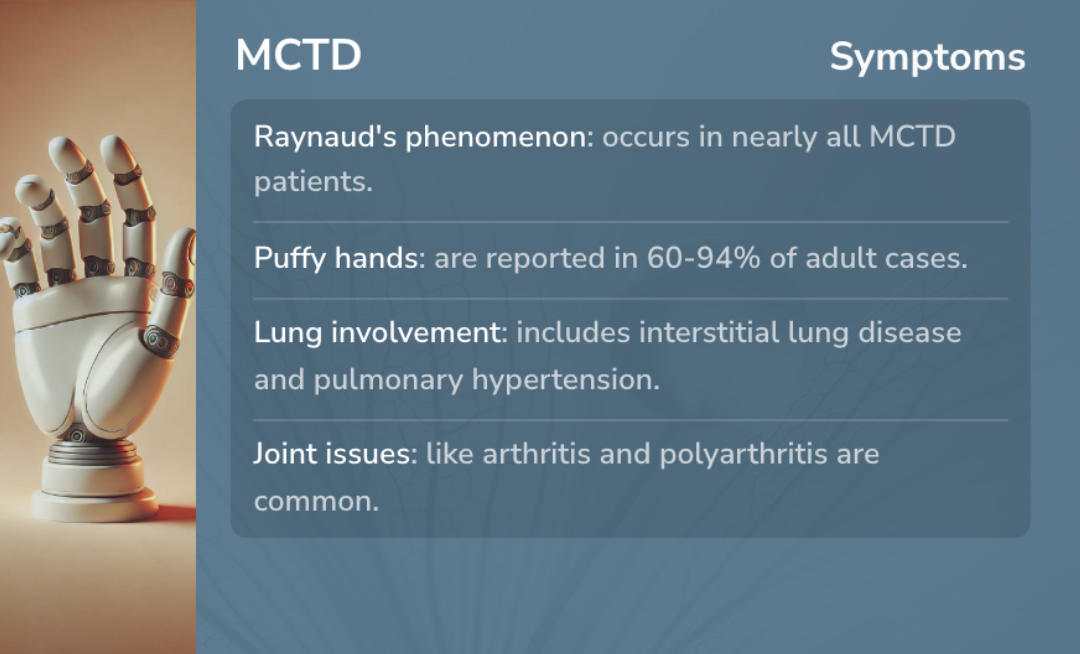
Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) is an early feature of mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD). It affects blood vessels, causing fingers and toes to turn white or blue in reaction to cold or stress. This condition often appears before other symptoms and is tied to changes in blood vessels.
Puffy or swollen hands usually occur with RP, indicating underlying inflammation. They are common, occurring in up to 94% of cases, highlighting their significance in identifying MCTD.
Puffy or swollen hands usually occur with RP, indicating underlying inflammation. They are common, occurring in up to 94% of cases, highlighting their significance in identifying MCTD.
“
Source Quotes:
Secondary RP, associated with... is seen in all CTDs, but it is most prevalent in SSc and MCTD.,Swollen or 'puffy' hands are among the most common disease manifestations reported in adult and juvenile MCTD cohorts.
Regarding clinical manifestations, the most common at disease onset are Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP)... and muscle weakness.,RP is one of the most consistent features.
Joint and Muscle Symptoms
Joint symptoms are widespread in MCTD, typically presenting as joint pain (arthralgias) or multiple joint inflammation (polyarthritis). These issues can cause noticeable joint deformities over time and are found in the majority of cases.
Muscle weakness is another common symptom, seen in most patients with MCTD. It affects various muscles but usually results in less permanent harm than other conditions, showing the disease's widespread impact on joints and muscles.
Muscle weakness is another common symptom, seen in most patients with MCTD. It affects various muscles but usually results in less permanent harm than other conditions, showing the disease's widespread impact on joints and muscles.
“
Source Quotes:
Joint symptoms are commonly associated with MCTD in most studies, and arthritis is included in all the criteria sets.,It appears that the MCTD-associated muscle involvement has the same distribution as PM/DM, but seems to cause less permanent damage.
In general, polyarthralgia is an early and common symptom in MCTD, occurs in approximately 60% of patients...,Between 80% and 90% of patients develop some muscle involvement.
Lung Complications in MCTD
Lung involvement is a common issue in mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), affecting many patients. Problems like interstitial lung disease (ILD) occur in 47-78% of cases, though they might not show symptoms initially.
Signs of lung issues include shortness of breath and chest pain, which can indicate more serious problems such as pulmonary hypertension. More than half of MCTD patients may have lung changes seen in imaging studies, showing the seriousness of these complications.
Signs of lung issues include shortness of breath and chest pain, which can indicate more serious problems such as pulmonary hypertension. More than half of MCTD patients may have lung changes seen in imaging studies, showing the seriousness of these complications.
“
Source Quotes:
The lung is a common site of complications of systemic connective tissue disease (CTD)...
Lung involvement is common in patients with MCTD, varying from 47% to 78%.,A study of 126 patients from Norway with MCTD found that 52% had abnormalities on high resolution computed tomography.
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) presents a blend of symptoms from disorders such as lupus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. Manifestations often include joint pain, muscle weakness, and skin changes, with the presence of a specific antibody often distinguishing MCTD from other conditions.
Studies highlight the variability in symptom progression, stressing the importance of monitoring to manage the unique spectrum of symptoms each patient experiences.
Studies highlight the variability in symptom progression, stressing the importance of monitoring to manage the unique spectrum of symptoms each patient experiences.

Literature Review
Bodolay, 2005
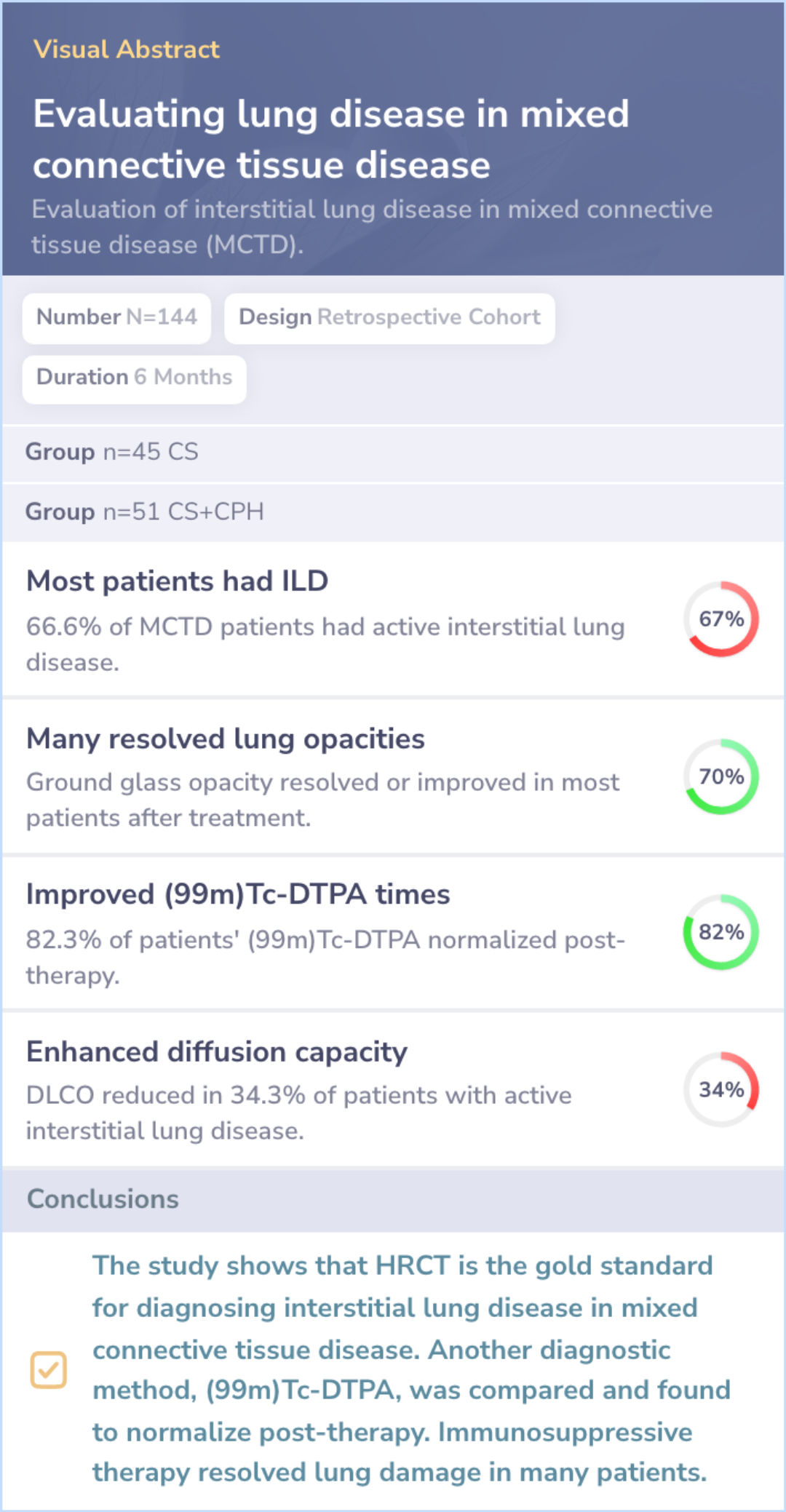
Frequency of interstitial lung disease (ILD):In this study, 66.6% of patients with mixed connective tissue disease had active interstitial lung disease.
Diagnostic findings of ILD:
HRCT results in ILD patients: 78.1% showed ground glass opacity; 21.8% had mild fibrosis.
Clearance times with 99mTc-DTPA: Patients had rapid clearance times, which normalized in 82.3% after therapy.
Pulmonary function changes: Reduced carbon monoxide diffusion was observed in 34.3% of ILD patients.
Effects of therapy on ILD:After 6 months of corticosteroid treatment, 69.8% showed a negative HRCT pattern, while fibrosis developed in 13.5% of patients.
Immune system markers in ILD patients:Active ILD patients had higher immune complex levels and reduced complement levels, both of which improved after therapy.
Comparison of diagnostic techniques:While HRCT remains the gold standard for ILD diagnosis, this study examined 99mTc-DTPA as an additional method for evaluation.
Literature Review
John, 2020
Most affected organ systems in MCTD:
Musculoskeletal system: 95.5% of patients showed involvement.
Skin and mucosa: 78.4% of patients had related symptoms.
Gastrointestinal system: 56% of patients had symptoms in this system.
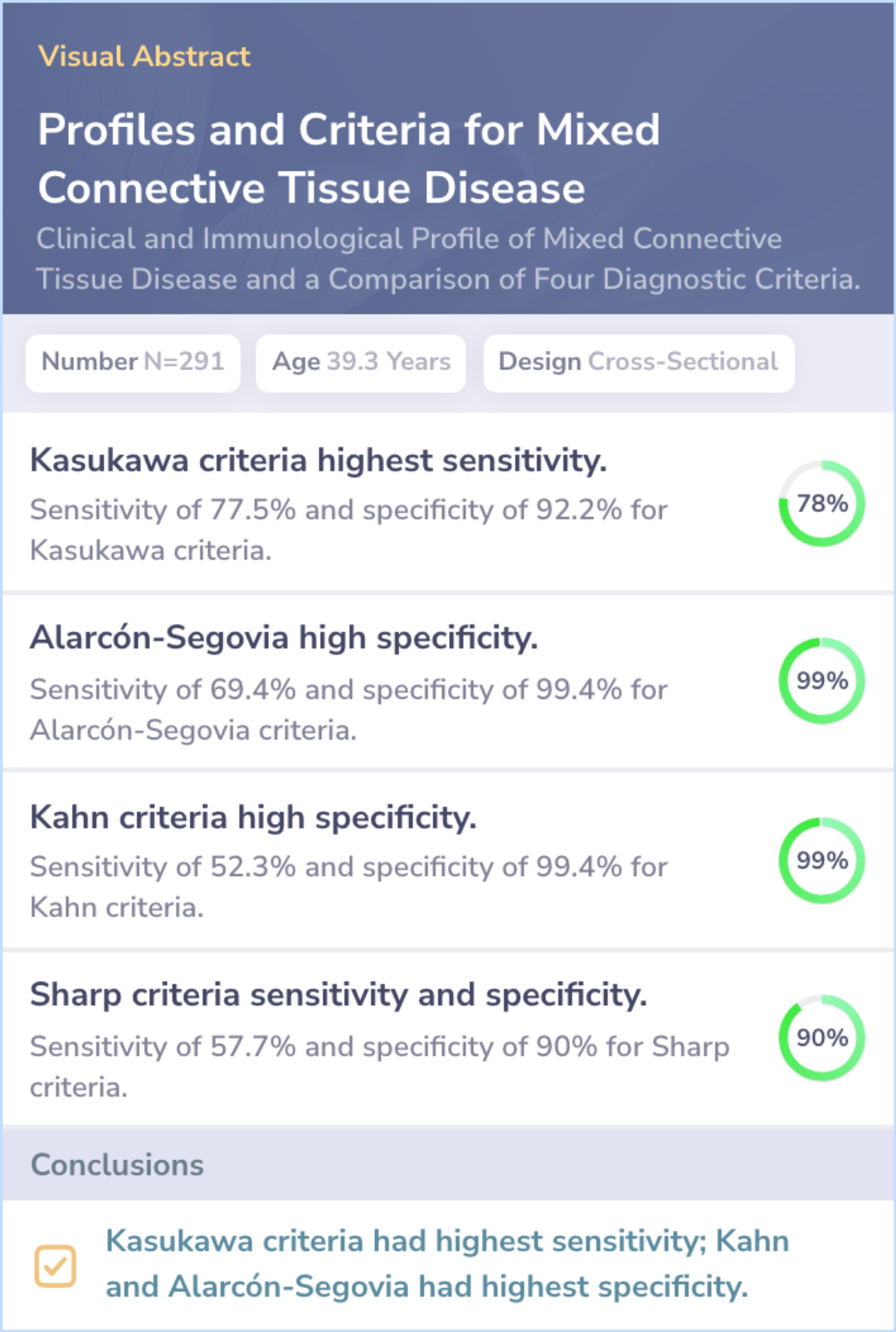
Gender and age distribution:92.8% of patients were women, with an average age of 39.3 years.
Sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic criteria:
Kasukawa criteria: Highest sensitivity at 77.5%, specificity of 92.2%.
Alarcón-Segovia criteria: Sensitivity of 69.4%, highest specificity at 99.4%.
Kahn criteria: Sensitivity of 52.3%, specificity of 99.4%.