Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
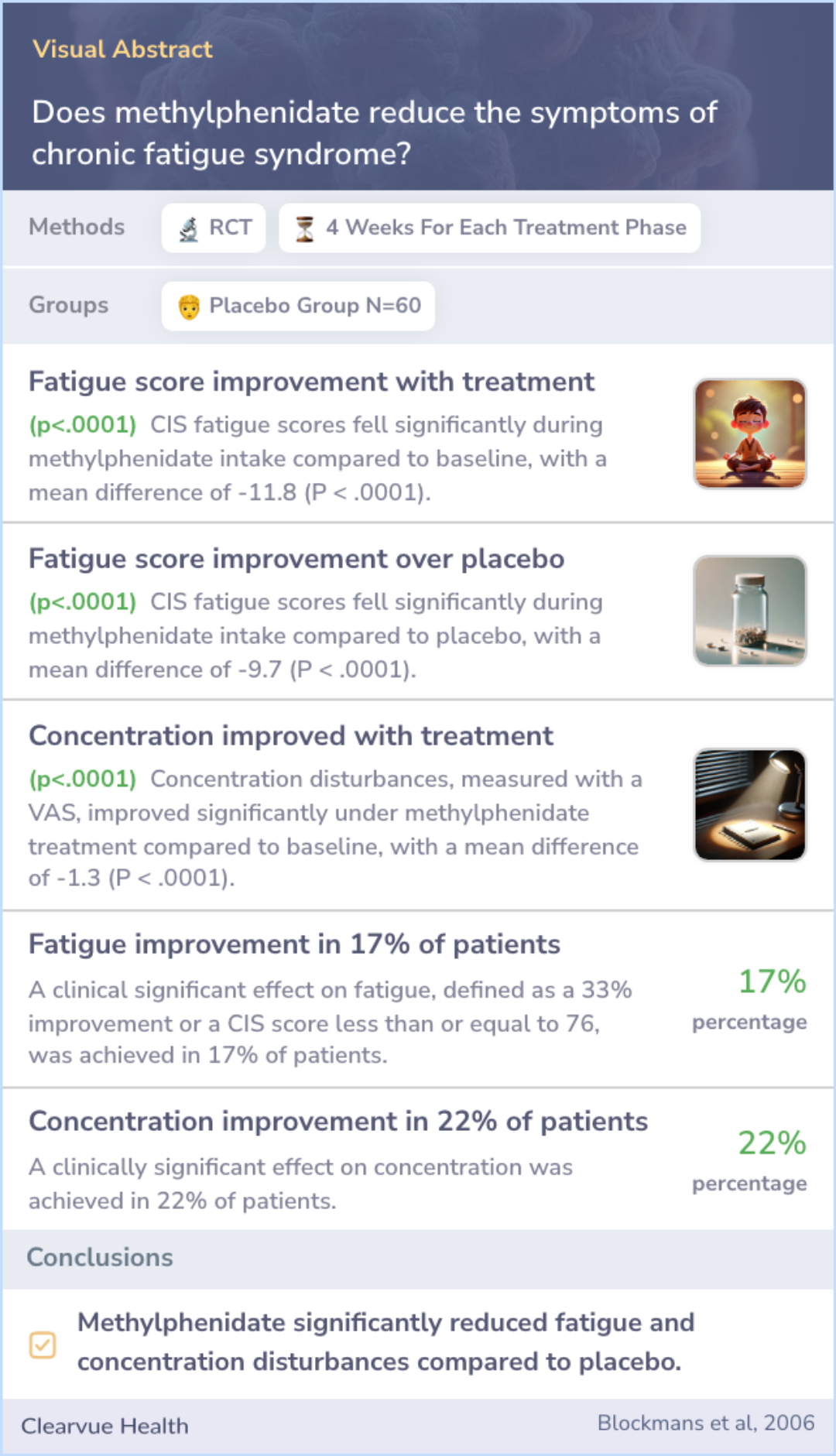
Does methylphenidate reduce the symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome?
Methylphenidate and chronic fatigue syndrome
October 18, 2024
author
Blockmans D, Persoons P, Van Houdenhove B, Bobbaers H
journal
Am J Med
Date Published
2006 Feb
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to investigate the short-term effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) on fatigue, concentration disturbances, and quality of life in chronic fatigue syndrome patients.
💡
What They Found
Researchers found that methylphenidate significantly reduced fatigue and concentration disturbances compared to a placebo.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate may be beneficial for some patients with chronic fatigue syndrome, particularly for reducing fatigue and concentration disturbances, aligning with current evidence on its use for ADHD and narcolepsy.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Chronic fatigue syndrome remains a mysterious condition with few effective treatments. Current therapies, like cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded exercises, offer limited success. This study examined whether methylphenidate, typically used for ADHD, could alleviate symptoms, especially fatigue and concentration issues.Methylphenidate helped with muscle pain and physical function but didn’t improve mood or mental function. These results suggest it might be a useful addition to treatment options, though further research is necessary.
Abstract: background
The objectives of this study were to investigate the short-term effects of methylphenidate, an amphetamine derivative, on fatigue, concentration disturbances, and quality of life.

Physical Improvement
"The physical functioning factor of quality of life was better after methylphenidate than at baseline or under placebo treatment, whereas there was no change in the mental functioning factor, except for vitality."
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Overview
"Whatever the exact nature of chronic fatigue syndrome may be, a symptom-relieving, inexpensive drug that is free of severe side effects would be most welcome."
Potential Relief for Patients
"Whatever the exact mechanisms of action of methylphenidate in chronic fatigue syndrome patients, treatment with this drug might be a valuable aid to the evidence-based treatment modalities cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded exercise."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study involving 60 patients diagnosed with chronic fatigue syndrome. The study ran from March 2003 to March 2004 at a specialized university hospital.Participants received either 10 mg of methylphenidate twice daily or a placebo for four weeks, then switched treatments. Fatigue and concentration were measured using the Checklist Individual Strength (CIS) and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS).
Abstract: methods
A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled crossover study was conducted in 60 patients who fulfilled the 1994 Centers for Disease Control criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome and had concentration difficulties. Patients were enrolled between Marc...more
Study Summary
Results
Participants reported less fatigue and better concentration with methylphenidate compared to placebo. Some saw significant reductions in both symptoms, suggesting the drug was effective for a small portion of the group. However, these improvements were only seen in a minority of participants.
Abstract: results
Fatigue scores fell significantly during methylphenidate intake in comparison with baseline (mean difference: -0.7, P = .010 for VAS; mean difference: -11.8, P <.0001 for CIS) and in comparison with placebo (mean difference: -1.0, P = .001 for VAS; m...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
A daily dose of 20 mg of methylphenidate was more effective than a placebo at reducing fatigue and improving concentration in a small group of patients. While promising, these short-term results need further research to understand long-term effects.
Abstract: conclusions
Methylphenidate at a dose of 2 x 10 mg/day is significantly better than placebo in relieving fatigue and concentration disturbances in a minority of chronic fatigue syndrome patients. Further studies are needed to investigate the long-term effects of...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
👨⚕️
Primary Uses of Methylphenidate
FDA-approved for treating ADHD in children and adults, and as a second-line treatment for narcolepsy.
💊
Off-Label Uses
Also used off-label for conditions like cancer-related fatigue, geriatric depression, and cognitive enhancement.
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Blocks reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Methylphenidate and chronic fatigue syndrome
Methylphenidate may offer some relief for patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Current guidelines emphasize addressing both fatigue and concentration issues effectively.Experts recommend a cautious approach when prescribing medications, aiming for meaningful improvements in symptoms while monitoring patient response.
Evidence Summary
ADHD Management with Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is widely used to manage ADHD in adults.
It enhances focus and concentration, while helping control impulsive behavior.
However, some may experience insomnia and reduced appetite as side effects.
Despite these drawbacks, it remains a key medication for improving attention and impulse control.
It enhances focus and concentration, while helping control impulsive behavior.
However, some may experience insomnia and reduced appetite as side effects.
Despite these drawbacks, it remains a key medication for improving attention and impulse control.
Evidence Summary
Effective ADHD Symptom Reduction: Medication and Therapy Combined
Combining methylphenidate, a common ADHD medication, with psychosocial treatments effectively reduces ADHD symptoms.
This combined approach improves attention and behavior more than using either method alone.
Patients benefit from better outcomes when treated with both medication and therapy compared to just one.
This combined approach improves attention and behavior more than using either method alone.
Patients benefit from better outcomes when treated with both medication and therapy compared to just one.
Evidence Summary
Cardiovascular Risks of Methylphenidate in Adults
The study examines whether methylphenidate, a medication for ADHD, affects heart health in adults.
Methylphenidate is widely used for treating ADHD in adults.
Concerns exist about its potential cardiovascular risks.
Researchers reviewed existing data to understand its impact on heart health better.
Methylphenidate is widely used for treating ADHD in adults.
Concerns exist about its potential cardiovascular risks.
Researchers reviewed existing data to understand its impact on heart health better.




