Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
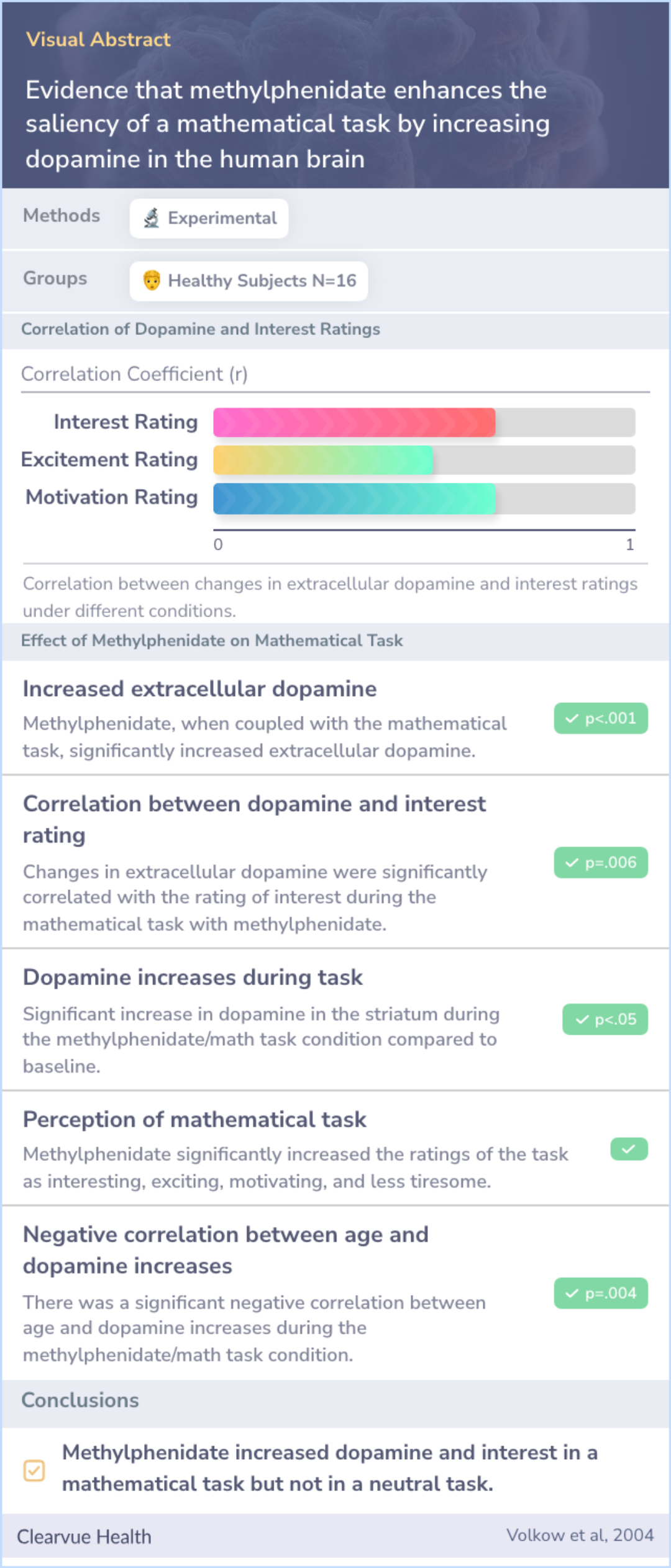
Evidence that methylphenidate enhances the saliency of a mathematical task by increasing dopamine in the human brain
Methylphenidate enhances mathematical task saliency through dopamine
October 18, 2024
author
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Telang F, Maynard L, Logan J, Gatley SJ, Pappas N, Wong C, Vaska P, Zhu W, Swanson JM
journal
Am J Psychiatry
Date Published
2004 Jul
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers studied if methylphenidate increases dopamine to make academic tasks more interesting.
💡
What They Found
They found that methylphenidate increased dopamine and interest in a mathematical task, but not in a neutral task.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate (Ritalin) may help improve attention and performance by making tasks more engaging, which supports its role in treating ADHD, as currently recommended.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Methylphenidate blocks dopamine transporters, which may be important for its therapeutic effects.
It is believed that small increases in dopamine during tasks are amplified by methylphenidate, enhancing the importance of the task and improving performance.
Methylphenidate increases dopamine levels more significantly when given with tasks that require cognitive performance compared to tasks that do not.
The drug also enhances how interesting and motivating tasks seem, suggesting it helps keep attention on important activities.
It is believed that small increases in dopamine during tasks are amplified by methylphenidate, enhancing the importance of the task and improving performance.
Methylphenidate increases dopamine levels more significantly when given with tasks that require cognitive performance compared to tasks that do not.
The drug also enhances how interesting and motivating tasks seem, suggesting it helps keep attention on important activities.
Abstract: background
Methylphenidate is the most commonly prescribed drug for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), yet its therapeutic mechanisms are poorly understood. The objective of this study was to assess if methylphenidate, by increasing dopamine (neur...more

Mechanism of Action
"Methylphenidate blocks the dopamine transporters, and this indirect dopamine agonist effect may be critical for its therapeutic effects."
Amplifying Saliency
"We postulate that methylphenidate's ability to increase the saliency of the task will increase the motivation it elicits and that this will result in improved performance."
Context Sensitivity
"Methylphenidate-induced dopamine transporter blockade would amplify dopamine-induced increases to salient stimuli and thus be context dependent."
Study Summary
Methods
Sixteen healthy subjects participated in the study and were given 20 mg of oral methylphenidate. To measure dopamine levels in the brain, they underwent a special type of brain scan called positron emission tomography (PET) using a compound that binds to dopamine receptors.
The researchers compared how the brain responded to methylphenidate during two different tasks: solving mathematical problems with the potential to earn money (an engaging task), and passively viewing cards without any reward (a neutral task). Additionally, they evaluated how interested the participants found the academic task when they took methylphenidate compared to a placebo.
The researchers compared how the brain responded to methylphenidate during two different tasks: solving mathematical problems with the potential to earn money (an engaging task), and passively viewing cards without any reward (a neutral task). Additionally, they evaluated how interested the participants found the academic task when they took methylphenidate compared to a placebo.
Abstract: methods
Healthy subjects (N=16) underwent positron emission tomography with [(11)C]raclopride (dopamine D(2) receptor radioligand that competes with endogenous dopamine for binding) to assess the effects of oral methylphenidate (20 mg) on extracellular dopam...more
Study Summary
Results
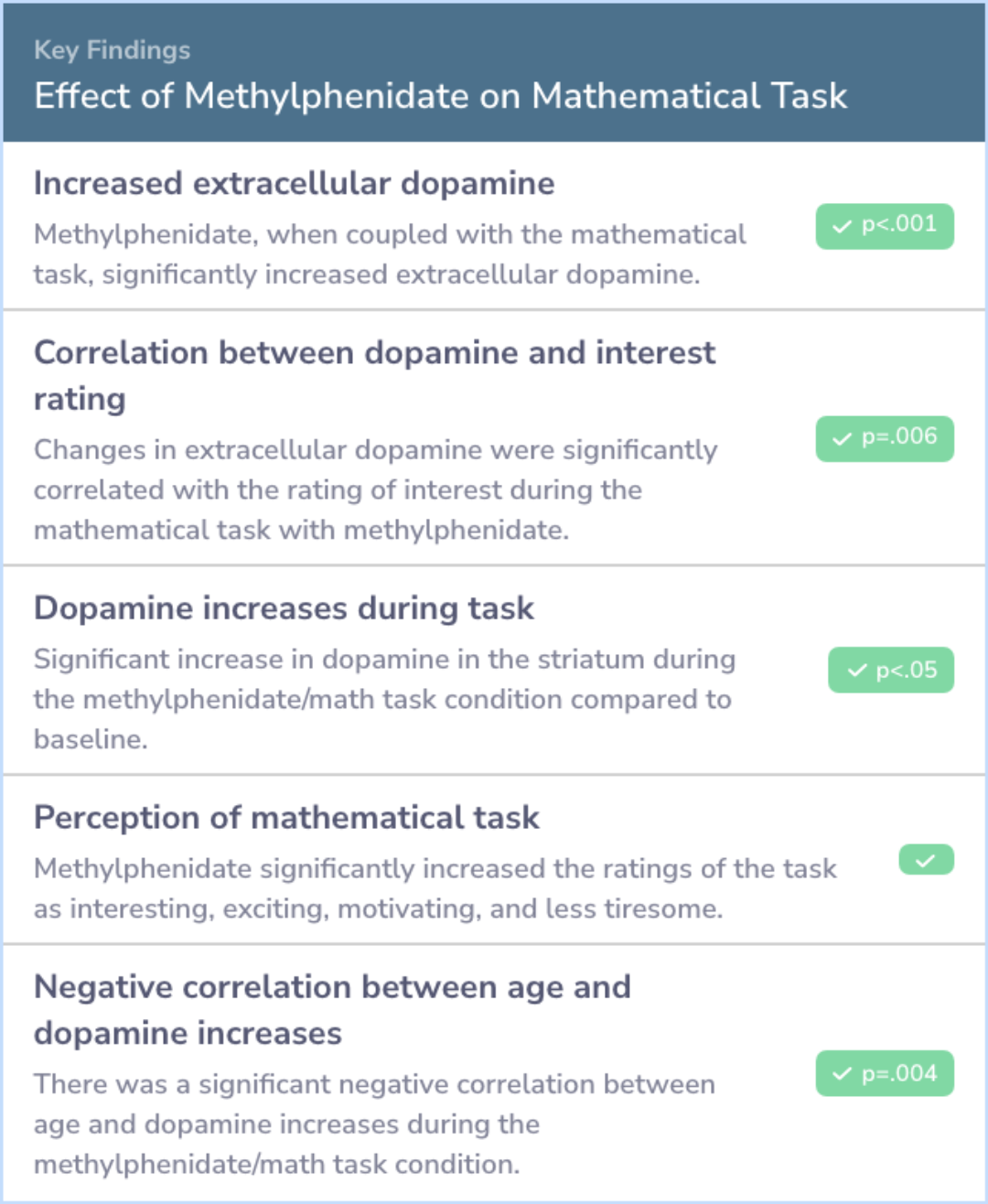
The study found that methylphenidate significantly boosted dopamine levels in the brain during the mathematical task but not during the neutral task. When participants took a placebo instead of methylphenidate, the mathematical task did not increase dopamine.
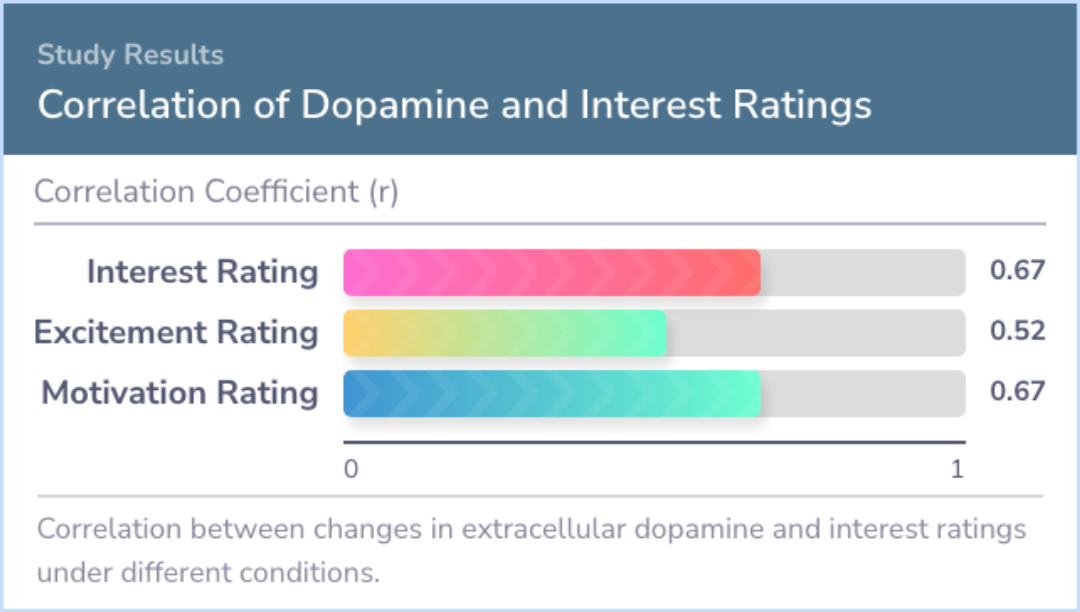
Moreover, participants reported higher levels of interest and motivation for the mathematical task when they took methylphenidate compared to when they took a placebo. These subjective reports were directly linked to the increases in dopamine observed in the brain.
Moreover, participants reported higher levels of interest and motivation for the mathematical task when they took methylphenidate compared to when they took a placebo. These subjective reports were directly linked to the increases in dopamine observed in the brain.
Abstract: results
Methylphenidate, when coupled with the mathematical task, significantly increased extracellular dopamine, but this did not occur when coupled with the neutral task. The mathematical task did not increase dopamine when coupled with placebo. Subjective...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The results confirmed that methylphenidate makes academic tasks more engaging by increasing dopamine in the brain. This increased interest and motivation for the task could help people pay attention and perform better. Therefore, enhancing the saliency or importance of academic tasks might be one of the ways methylphenidate helps manage ADHD symptoms.
These findings also suggest that making schoolwork more interesting could be an effective non-drug strategy to help treat ADHD, showing the value of engaging educational approaches.
These findings also suggest that making schoolwork more interesting could be an effective non-drug strategy to help treat ADHD, showing the value of engaging educational approaches.
Abstract: conclusions
The significant association between methylphenidate-induced dopamine increases and the interest and motivation for the task confirms the prediction that methylphenidate enhances the saliency of an event by increasing dopamine. The enhanced interest f...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
👨⚕️
Primary Uses of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate treats ADHD and narcolepsy, highlighting its relevance in cognitive and motivational enhancements.
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate increases dopamine concentration by blocking reuptake, relevant to task saliency and motivation.
🔬
Neuroprotective Effects
Regulates dopamine levels, potentially beneficial for cognitive tasks and interest modulation.
💊
Dosage and Formulations
Available in various formulations and dosages, ensuring tailored treatment for different cognitive and behavioral needs.
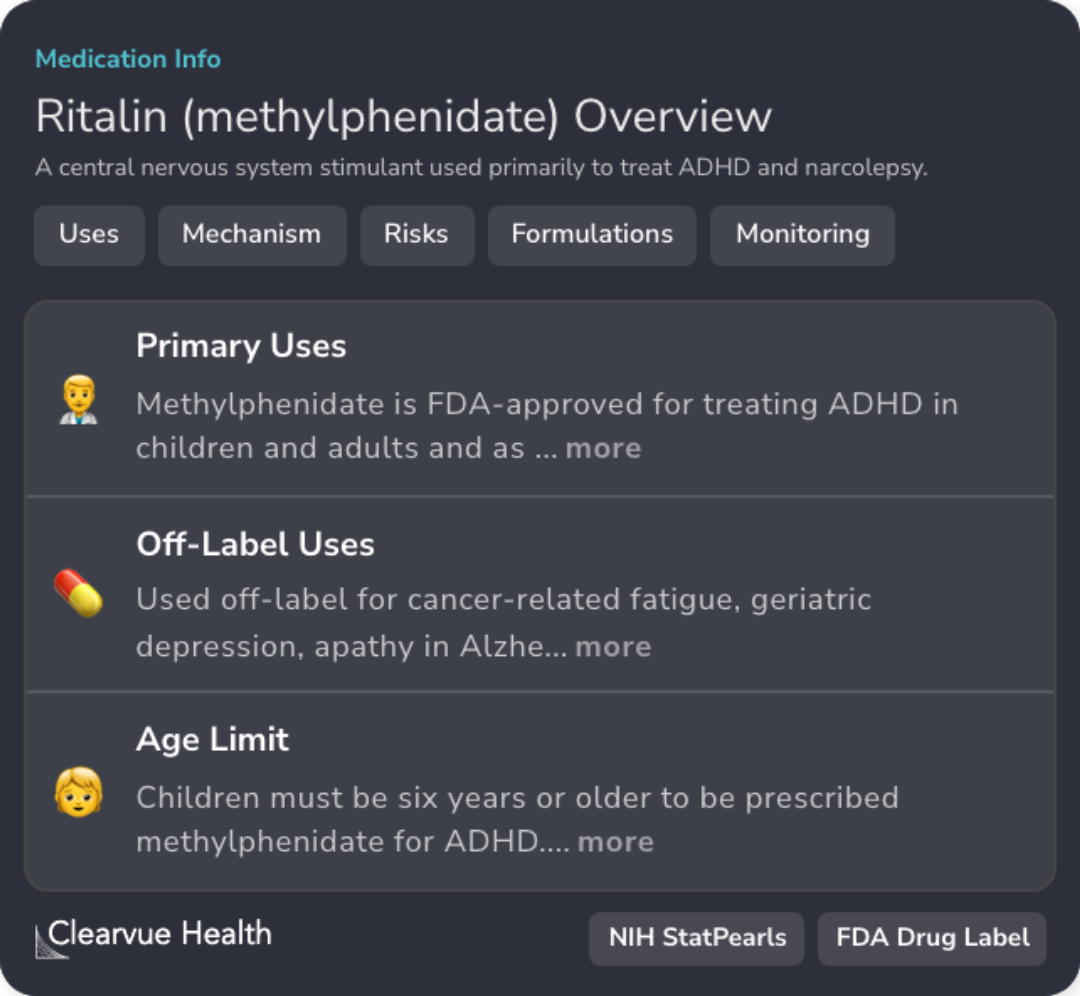
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Methylphenidate enhances mathematical task saliency through dopamine
In line with the study's findings on methylphenidate enhancing the saliency of academic tasks through increased dopamine levels, current professional guidelines emphasize important clinical aspects of methylphenidate therapy.
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both children and adults and acts by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine in presynaptic neurons, thus increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
Various oral formulations exist, differing in the duration of drug release, ensuring flexible dosing options for patients.
While long-term use in children may result in growth retardation, combining medication with non-pharmacologic treatments significantly enhances self-esteem and social functioning.
However, it is essential to monitor dosages, as exceeding 60 mg for immediate-release or 120 mg for extended-release formulations can be toxic and require supportive care. Excessive dosages can also lead to undesirable effects like the overexpression of deltaFosB in the striatum.
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both children and adults and acts by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine in presynaptic neurons, thus increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
Various oral formulations exist, differing in the duration of drug release, ensuring flexible dosing options for patients.
While long-term use in children may result in growth retardation, combining medication with non-pharmacologic treatments significantly enhances self-esteem and social functioning.
However, it is essential to monitor dosages, as exceeding 60 mg for immediate-release or 120 mg for extended-release formulations can be toxic and require supportive care. Excessive dosages can also lead to undesirable effects like the overexpression of deltaFosB in the striatum.
Evidence Summary
Dopamine Changes with Oral Methylphenidate
Taking methylphenidate affects dopamine levels in the brain, leading to changes in brain activity.
The medication, when ingested, influences dopamine production and can alter how the brain responds.
Understanding these changes helps us see how this medication impacts its users and their brain functions.
The medication, when ingested, influences dopamine production and can alter how the brain responds.
Understanding these changes helps us see how this medication impacts its users and their brain functions.
Evidence Summary
Exploring Brain Activity Changes with ADHD Medication
This article investigates how a medication used for ADHD affects brain activity using fMRI scans.
It details how the drug impacts brain functions in individuals with ADHD.
Researchers employed fMRI technology to track changes in brain activity when patients were on the medication.
The goal was to gain insight into how the medication helps manage ADHD symptoms by analyzing these brain function changes.
It details how the drug impacts brain functions in individuals with ADHD.
Researchers employed fMRI technology to track changes in brain activity when patients were on the medication.
The goal was to gain insight into how the medication helps manage ADHD symptoms by analyzing these brain function changes.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate Enhances Cognitive Functions in ADHD
The article explores how methylphenidate helps improve cognitive functions in individuals with ADHD.
It enhances attention, focus, and mental performance.
Research backs these findings, highlighting the medication's role in aiding those diagnosed with ADHD.
Methylphenidate is commonly used to treat ADHD, showcasing its effectiveness in improving cognitive abilities.
It enhances attention, focus, and mental performance.
Research backs these findings, highlighting the medication's role in aiding those diagnosed with ADHD.
Methylphenidate is commonly used to treat ADHD, showcasing its effectiveness in improving cognitive abilities.



