Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
Methylphenidate improves response inhibition in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Methylphenidate improves response inhibition in adult ADHD
August 27, 2024
author
Aron AR, Dowson JH, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW
journal
Biol Psychiatry
Date Published
2003 Dec 15
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
Researchers studied how methylphenidate (Ritalin) affects response inhibition in adults with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
They found that unmedicated adults with ADHD had slower response times, and this impairment was improved by taking methylphenidate (Ritalin).
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate (Ritalin) can help improve response inhibition in adults with ADHD, which is aligned with existing evidence that it aids in similar functions in children.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study confirmed a response inhibition deficit in adult ADHD while showing that stimulant medication, methylphenidate (MPH), can improve this condition.
The right frontal cortex plays a key role in response inhibition, and deficits in this area might underlie challenges in ADHD.
Previous research established that MPH enhances response inhibition in children with ADHD, and this study supports the idea that similar benefits apply to adults.
The right frontal cortex plays a key role in response inhibition, and deficits in this area might underlie challenges in ADHD.
Previous research established that MPH enhances response inhibition in children with ADHD, and this study supports the idea that similar benefits apply to adults.
Abstract: background
Response inhibition is an executive function that requires voluntary control over responses when there is a change of context. The right inferior frontal cortex is necessary for response inhibition, and a deficit in right frontostriatal circuitry mig...more

Response Inhibition Deficit in Adult ADHD
"This study provides evidence for a response inhibition deficit in adult ADHD and suggests that it may be ameliorated by stimulant medication."
Potential for Treatment Improvement
"Showing that a response inhibition deficit in adult ADHD responds to stimulant medication could have importance for the treatment of the disorder."
Exploring the Underlying Brain Mechanisms
"Pharmacologic neuroimaging might elucidate MPH effects in adult ADHD."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers assessed response inhibition using the 'tracking' stop-signal test. This test was administered to 13 adults diagnosed with ADHD and 13 healthy control subjects who had similar ages and intelligence quotients. Adults with ADHD were tested both while they were taking medication and while they were not. The control group did not take any medication.
By comparing the reaction times of these two groups, researchers aimed to determine how effective methylphenidate (MPH) was in improving the response inhibition in adults with ADHD.
By comparing the reaction times of these two groups, researchers aimed to determine how effective methylphenidate (MPH) was in improving the response inhibition in adults with ADHD.
Abstract: methods
Response inhibition was assessed with the 'tracking' stop-signal test in 13 adults with a diagnosis of ADHD, both while taking and while not taking medication, and 13 healthy, unmedicated, age- and intelligence quotient-matched control subjects.
Study Summary
Results
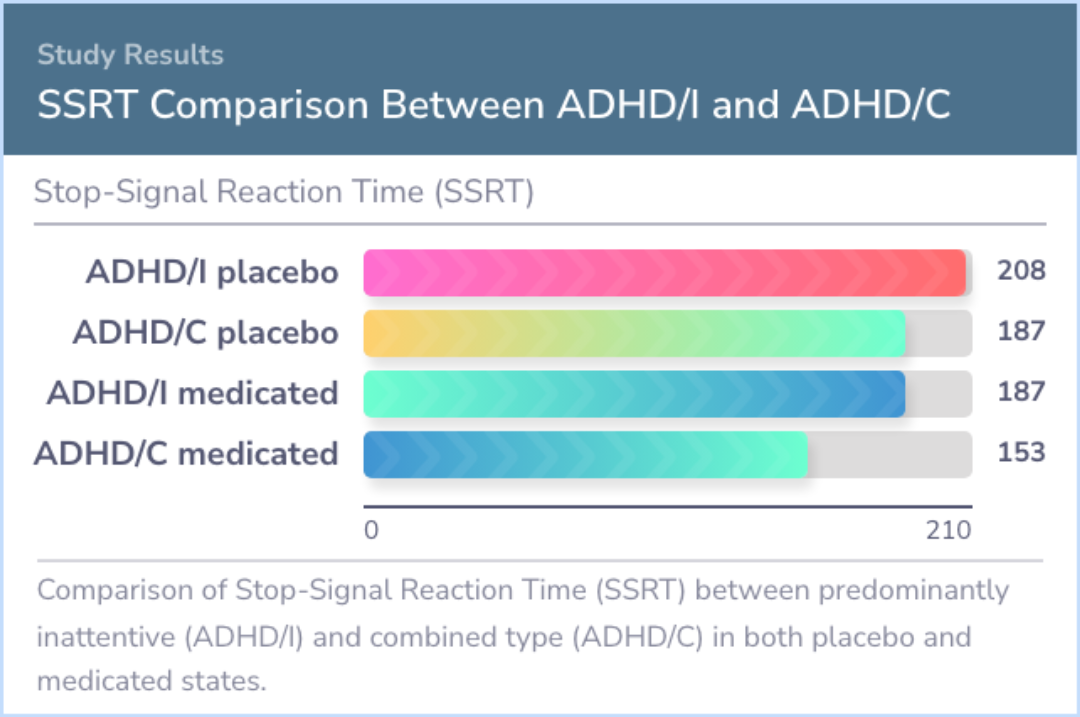
The findings showed that adults with ADHD who were not taking medication had significantly slower stop-signal reaction times compared to the healthy control subjects. This means they had more difficulty in stopping their responses quickly when required.
However, when adults with ADHD were on medication, their response times improved notably. This indicates that methylphenidate (MPH) helped enhance their ability to control their responses, making them more comparable to the healthy control group.
However, when adults with ADHD were on medication, their response times improved notably. This indicates that methylphenidate (MPH) helped enhance their ability to control their responses, making them more comparable to the healthy control group.
Abstract: results
Stop-signal reaction time was significantly slower in unmedicated adults with ADHD relative to healthy control subjects, and this deficit was significantly ameliorated by medication.

Study Summary
Conclusions
The study concluded that adults with ADHD exhibit difficulties in response inhibition, similar to individuals with damage to the right inferior frontal cortex. This highlights a potential neurological basis for the response inhibition issues in ADHD.
These difficulties were significantly reduced with the use of stimulant medication like methylphenidate (MPH, known as Ritalin or Concerta). This suggests that MPH can be an effective treatment for improving response inhibition in adults with ADHD, much like it is in children.
These difficulties were significantly reduced with the use of stimulant medication like methylphenidate (MPH, known as Ritalin or Concerta). This suggests that MPH can be an effective treatment for improving response inhibition in adults with ADHD, much like it is in children.
Abstract: conclusions
Adult ADHD patients had a response inhibition profile similar to that produced by lesions to the right inferior frontal cortex, which was remedied by stimulant medication.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Core Effect of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate blocks norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake, raising their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
👨⚕️
Primary Usage in ADHD
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both children and adults.
💊
Formulation Choices
Available in immediate-release, extended-release, tablets, chewables, solutions, and transdermal patches.
👀
Monitoring Necessities
Regularly monitor for side effects, including cardiovascular issues, psychiatric reactions, and growth suppression.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Methylphenidate improves response inhibition in adult ADHD
The findings suggest that adult ADHD manifests in ways similar to responses seen in childhood ADHD.
ADHD persists into adulthood, impacting various aspects of life.
Stimulant medications significantly improve attention, on-task behaviors, and daily functioning in adults, which aligns with the amelioration observed in the study.
However, clinicians must monitor blood pressure and heart rate elevations that can result from stimulant treatments.
Methylphenidate is recommended when behavioral interventions alone are insufficient.
ADHD persists into adulthood, impacting various aspects of life.
Stimulant medications significantly improve attention, on-task behaviors, and daily functioning in adults, which aligns with the amelioration observed in the study.
However, clinicians must monitor blood pressure and heart rate elevations that can result from stimulant treatments.
Methylphenidate is recommended when behavioral interventions alone are insufficient.
Evidence Summary
Balancing Benefits and Side Effects of Methylphenidate in ADHD Treatment
Methylphenidate is widely prescribed for adults with ADHD, helping them to stay focused and control impulsive behaviors. However, like many medications, it can come with side effects, including trouble sleeping and a reduced appetite.
The medication's effectiveness in improving attention and impulse control makes it a common choice, but users should be mindful of potential sleep disturbances and changes in appetite.
The medication's effectiveness in improving attention and impulse control makes it a common choice, but users should be mindful of potential sleep disturbances and changes in appetite.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate’s Effect on Brain Activity in ADHD
Researchers explored how methylphenidate, a medication for ADHD, impacts brain activity tied to attention. Using brain imaging, they observed changes in attention-related regions in individuals with ADHD after taking the medication.
The study shows how methylphenidate affects neural activity, improving focus by altering brain regions involved in attention, giving a clearer picture of its effects on the ADHD brain.
The study shows how methylphenidate affects neural activity, improving focus by altering brain regions involved in attention, giving a clearer picture of its effects on the ADHD brain.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate: Enhancing Focus and Working Memory
Methylphenidate, commonly known for treating ADHD, also enhances working memory. This boost allows for better performance in tasks requiring focus, making it beneficial in both educational and workplace settings.
Research highlights that methylphenidate not only improves attention but also supports working memory, key in maintaining concentration during complex tasks.
Research highlights that methylphenidate not only improves attention but also supports working memory, key in maintaining concentration during complex tasks.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate Enhances Mental Performance in ADHD Patients
Methylphenidate, a medication for ADHD, boosts cognitive functions in patients. The drug significantly helps in enhancing attention, focus, and mental performance. Research shows these improvements, bolstering the medication's role in managing ADHD effectively.
Methylphenidate aids those diagnosed with ADHD by improving their cognitive abilities, enabling better attention and overall mental performance.
Methylphenidate aids those diagnosed with ADHD by improving their cognitive abilities, enabling better attention and overall mental performance.
Evidence Summary
How Methylphenidate Boosts Focus and Attention
Methylphenidate boosts levels of certain brain chemicals in the prefrontal cortex. This increase is associated with better attention and focus. These changes help explain why some medications are effective for treating attention disorders.
By increasing these brain chemicals, methylphenidate helps to improve attention and focus, showing how it works to address attention issues.
This mechanism illustrates the link between brain chemistry and improved symptoms in attention disorders.
By increasing these brain chemicals, methylphenidate helps to improve attention and focus, showing how it works to address attention issues.
This mechanism illustrates the link between brain chemistry and improved symptoms in attention disorders.