Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
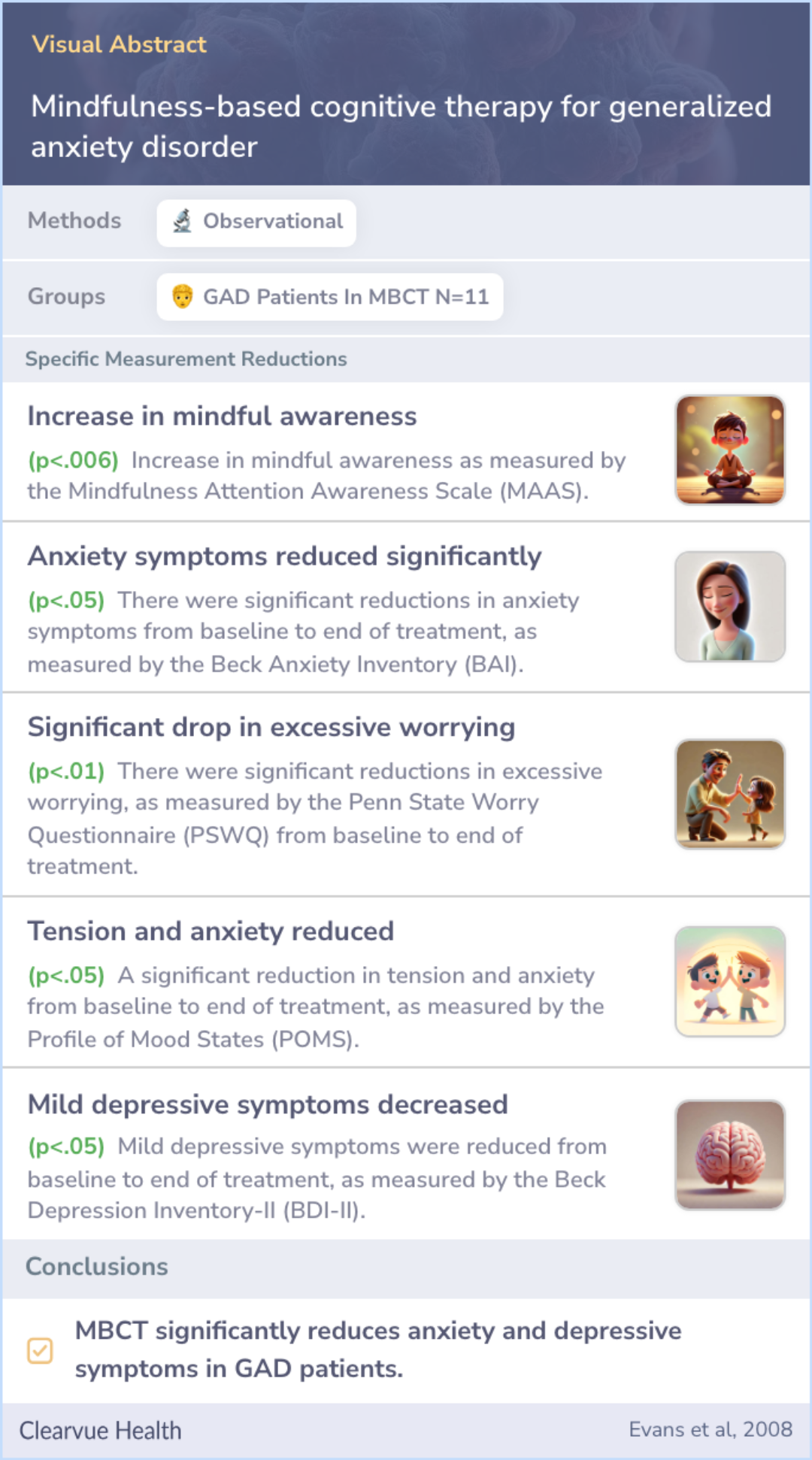
Visual Abstract
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, Stowell C, Smart C, Haglin D
journal
J Anxiety Disord
Date Published
2008 May
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
💡
What They Found
Researchers found a significant reduction in anxiety and depressive symptoms among participants who underwent MBCT.
📚
What This Means
These findings indicate that MBCT may help reduce anxiety and mood symptoms in GAD patients, aligning with current approaches that combine cognitive strategies with mindfulness practices.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study explored mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) as a potential treatment for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It focused on how mindfulness practices might help patients by shifting their attention from worries about the future to the present moment.
Results suggested that participants found value in the experience, with many reporting lasting positive effects, enhancing their awareness and acceptance of self and emotions.
Results suggested that participants found value in the experience, with many reporting lasting positive effects, enhancing their awareness and acceptance of self and emotions.
Abstract: background
While cognitive behavior therapy has been found to be effective in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), a significant percentage of patients struggle with residual symptoms. There is some conceptual basis for suggesting that cultivati...more

Mindfulness and Awareness
"Mindfulness, moment-to-moment non-judgmental awareness, is cultivated through the regular practice of mindfulness meditation and emphasizes an open awareness to the contents of the mind."
Feasibility of Mindfulness Therapy
"It appears that a mindfulness-based therapeutic approach is also a feasible and acceptable treatment for individuals with GAD since all the subjects admitted to the study participated and completed the 8-week group treatment."
Focus Shift
"Mindfulness may provide a useful alternative way of responding for individuals with GAD since the nature of worry is future directed, training in present-moment mindful awareness can shift the focus from future anxieties."
Study Summary
Methods
Participants for this study were chosen from a major academic medical center. They attended a group program called Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT). During the study, they completed surveys assessing their levels of anxiety, depression, worry, and awareness of their daily experiences.
These surveys were filled out both at the beginning and the end of the therapy program to compare how participants' emotions and awareness changed throughout the course. This method allowed researchers to gauge the potential impact of MBCT on their mental states.
These surveys were filled out both at the beginning and the end of the therapy program to compare how participants' emotions and awareness changed throughout the course. This method allowed researchers to gauge the potential impact of MBCT on their mental states.
Abstract: methods
Eligible subjects recruited to a major academic medical center participated in the group MBCT course and completed measures of anxiety, worry, depressive symptoms, mood states and mindful awareness in everyday life at baseline and end of treatment.

Study Summary
Results
Out of the participants, eleven people completed the study, comprising six women and five men, with an average age of 49. By the end of the treatment, participants showed a notable decrease in both anxiety and depression levels, indicating a possible benefit from the mindfulness program.
These results suggest that integrating mindfulness into therapy could significantly help in reducing both anxiety and depression, though further research is necessary to validate these findings across larger groups.
These results suggest that integrating mindfulness into therapy could significantly help in reducing both anxiety and depression, though further research is necessary to validate these findings across larger groups.
Abstract: results
Eleven subjects (six female and five male) with a mean age of 49 (range=36-72) met criteria and completed the study. There were significant reductions in anxiety and depressive symptoms from baseline to end of treatment.


Study Summary
Conclusions
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) appears to be a suitable, promising method for lowering anxiety and mood-related symptoms in individuals struggling with generalized anxiety disorder. It also aids in enhancing everyday mindfulness and awareness.
To build on these initial positive findings, there is a need to conduct a comprehensive, randomized clinical trial to thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of MBCT in treating GAD on a larger scale.
To build on these initial positive findings, there is a need to conduct a comprehensive, randomized clinical trial to thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of MBCT in treating GAD on a larger scale.
Abstract: conclusions
MBCT may be an acceptable and potentially effective treatment for reducing anxiety and mood symptoms and increasing awareness of everyday experiences in patients with GAD. Future directions include development of a randomized clinical trial of MBCT f...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Residual Symptoms Post-Therapy
Many GAD patients continue experiencing residual symptoms despite CBT, indicating the need for alternative strategies like MBCT.
🧘
Mindfulness and Anxiety Management
Mindfulness cultivation offers potential benefits for GAD management, linking it to mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT).
🔄
Background of MBCT
MBCT, rooted in MBSR, blends mindfulness meditation with cognitive strategies to address anxiety and mood disorders.
📉
MBCT's Effectiveness in Depression
Evidence supports MBCT in reducing depression relapse, suggesting possible benefits for GAD patient management.
🔗
Complex Nature of GAD
GAD often coexists with other disorders, complicating treatment and pointing to the need for comprehensive strategies like MBCT.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for GAD
In line with the abstract's findings on MBCT, current professional recommendations emphasize CBT as an effective method for GAD by combining patient experiences with reasoning exercises.
Mindful approaches, such as MBSR, show promise in reducing symptoms, aligning with MBCT's potential.
Therapists often utilize techniques like cognitive restructuring and regular symptom monitoring to maintain long-term benefits and prevent relapse.
Mindful approaches, such as MBSR, show promise in reducing symptoms, aligning with MBCT's potential.
Therapists often utilize techniques like cognitive restructuring and regular symptom monitoring to maintain long-term benefits and prevent relapse.
Evidence Summary
Mindfulness Meditation for Anxiety and Well-Being
Mindfulness meditation provides a way to focus thoughts and calm the mind, which can help reduce anxiety and stress. This practice has shown positive results for those dealing with anxiety disorders.
By consistently practicing mindfulness, individuals may experience greater overall well-being, as it helps them become more present and relaxed in their daily lives.
By consistently practicing mindfulness, individuals may experience greater overall well-being, as it helps them become more present and relaxed in their daily lives.
Evidence Summary
Mindfulness Eases Worry and Improves Emotional Control
Mindfulness helps individuals with generalized anxiety disorder manage their emotions and lessen excessive worry. By incorporating mindfulness techniques, people can improve their ability to regulate emotions, reducing the constant concern that characterizes this condition.
Practicing mindfulness can also alleviate some of the symptoms linked to generalized anxiety disorder, providing a potential tool for better emotional control and symptom reduction.
Practicing mindfulness can also alleviate some of the symptoms linked to generalized anxiety disorder, providing a potential tool for better emotional control and symptom reduction.
Evidence Summary
Managing Anxiety with Acceptance-Based Therapy
Acceptance-based therapy offers a way to manage generalized anxiety by embracing anxious thoughts and feelings, instead of trying to remove them. This approach promotes mindfulness and helps lower anxiety by encouraging people to accept their emotions.
The therapy focuses on building skills to live with anxiety more comfortably, shifting the goal from eliminating anxiety to managing its presence in daily life.
The therapy focuses on building skills to live with anxiety more comfortably, shifting the goal from eliminating anxiety to managing its presence in daily life.



