Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Validation and standardization of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Screener (GAD-7) in the general population
Validation of GAD-7 in the general population
October 30, 2024
author
Löwe B, Decker O, Müller S, Brähler E, Schellberg D, Herzog W, Herzberg PY
journal
Med Care
Date Published
2008 Mar
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
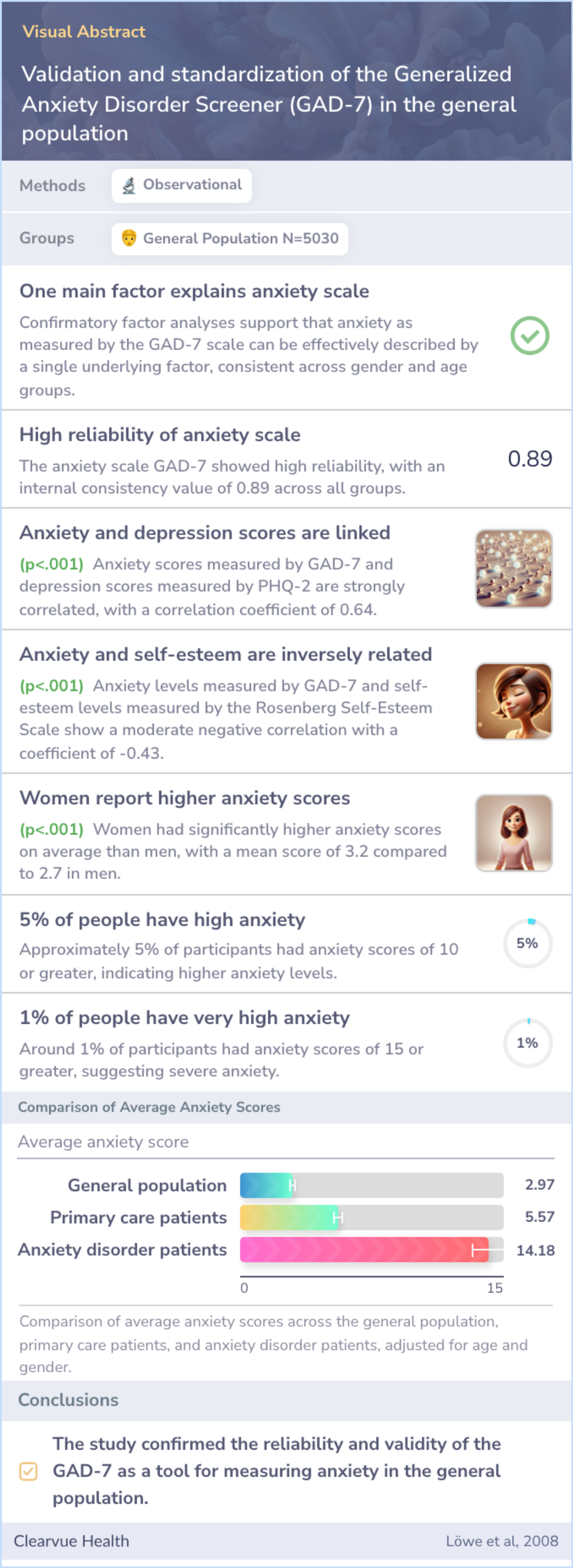
The study aimed to evaluate the reliability, construct validity, and factorial validity of the GAD-7 in the general population and to generate normative data.
💡
What They Found
The study found that the GAD-7 is a reliable and valid measure of anxiety in the general population, with consistent internal consistency across subgroups and generated normative data based on gender and age.
📚
What This Means
The findings confirm that GAD-7 is a reliable tool for measuring anxiety, aligning with the current evidence that highlights the importance of such tools in diagnosing anxiety-related disorders like generalized anxiety disorder.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to evaluate the GAD-7, a self-report measure for anxiety, across various demographics. Researchers sought to confirm its reliability and validity, ensuring it could effectively identify anxiety levels in different age and gender groups.
The findings suggest that the GAD-7 can serve as a trustworthy tool, with consistent results across demographics. This empowers both clinicians and individuals to better understand anxiety's presence and severity in the general population.
The findings suggest that the GAD-7 can serve as a trustworthy tool, with consistent results across demographics. This empowers both clinicians and individuals to better understand anxiety's presence and severity in the general population.
Abstract: background
To investigate reliability, construct validity, and factorial validity of the GAD-7 in the general population and to generate normative data.

Reliability and Validity of GAD-7
"This study, including more than 5000 subjects, gives evidence that the GAD-7 is a reliable and valid self-report measure for anxiety in the general population."
Construct Validity Support
"Construct validity is also supported by the extent to which the GAD-7 sum score was associated with known risk factors of generalized anxiety disorders, such as gender, age, educational level, partnership, employment status, and household income."
Normative Data Provision
"Another main result of this study is the standardization of the GAD-7 with the provision of normative data."
Study Summary
Methods
The researchers conducted a comprehensive, face-to-face survey across Germany from May to June 2006, including 5,030 participants, slightly more women, averaging about 48 years of age.
Participants completed questionnaires including the GAD-7 and other scales assessing depression and self-esteem, alongside demographic questions, to offer a robust analysis of anxiety and its relation to various factors.
Participants completed questionnaires including the GAD-7 and other scales assessing depression and self-esteem, alongside demographic questions, to offer a robust analysis of anxiety and its relation to various factors.
Abstract: methods
Nationally representative face-to-face household survey conducted in Germany between May 5 and June 8, 2006. Five thousand thirty subjects (53.6% female) with a mean age (SD) of 48.4 (18.0) years. The survey questionnaire included the GAD-7, the 2-it...more

Study Summary
Results
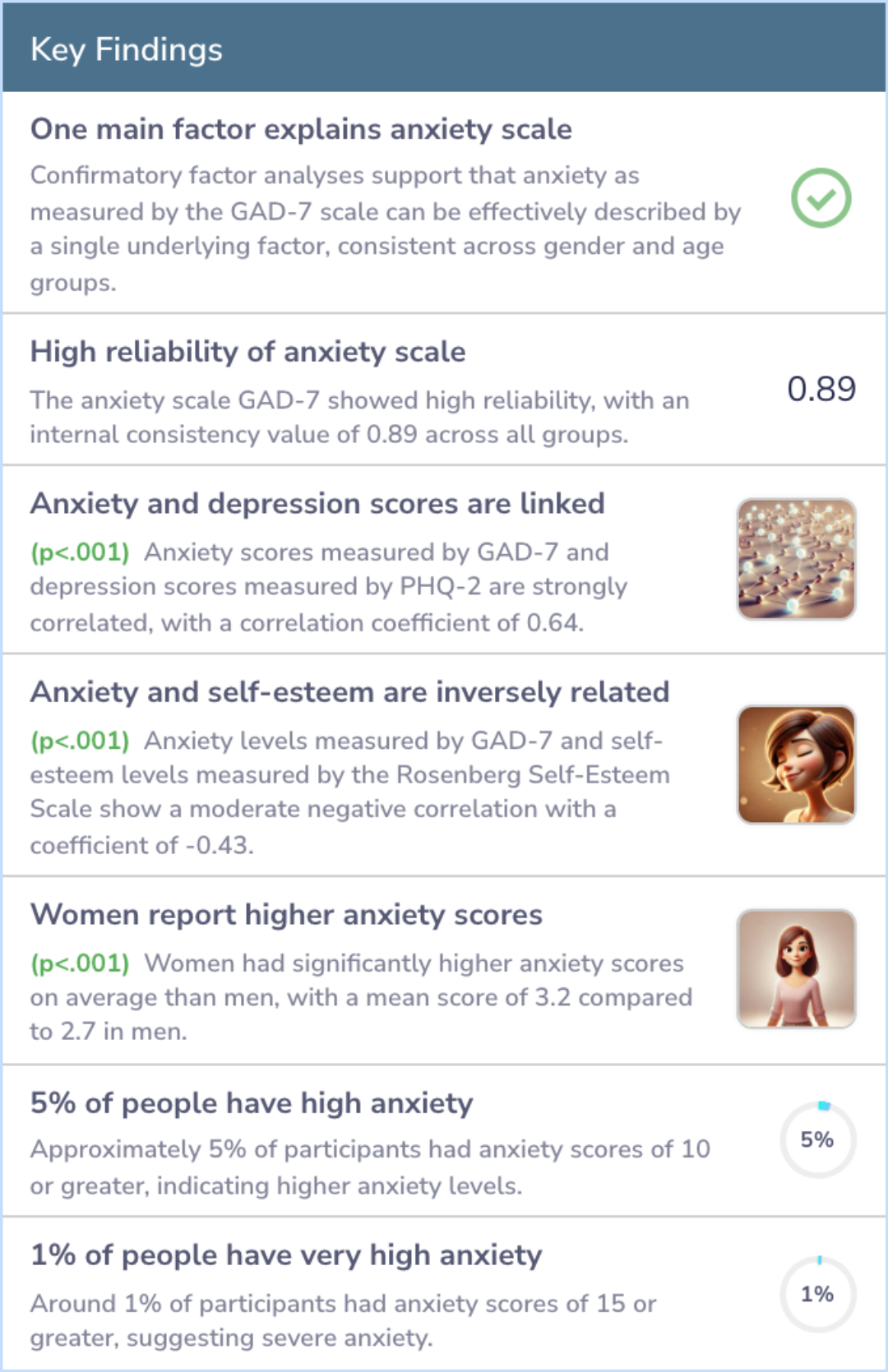
The study confirmed that the GAD-7 has a consistent structure across different genders and ages. This tool reliably measures anxiety with internal consistency demonstrated. It aligns well with other measures like a depression module and self-esteem scale.
Findings showed women often reported higher anxiety scores than men. Norms for different groups were established, with around 5% scoring 10+ on the GAD-7 scale, indicating notable anxiety.
Findings showed women often reported higher anxiety scores than men. Norms for different groups were established, with around 5% scoring 10+ on the GAD-7 scale, indicating notable anxiety.
Abstract: results
Confirmatory factor analyses substantiated the 1-dimensional structure of the GAD-7 and its factorial invariance for gender and age. Internal consistency was identical across all subgroups (alpha = 0.89). Intercorrelations with the PHQ-2 and the Rose...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
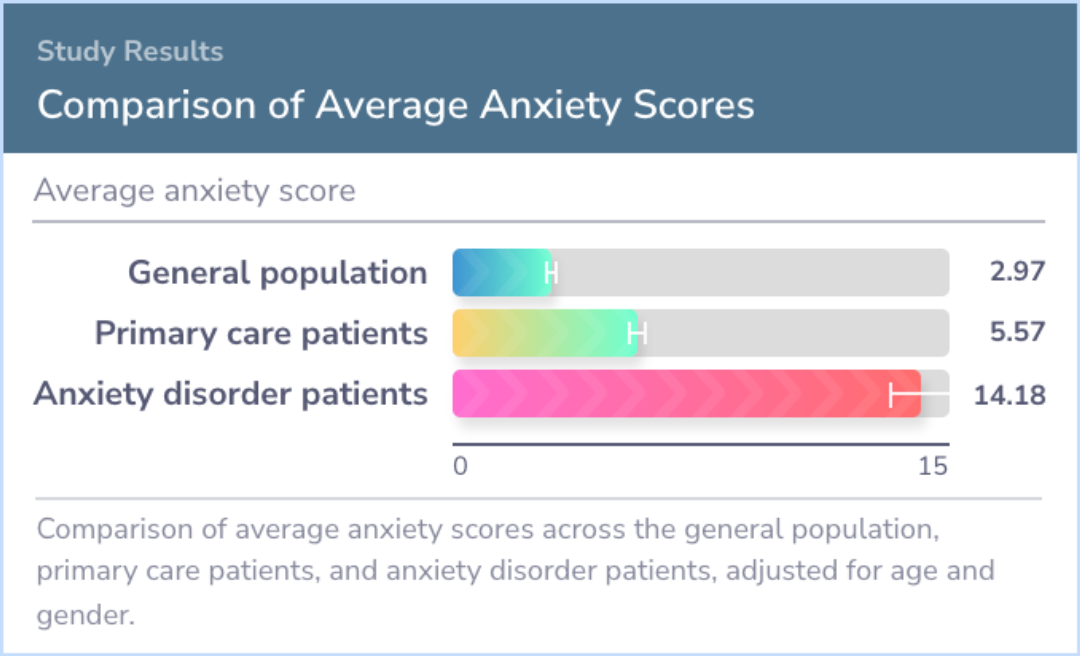
The study provides solid evidence that the GAD-7 is a reliable and valid indicator of anxiety levels in the general population. The established norms allow for practical comparisons, so individuals can see where they stand relative to a broader group.
Clinicians and researchers can use this data confidently when interpreting anxiety levels, enhancing the tool's application in various settings.
Clinicians and researchers can use this data confidently when interpreting anxiety levels, enhancing the tool's application in various settings.
Abstract: conclusions
Evidence supports reliability and validity of the GAD-7 as a measure of anxiety in the general population. The normative data provided in this study can be used to compare a subject's GAD-7 score with those determined from a general population refere...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
📝
GAD-7 Tool
The GAD-7 is a screening tool to evaluate generalized anxiety disorder severity.
😟
Excessive Worry
Persistent, unrealistic worry impacts daily life in generalized anxiety disorder.
💭
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
CBT focuses on changing thought patterns and exposure to anxiety-provoking situations.
📅
DSM-5 Criteria
Excessive anxiety and worry occur more days than not for at least 6 months.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Validation of GAD-7 in the general population
In line with the study's validation of the GAD-7 in the general population, professional guidelines routinely use the GAD-7 for screening and monitoring anxiety symptoms.
SSRIs and SNRIs stand as the preferred initial pharmacotherapy options for generalized anxiety disorder.
CBT demonstrates consistent effectiveness across various demographics, with therapist competence enhancing treatment outcomes significantly.
Physical symptoms like muscle tension in GAD are often overlooked, which affects accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
Augmentative therapies such as aerobic exercise and mindfulness-based interventions further contribute to reducing anxiety symptoms.
SSRIs and SNRIs stand as the preferred initial pharmacotherapy options for generalized anxiety disorder.
CBT demonstrates consistent effectiveness across various demographics, with therapist competence enhancing treatment outcomes significantly.
Physical symptoms like muscle tension in GAD are often overlooked, which affects accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
Augmentative therapies such as aerobic exercise and mindfulness-based interventions further contribute to reducing anxiety symptoms.
Evidence Summary
Managing Anxiety: Understanding GAD Symptoms and Treatments
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is marked by persistent worry and anxiety, affecting daily life through constant unease and stress. Those with GAD may experience symptoms like restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and physical discomfort.
Various treatments and coping strategies, including therapy and lifestyle changes, can help manage these symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by GAD.
Various treatments and coping strategies, including therapy and lifestyle changes, can help manage these symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by GAD.
Evidence Summary
Transforming Anxiety: Two Effective Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a structured approach to tackling anxiety by transforming negative thought patterns and behaviors, providing individuals with tools to challenge their anxious thoughts. In contrast, Applied Relaxation emphasizes physical techniques that promote muscle relaxation, helping to ease anxiety symptoms through controlled breathing and relaxation exercises.
Both methods provide distinct strategies for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), catering to different preferences and therapeutic needs, highlighting the varied ways to address anxiety effectively.
Both methods provide distinct strategies for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), catering to different preferences and therapeutic needs, highlighting the varied ways to address anxiety effectively.
Evidence Summary
Medications for Managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Comparative Review
This review examines various medications for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), drawing from clinical evidence and expert guidelines to assess their effectiveness and safety.
It provides insights into how each drug compares in addressing GAD symptoms, highlighting strengths and potential limitations identified in studies.
The discussion centers on treatment recommendations based on clinical data, offering a grounded perspective on the options available.
It provides insights into how each drug compares in addressing GAD symptoms, highlighting strengths and potential limitations identified in studies.
The discussion centers on treatment recommendations based on clinical data, offering a grounded perspective on the options available.