Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose, or sugar, in the blood. Insulin sensitivity allows the body to use blood glucose effectively. Insulin resistance is when the body can not properly use blood glucose. The levels of sensitivity and resistance are influenced by health behaviors like weight loss and diet.
Influence of caffeine
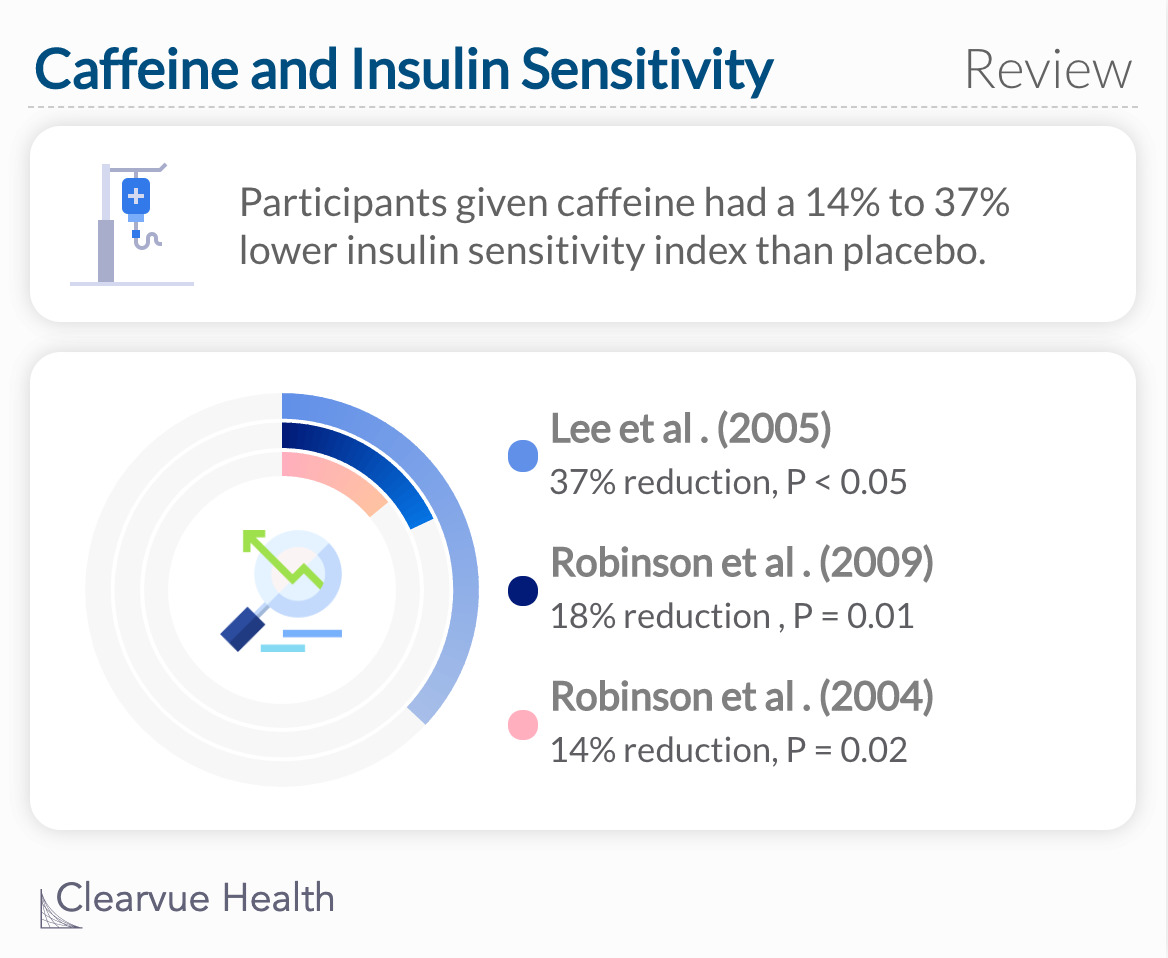
Researchers systematically reviewed nine trials with 134 participants that measured caffeine and insulin sensitivity. Particularly, they looked at studies of type-2 diabetes patients.
Source: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials of the effects of caffeine or caffeinated drinks on blood glucose concentrations and insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes mellitus
Participants who were given caffeine had a lower insulin sensitivity index than those in the placebo group. This means that caffeine can inhibit the body’s ability to use blood glucose effectively.
More Information on Caffeine
Caffeine
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Caffeine
Caffeine has been shown to be most healthy for your body and mind. There are certain negative effects that have come up in studies, however they are mostly specific to individuals with certain conditions such as anxiety and migraine headaches.
Coffee as a caffeine source
Source: Coffee Consumption and Insulin Sensitivity
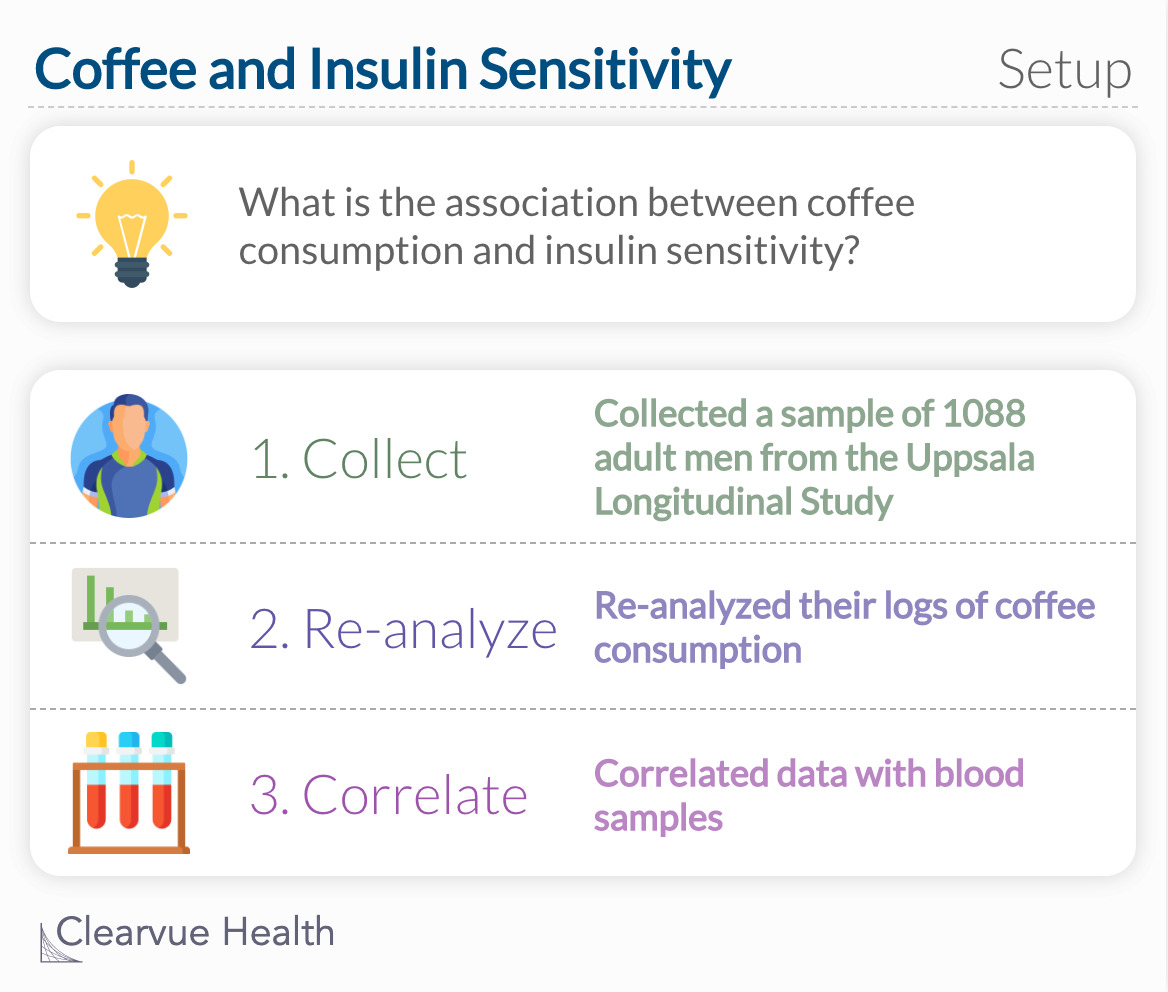
To see how coffee influences insulin, data were reanalyzed from the Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men where participants were instructed to keep logs of their dietary habits and other behaviors.
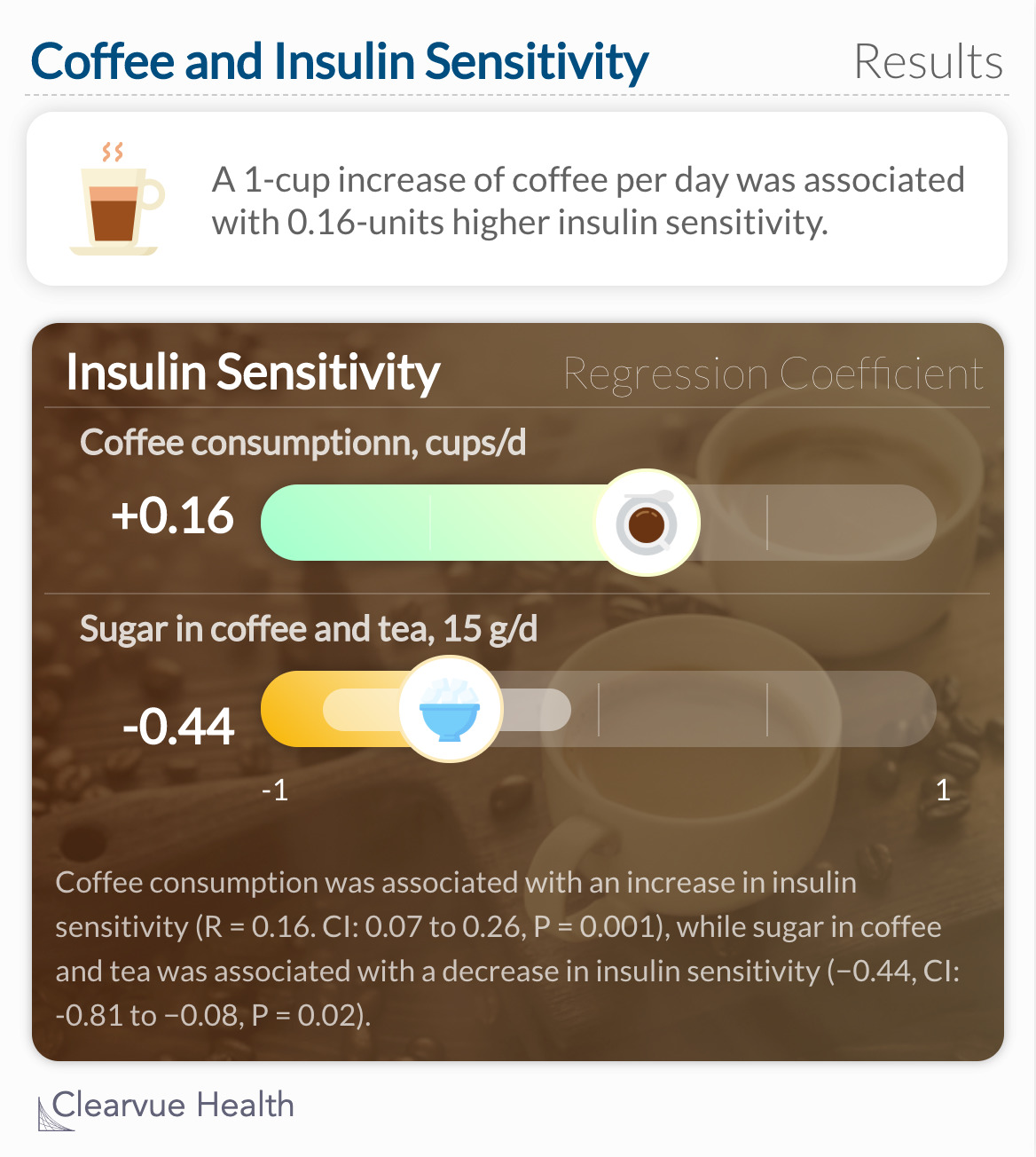
Researchers considered other factors that may influence insulin sensitivity such as sugar, cream, pastries, and smoking status. With these factors considered, they found that a 1-cup increase of coffee per day was associated with 0.16-units higher insulin sensitivity. They also found significant associations between insulin sensitivity, sugar intake, and body mass index.
How can caffeine decrease insulin sensitivity while coffee increases it? Well, the insulin benefit must be coming from a different source in the coffee.
“
It is possible that antioxidants in coffee could improve insulin sensitivity, given that insulin sensitivity has been reported to be associated with the activity of antioxidants.
JAMA
Overall, these studies are particularly useful for those with diabetes. Caffeine on its own and added sugar were associated with decreased insulin sensitivity. This information is useful for diet management, along with maintaining a relationship with doctors and nutritionists.