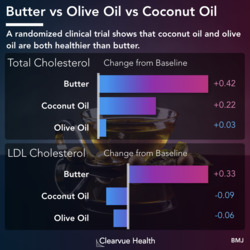
Study 1: Zyrtec (Cetirizine) vs Claritin (loratadine) for Seasonal Allergies

Figure 1: Study 1: Zyrtec (Cetirizine) vs Claritin (loratadine) in the Lab. Zyrtec (cetirizine) was shown to be significantly better than Claritin (loratadine) in a controlled environment. A small clinical trial showed that Zyrtec was better at reducing symptoms compared to Claritin and a control. Patients on Zyrtec reported a 48% reduction in their symptoms, compared to 33% in patients on Claritin and 5% in patients on a placebo control.
When it comes to treating seasonal allergies, there are sometimes too many options at the drug store. Some may know that benadryl makes you sleepy while others do not. However, deciding between Zyrtec or Claritin may be a little more difficult.
Both are what we call second generation antihistamines. These function like Benadryl, but they do not cause as much drowsiness.
In general, both are effective and both drugs use similar mechanisms. However, in two clinical trials, researchers have found that there are significant differences between the two when they tested them head to head.
In a head-to-head clinical trial conducted on volunteers in a lab, researchers found that volunteers who were assigned to take Zyrtec reported more symptom reduction than patients who were assitned to take Claritin. Both were more effective than the patients who were assigned to take a placebo.
+
+
Trial Design - This allergy study used a Clinical trial, the best type of clinical research. Unlike cohort studies, clinical trials can detect causality and are less susceptible to bias.
+
Effect Size - This study showed a significant and clinically relevant effect.
-
Sample Size - While small studies can find good results with a strong signal, they have less statistical power to detect a signal. They are also more susceptible to biases, making their conclusions less reliable.
Placebos are used as controls in clinical trials. When patients are given a pill, patients often report improvement in their symptoms whether the pill is effective or not. For example, patients given sugar pills in depression trials often report improvements in their depression. In order to tell whether a potential treatment is effective, or whether patients are experiencing the placebo effect, clinical trials will often compare the results with patients who are given a placebo control.
More Info: Second generation antihistamines
While first generation antihistamines like Benadryl (diphenhydramine) are every effective in treating allergies, they are well known to cause significant drowsiness. In order to reduce this often unwanted side effect, second generation antihistamines were developed. These drugs, including Benadryl and Zyrtec, have the same mechanisms as first generation antihistamines but without their effects on the central nervous system, which is responsible for drowsiness.
Source: Cetirizine, loratadine, or placebo in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis: Effects after controlled ragweed pollen challenge in an environmental exposure unit
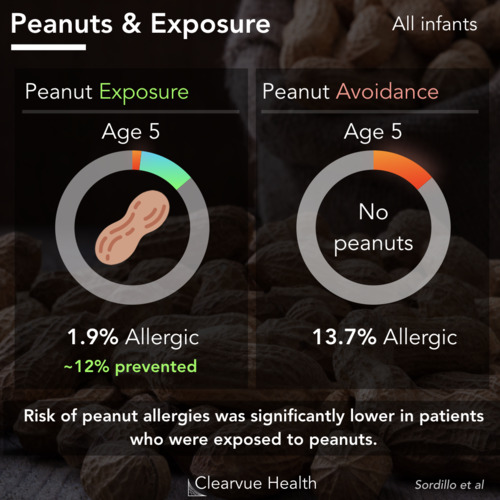
Study 2: Treating Outdoor Seasonal Allergies in a Park

Figure 2: Study 2: Treating Outdoor Seasonal Allergies in a Park. Zyrtec (cetirizine) was shown to be significantly better than Claritin (loratadine) treating outdoor allergies. A small clinical trial conducted in a park showed that Zyrtec was better at reducing symptoms compared to Claritin and a control in a real-world park setting.
So we know Zyrtec works better in a lab, what about in the real world? Do the results in the controlled environment of a lab translate to better outcomes outside?
A second study answered this by testing volunteers during a day in the park. Since most of us don't live inside labs, this provides a better estimate of how these medications work in the real world.
Researchers found that Zyrtec was again consistently more effective at reducing seasonal allergy symptoms than Claritin over the first 12 hours. The results held constant over the second day as well. (Not Shown)
Source: Comparative outdoor study of the efficacy, onset and duration of action, and safety of cetirizine, loratadine, and placebo for seasonal allergic rhinitis
+
+
Trial Design - This outdoor allergies study used a Clinical trial, the best type of clinical research. Unlike cohort studies, clinical trials can detect causality and are less susceptible to bias.
+
Sample Size - The trial studied 279 patients, which was enough to discern significant differences in efficacy and side effects.
-
Effect Size - The effect size found in this study was small, though significant.
Side Effects in Zyrtec vs Claritin

Figure 3: Side Effects in Zyrtec vs Claritin. In a small clinical trial, researchers found that patients on Claritin had significantly more headaches (23% vs 11%), while patients on Zyrtec had significantly more sleepiness. (13% vs 5.4%)
What about side effects? Both drugs are exceedingly safe. However, the clinical trial in the park showed that there were significant differences in side effects between the two drugs.
Volunteers who took Claritin were much more likely to get headaches than patients who took Zyrtec. (23% vs 11%). On the other hand, patients who took Zyrtec were significantly more likely to report feeling sleepy. (13% vs 5.4%)
Key Takeaways
At the end of the day, both Zyrtec and Claritin are effective drugs. You can't go wrong no matter which one you choose. Different patients will respond differently to each one. Side effects may be different as well. When it comes to seasonal allergies, go with the one you feel best on.