Heart Disease Risk & Dental Health

Figure 1: Heart Disease Risk & Dental Health. Boys with gum disease and cavities had significantly higher risks of developing thickened arteries and heart disease. Boys with gum disease had a 69% higher risk of developing thickened arteries as adults. Boys with cavities had a 46% higher risk of developing thickened arteries as adults.
A new study shows a surprising link between dental health and heart disease. Individuals with gum disease and cavities when they are kids have a significantly higher risk of heart disease as adults.
Once researchers split the volunteers by gender, they found that boys appear to suffer more from this effect than girls. In fact, girls do not show any significant relationship.
Boys on the other hand have a 69% higher risk of developing thickened arteries if they had gum disease as kids. They have a 46% risk of developing thickened arteries as adults if they had cavities as kids.
Source: Association of Childhood Oral Infections With Cardiovascular Risk
Factors and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Adulthood
Correlation does not imply causation
Of note, this study only looked at correlations, which do not imply caustion. While causal relationships are correlated, correlated events are not necessarily causal. One common example is the link between churches and crime. The number of churches in a square mile is significantly correlated with crime. However, this is not evidence that churches cause crime. Rather, it reflects that fact areas with many churches have a higher populations.
This study used multivariable adjustment to reduce possible confounding. Observational studies all have the risk of confounding, where a correlation between two variables is caused by another factor. For example, individuals who drive luxury cars likely have a higher rate of having kids who attend college. The car doesn't lead to college, rather both correlate with a 3rd factor: income. Multivariable adjustment removes the effect of many possible confounding variables to produce a more accurate result.
Intima Media Thickness

Figure 2: Intima Media Thickness Diagram. Panel on the left shows a normal artery with thin walls, which allows for small clots to pass harmlessly though. The panel on the right shows an artery with thick walls, where a clot can easily block the artery. The pink represents the middle of the artery. The brown spot represents a blood clot. The tan walls represent the artery walls.
While heart attacks and strokes affect different organs, they have similar underlying causes. Atherosclerosis, the medical condition where your arteries become thickened and hardened, increases the width of the walls of your arteries.
Thickened artery walls decreases the width of the channel of arteries, the lumen, and increases the risk that a blood clot can cause a clog.
Intima Media Thickness refers to the thickness of the carotid artery walls, the arteries running to your head. This test estimates the extent of atherosclerosis in a patient, and their risk of developing heart disease and stroke.
Link Between Blood Pressure and Dental Health

Figure 3: Link Between Blood Pressure and Dental Health. Having multiple signs of oral cavity infections as a child correlates with a higher blood pressure in adulthood. The red line shows the average blood pressure of volunteers who had 2 symptoms of oral cavity infections as kids. The yellow line shows the average blood pressure of volunteers who had 1 symptom of oral cavity infections as kids. The green line shows the average blood pressure of volunteers who had no symptoms of oral cavity infections as kids.
A similar effect was seen for blood pressure. Individuals with more symptoms of oral cavity infections as kids, including gum bleeding and vacities, had a higher risk of higher blood pressure as adults. On average, volunteers without any dental symptoms as a kid had a systolic blood presusre of 114 as adults. Meanwhile, kids who had 2 symptoms had an average systolic blood pressure of 120 as adults.
Source: Association of Childhood Oral Infections With Cardiovascular Risk
Factors and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Adulthood
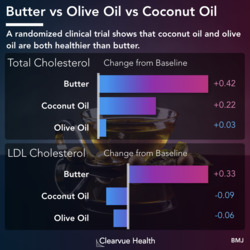
Related: Emotional Stress and Heart Disease
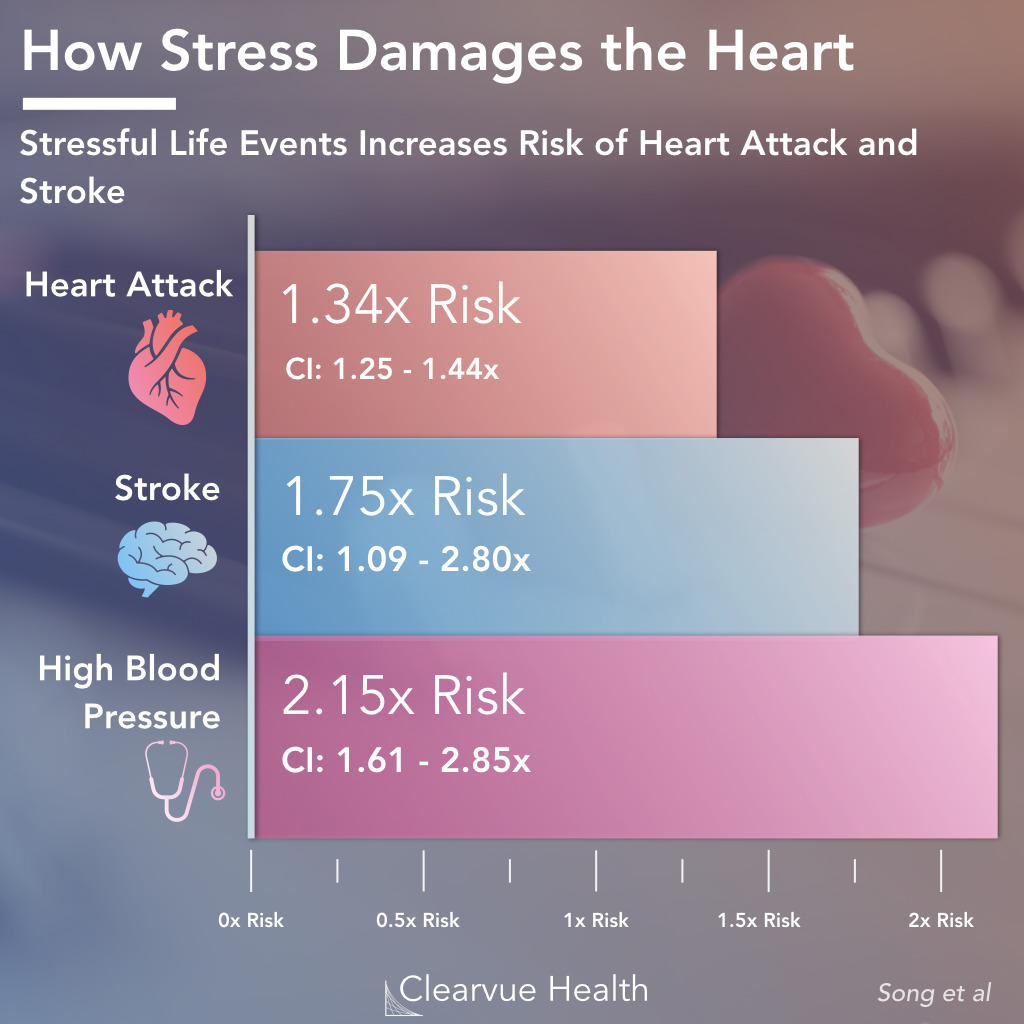
Another surprising risk factor for heart disease was found in emotional stress. Stressful life events harm the mind and the body.
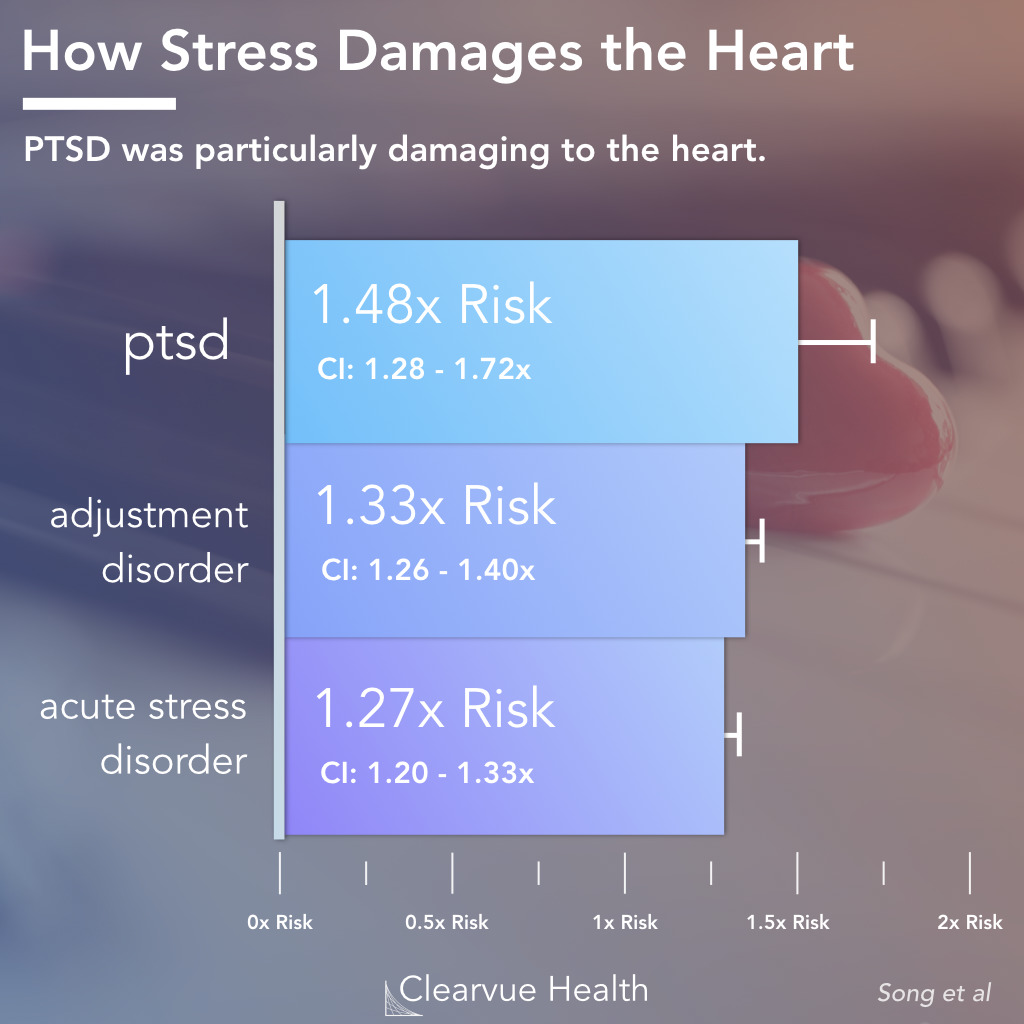
New research shows significantly higher risks of heart attack and stroke after psyciatric diagnoses from stressful life events. PTSD was the most damaging stress-related disorder.
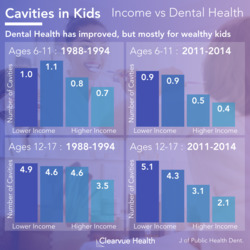
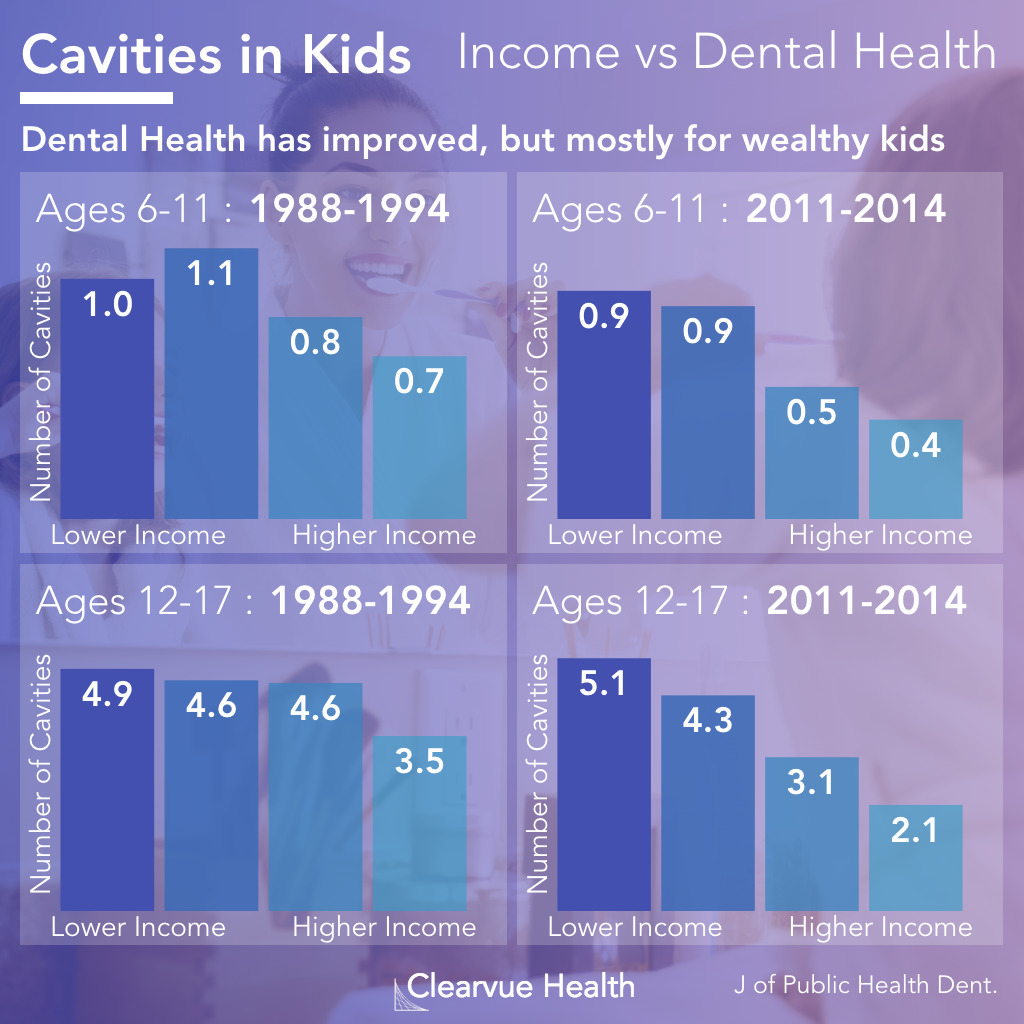
Related: Cavities and Income
Unfortunately, most of the improvements in dental health have not been equally distributed. Over the last 20 years, improvements in dental health have been concentrated in wealthy families. Research has shown that water fluoridation can reduce much of this disparity.
Key Takeaways
This study shows a significant link between dental health and heart health. While we don't know whether cavities directly cause heart disease, we do know that kids who had taken better care of their teeth had better health as adults.
This study, along with several others, have shown that dental health and general health are intimately connected. Taking good care of your teeth isn't just important for keeping your dentist happy, it may also help ensure a long healthy life.