Background:
Key Facts
Examples

How they work
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by counteracting free radicals.

Effect on Disease
Research on Antioxidants and disease prevention has shown mixed results.
Common Sources

Chocolate

Berries & Fruit

Coffee

beta-carotene
Your body makes vitamin A with beta-carotene, commonly found in carrots.

Vitamin C
Found in all sorts of fruits, Vitamin C is a very commonly consumed antioxidant.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in nuts and seeds.

TL;DR

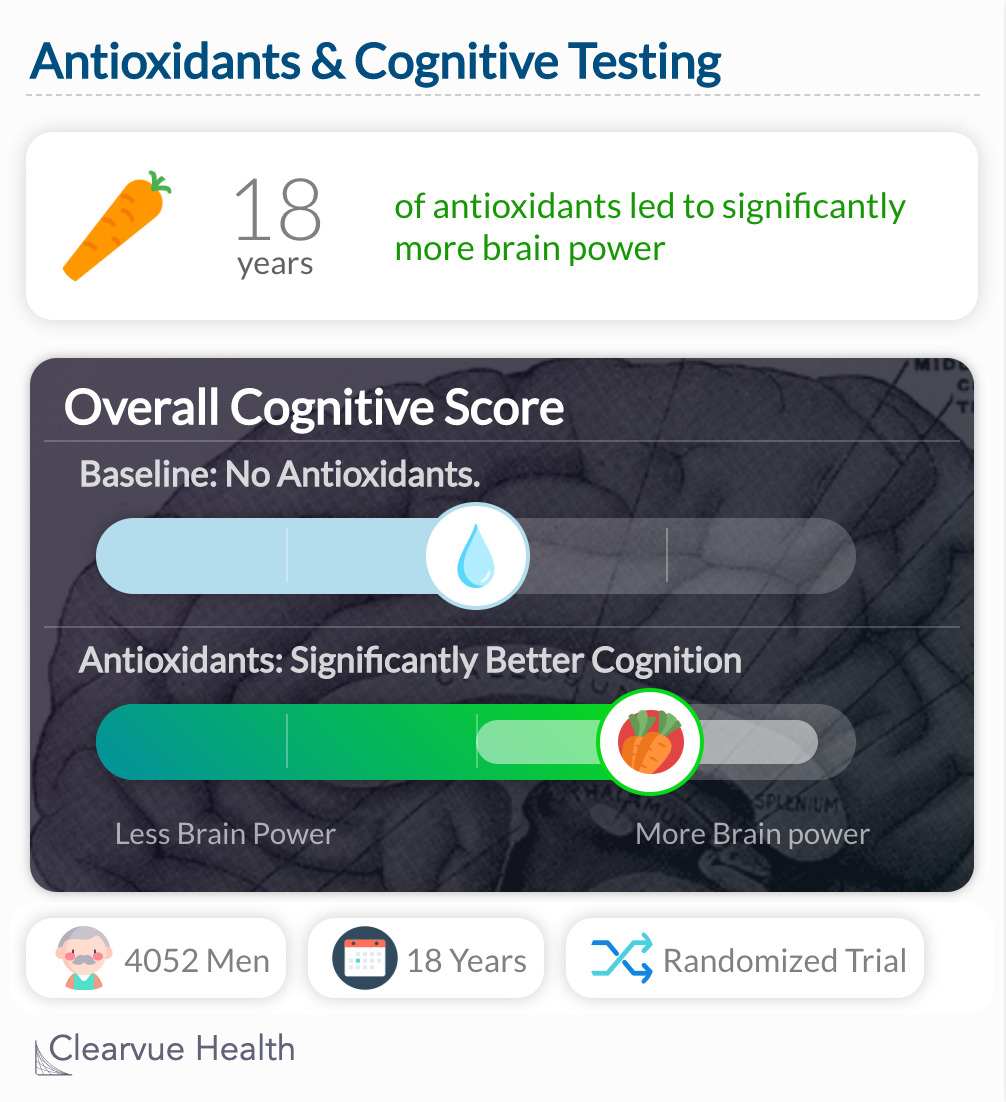
1. Long Term Antioxidant Use May Show Benefits
One study found that taking beta-carotene, an antioxidant from carrots, over 15 years led to more "brain power" as measured by cognitive testing.

2. More Vitamin E = More Intelligence?
A recent study found people who had more vitamin E, commonly found in fruits and nuts, also performed better on intelligence testing.

3. More Study is Needed
We need more research before we know for sure whether antioxidants can boost the brain. The research on antioxidants is still thin, and inconsistent. Some studies have shown negative results, particularly with short term dosing.
Study 1
Data Source
"As expected, results appeared strongest with long-term supplementation. While treatment with beta carotene for 3 years or less had no impact on cognitive performance, at least 15 years' treatment provided significant benefits consistently across several cognitive measures. In this generally healthy population, the extent of protection conferred by long-term treatment appeared modest; nonetheless, studies have established that very modest differences in cognition, especially verbal memory, predict substantial differences in eventual risk of dementia"
Study 2:
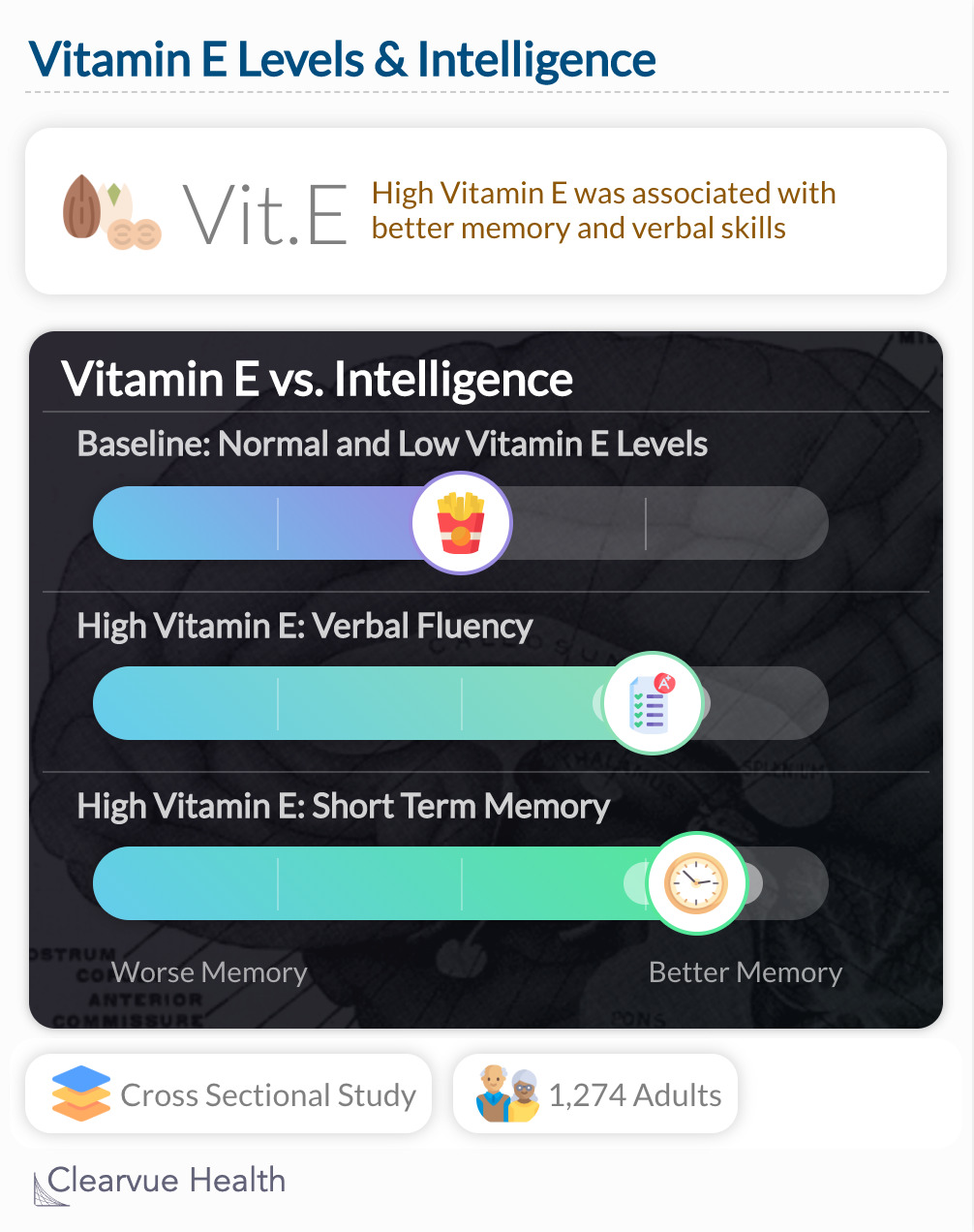
High Vitamin E was associated with better memory and verbal skills. Those with one standard deviation more of Vitamin E scored higher on immediate recall (β=+0.64±0.19, p=0.001) and had better verbal fluency. (β=+0.53±0.16, p=0.001)

Our Take
This study shows an interesting relationship between the amount of Vitamin E in your blood and your brain's performance on Cognitive Testing. However, this study doesn't necessarily show that Vitamin E is better for your brain, as it only shows a correlation.
Data Source
"We found that vitamin E was positively associated with performance in domains of verbal memory and fluency in the total population and psychomotor speed among women. The association between vitamin E and verbal memory was only partially mediated by depressive symptoms."
More Information



Background:

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#neuro
Scroll for more ->



#antioxidants
Scroll for more ->
#new
Scroll for more ->