TL;DR

1. Antioxidants May Help
Unlike other applications, antioxidants have shown real promise for the prevention of age related eye disease. (AMD)

2. Type Matters
Not all antioxidants are created equal however. One study showed that Zinc may have a particularly strong protective effect.

3. Eat your vegetables
When it comes to nutrition, another study suggests that vegetables may be better than carrots when it comes to antioxidants. Patients given lutein had better outcomes than those given beta-carotene, which comes from carrots.



Study 1
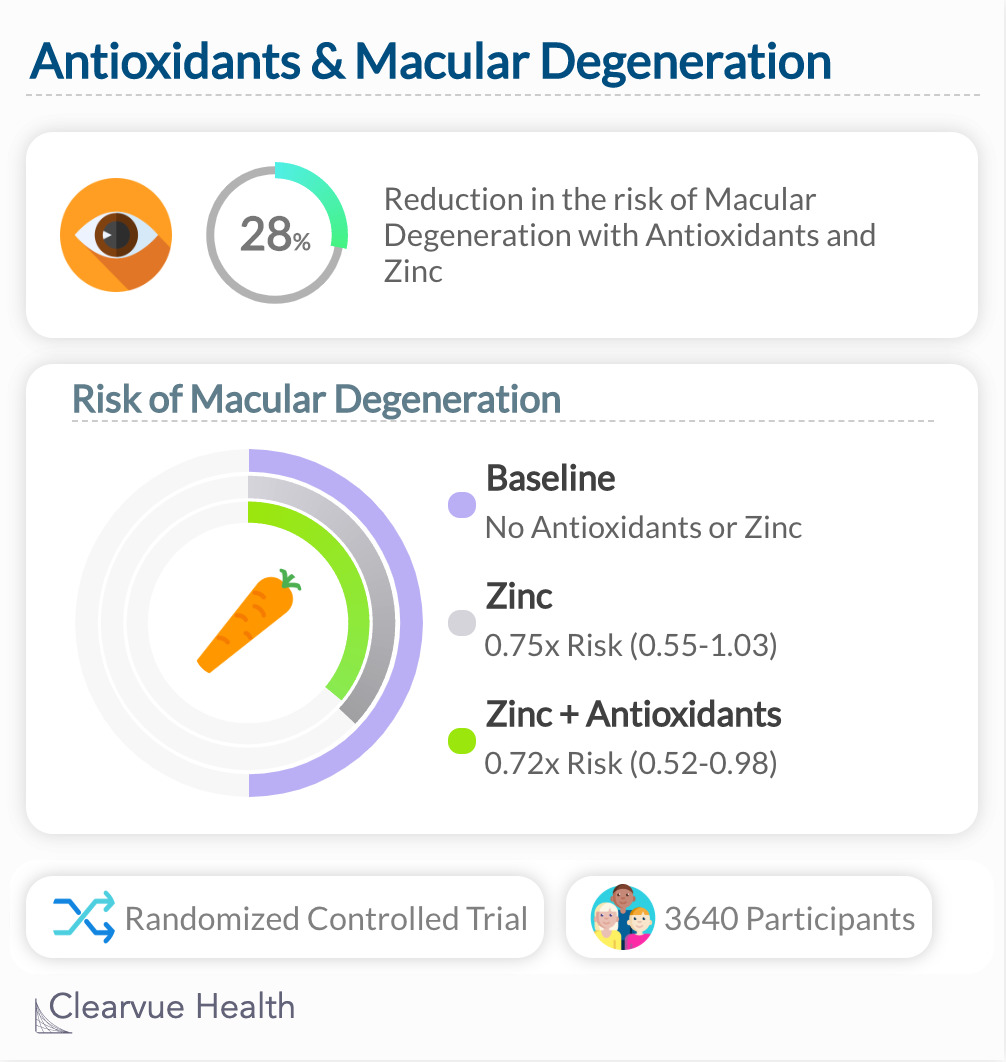
This study found that zinc and other antioxidants could potentially reduce your risk of age-related macular degeneration. Those who were assigned to take zinc and antioxidants showed the highest reduction in their risk of age-related macular degeneration (OR 0.72; 99% confidence interval [CI], 0.52–0.98)).

Our Take
This study shows that the type of antioxidant you take matters. In this case, zinc showed the greatest benefit. All other antioxidants may have helped, but not nearly as much as Zinc.
Data Source
"Persons older than 55 years should have dilated eye examinations to determine their risk of developing advanced AMD. Those with extensive intermediate size drusen, at least 1 large druse, noncentral geographic atrophy in 1 or both eyes, or advanced AMD or vision loss due to AMD in 1 eye, and without contraindications such as smoking, should consider taking a supplement of antioxidants plus zinc such as that used in this study."
Study 2:
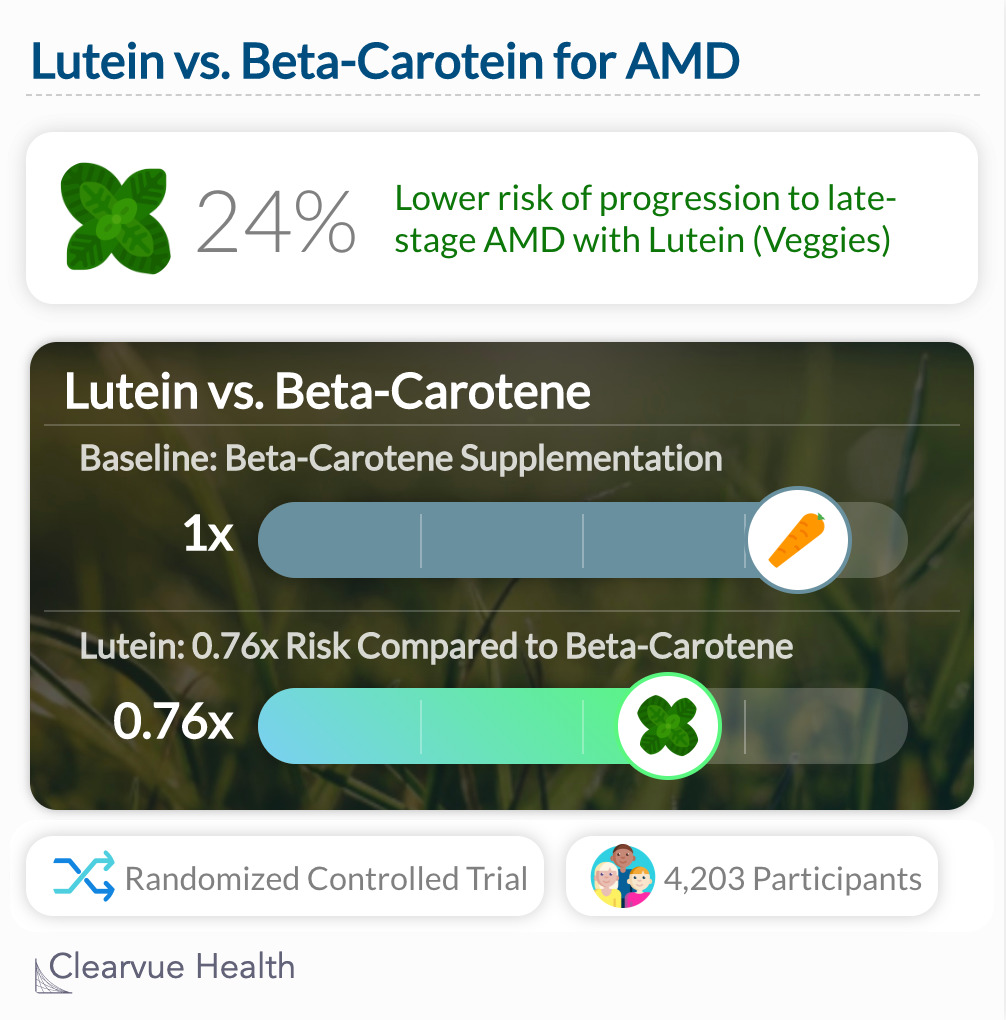
Researchers found that lutein showed significantly more protection against age-related macular degeneration than beta-carotene. (HR 0.76, 95% CI, 0.61-0.96; P = .02) This suggests that leafy green veggies may in fact be the way to go for eye and vision health.

Our Take
Generally, secondary analyses such as this study are not as reliable as primary analysis. However, these data suggest an interesting connection between the type of antioxidant you take in and eye health.
Data Source
"The pure “head-to-head” exploratory analyses of lutein/zeaxanthin alone vs. beta-carotene alone showed beneficial effects of lutein/zeaxanthin for reducing progression to late AMD, in particular neovascular AMD. These data were further strengthened by the additional analyses of comparison of those assigned to lutein/zeaxanthin plus beta-carotene vs. beta-carotene alone as lutein/zeaxanthin was again beneficial in reducing the risk of late AMD and neovascular AMD."
Background
Key Facts
Examples

How they work
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by counteracting free radicals.

Effect on Disease
Research on Antioxidants and disease prevention has shown mixed results.
Common Sources

Chocolate

Berries & Fruit

Coffee

beta-carotene
Your body makes vitamin A with beta-carotene, commonly found in carrots.

Vitamin C
Found in all sorts of fruits, Vitamin C is a very commonly consumed antioxidant.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in nuts and seeds.

More Information

#antioxidants
Scroll for more ->
#vision
Scroll for more ->
#new
Scroll for more ->