Background
Key Facts
Key Functions
Key Facts
- TypeEssential, Water soluble
- Other Namesascorbic acid
- Daily AllowanceWomen: 75mg, Men:90mg
Appearance

Key Sources

Fruits

Vegetables

Peas

Collagen
Your body needs Vitamin C to create collagen, a critical component of joints and connective tissue.
Wound Healing
Vitamin C helps your body heal wounds
Immunity
Vitamin C helps your body fight off infection

Vitamin C Benefit #1:
Vitamin C & Cold Prevention
Did you know that vitamin C may help prevent the common cold? Individuals at high risk, including skiiers and marathon runners, were far less likely to catch a cold according to one meta-analysis.
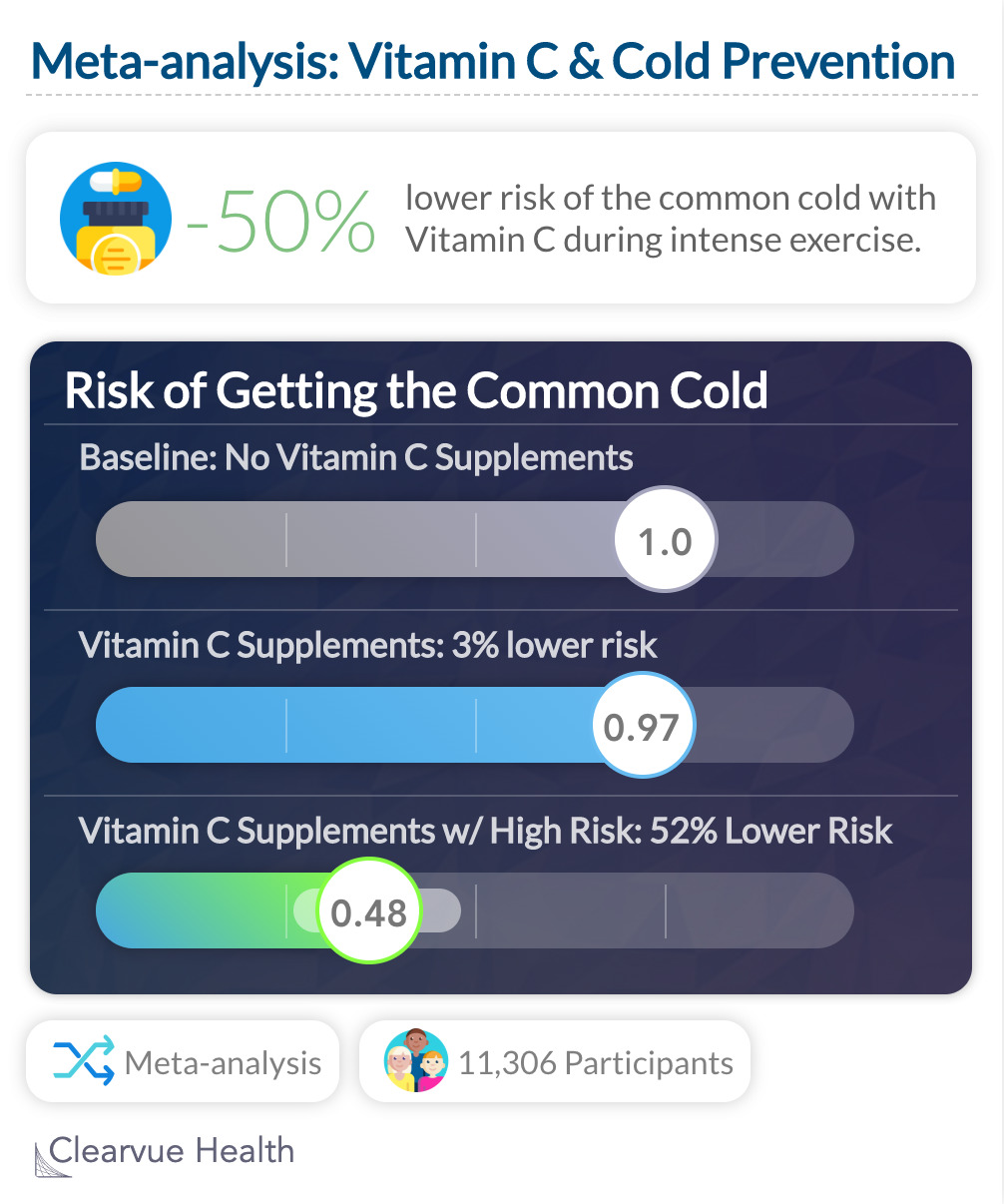
A meta-analysis of 29 trials found that taking vitamin C can slightly lower your risk of getting the cold. RR 0.97 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.94 to 1.00). Among skiers, marathon runners, and soldiers in subarctic exercises, this was much more effective, with a approx. 50% risk reduction: 0.48 (95% CI 0.35 to 0.64)
Data Source
""The failure of vitamin C supplementation to reduce the incidence of colds in the general population indicates that routine vitamin C supplementation is not justified, yet vitamin C may be useful for people exposed to brief periods of severe physical exercise.""

Vitamin C & Cold Length
Not only does vitamin C help prevent colds, it can also help you recover faster, provided that you take it before catching it.
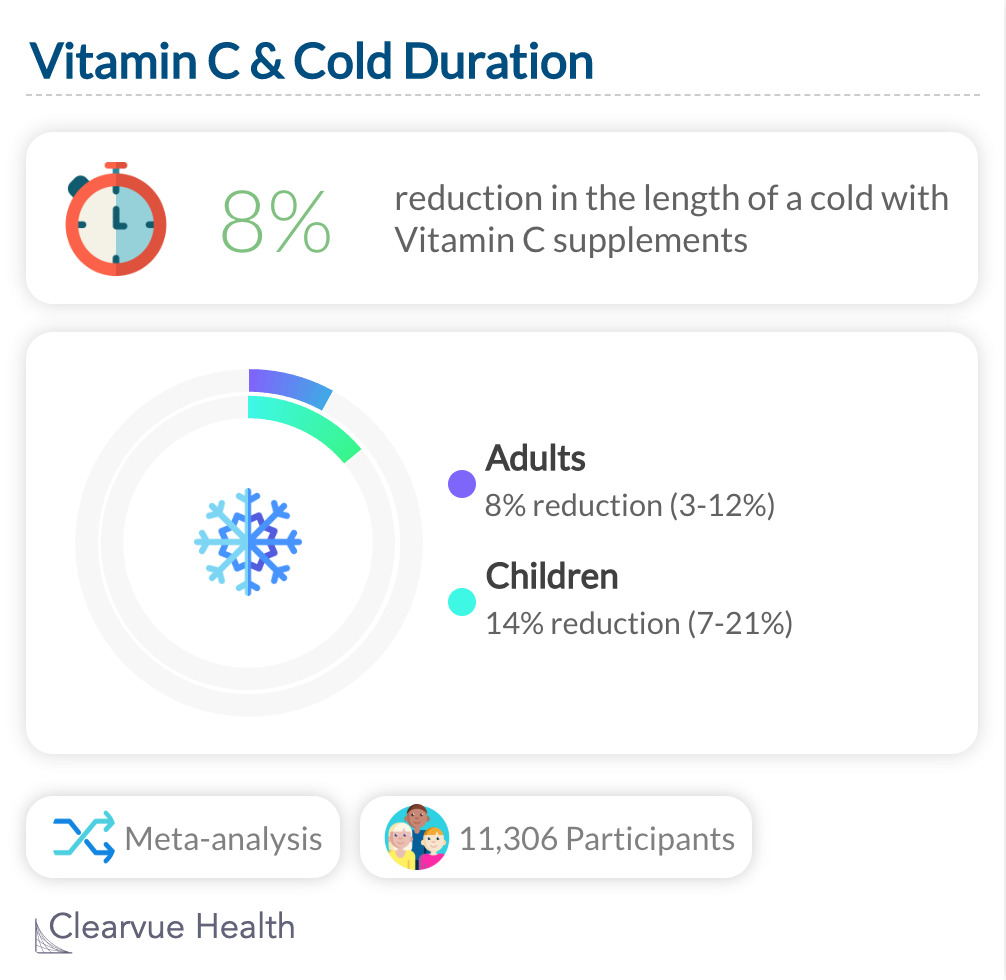
A meta-analysis found that taking Vitamin C can potentially reduce the length of your cold by 8% for adults and 14% for children.
Data Source
"Duration of cold episodes that occurred during prophylaxis was significantly reduced in both children and adults. For children this represented an average reduction of 14% in symptom days, while in adults the reduction was 8%."

Vitamin C Benefit #2


Vitamin C & Cognitive Decline
One study showed a dose-dependent relationship between Vitamin C consumption and cognitive decline. The more vitamin C a participant took, the lower their risk of cognitive decline.
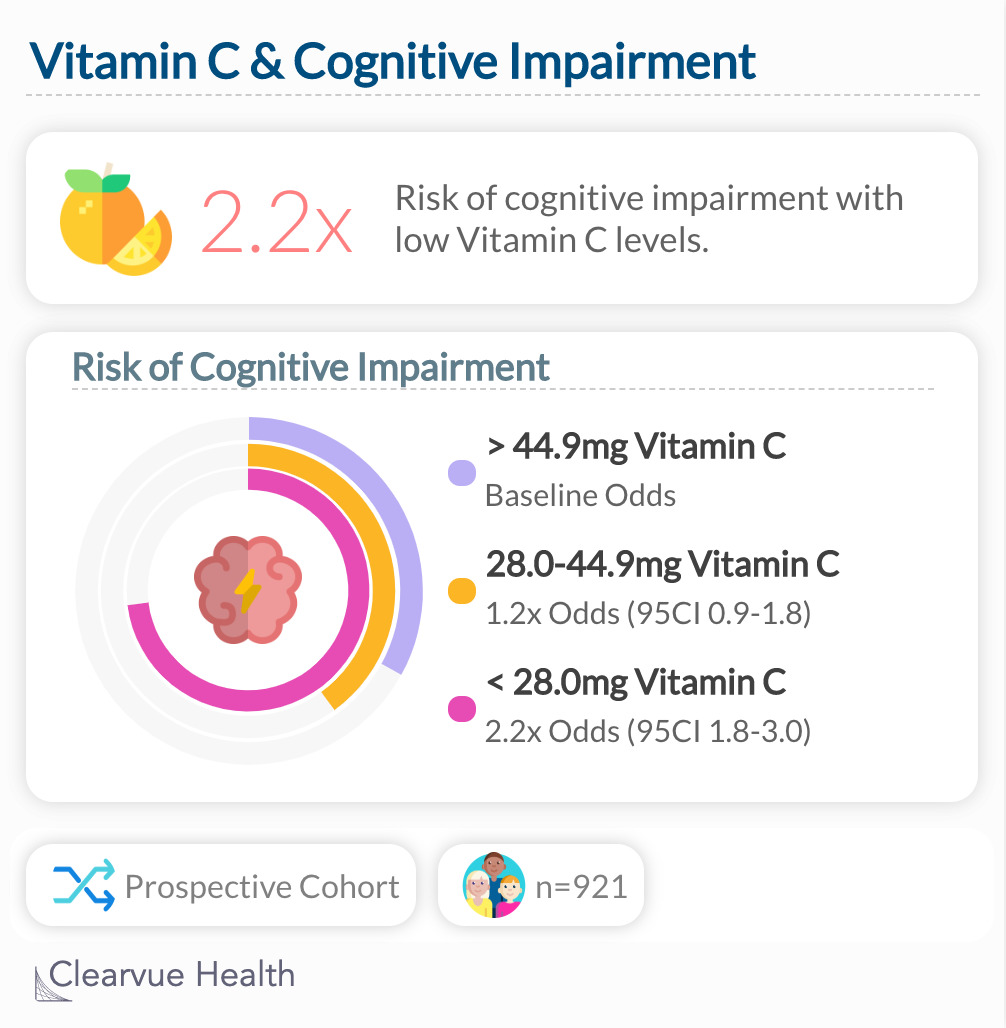
A study out of the UK found that those who consumed the least Vitamin C had the highest risk of cognitive impairment. They had over twice the odds compared to those who consumed the most Vitamin C (2.2x odds, 95CI 1.8-3.0)
Data Source
"Vitamin C status may be a determinant of cognitive function in elderly people through its effect on atherogenesis. A high vitamin C intake may protect against both cognitive impairment and cerebrovascular disease."
Vitamin C & Alzheimer's Disease
One study showed that Vitamin C may also have a benefit in preventing Alzheimer's disease. Individuals who choose to take Vitamin C and Vitamin E together have a significantly lower risk.
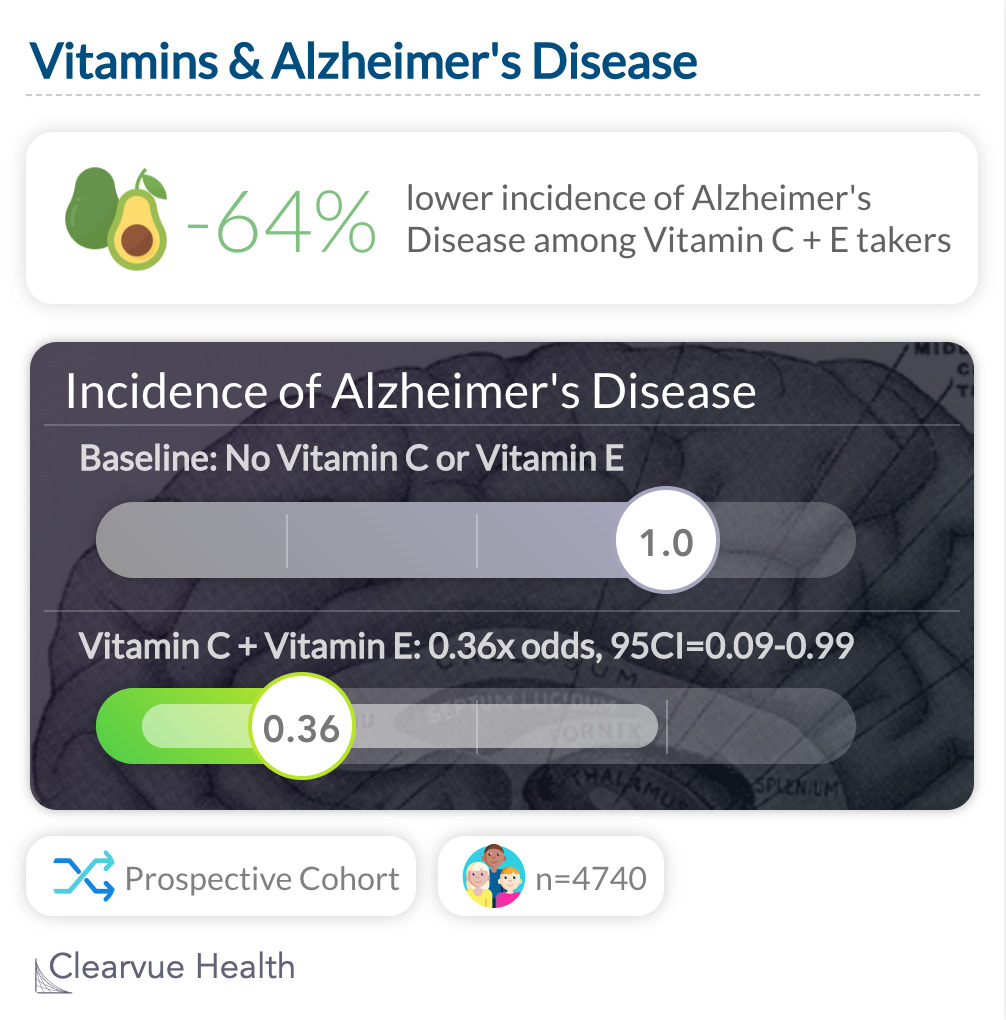
A study out of Utah found that those who took Vitamin C and Vitamin E supplements combined had a significantly lower risk of developing Alzheimer's Disease over 3 years.
Data Source
"Use of vitamin E and vitamin C supplements in combination is associated with reduced prevalence and incidence of AD. Antioxidant supplements merit further study as agents for the primary prevention of AD."
Benefit #3

Fruits Benefit the heart
A meta-analysis of 95 studies showed that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can benefit the heart.
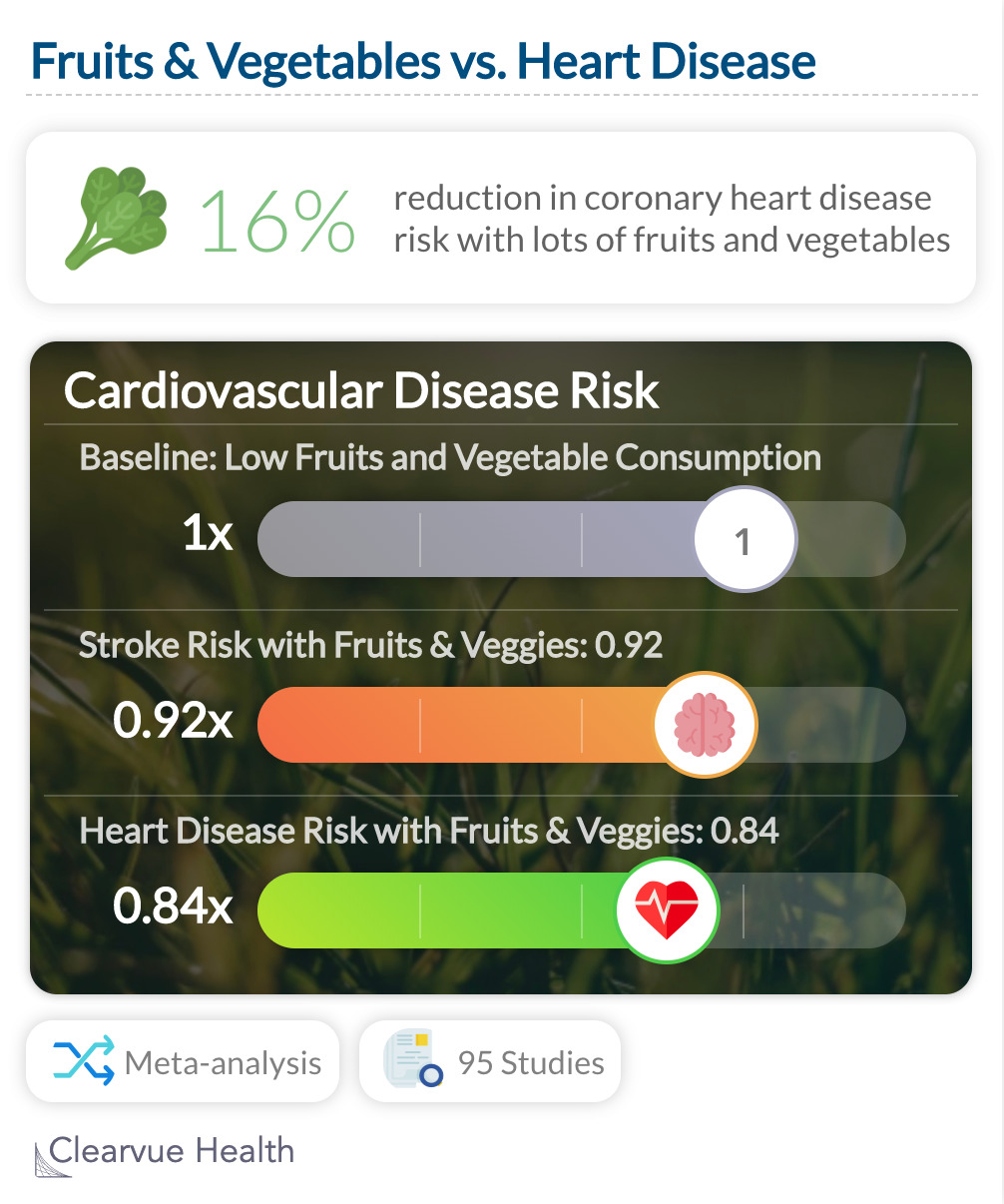
A meta-analysis of 95 studies showed that generally, high fruit and vegetable consumption is correlated with a lower risk of heart disease 0.84 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92) and a lower risk of stroke: 0.92 (95% CI: 0.90–0.95)
Data Source
"Fruit and vegetable intakes were associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer and all-cause mortality. These results support public health recommendations to increase fruit and vegetable intake for the prevention of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and premature mortality."
Vitamin C & Blood Pressure Benefits
Part of this effect may be driven by Vitamin C's effect on blood pressure. Overall, studies have found that Vitamin C reduces systolic blood pressure by just under 4 mmHg. It's a small, but significant, reduction.
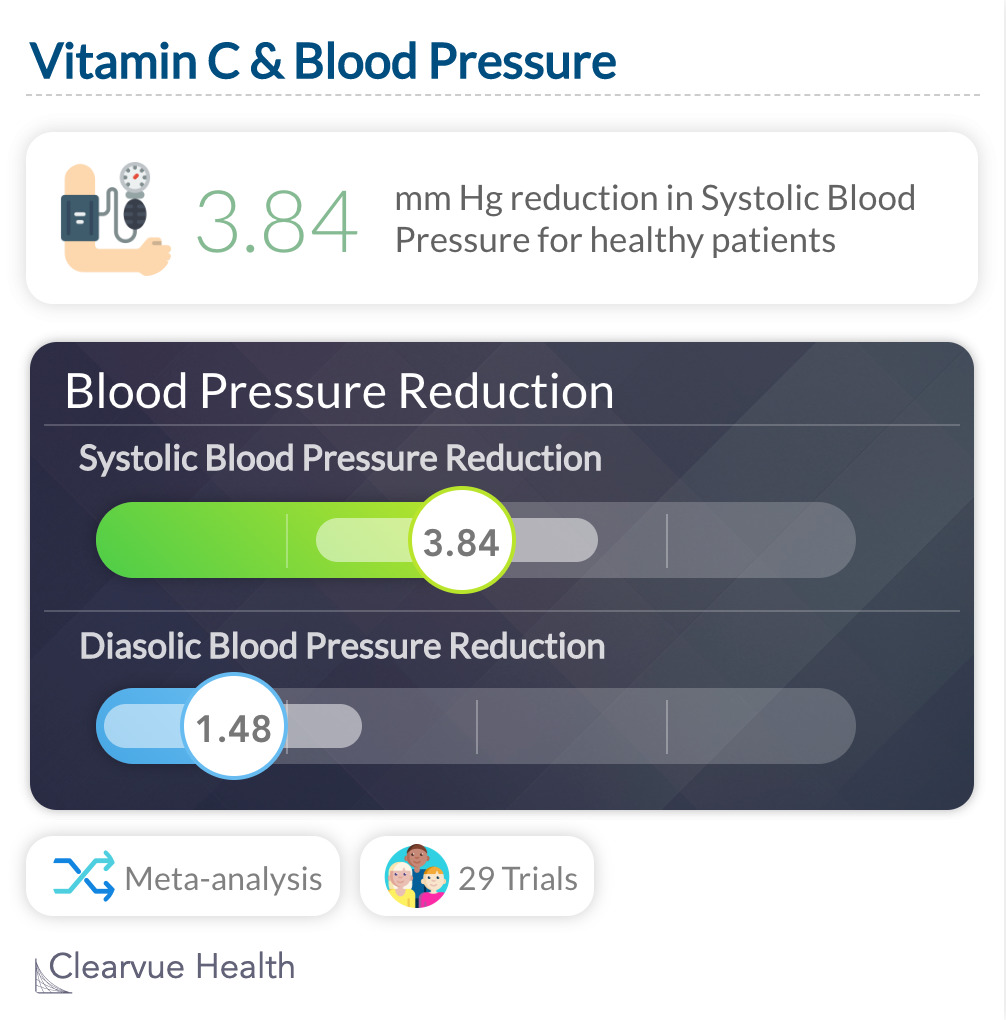
A meta-analysis found that short term Vitamin C therapy can significantly reduce blood pressure for healthy people. Participants were given an average of 500mg/day of Vitamin C for an average of 8 weeks.
Data Source
"In short-term trials, vitamin C supplementation reduced SBP and DBP. Long-term trials on the effects of vitamin C supplementation on BP and clinical events are needed."
Bonus Benefit
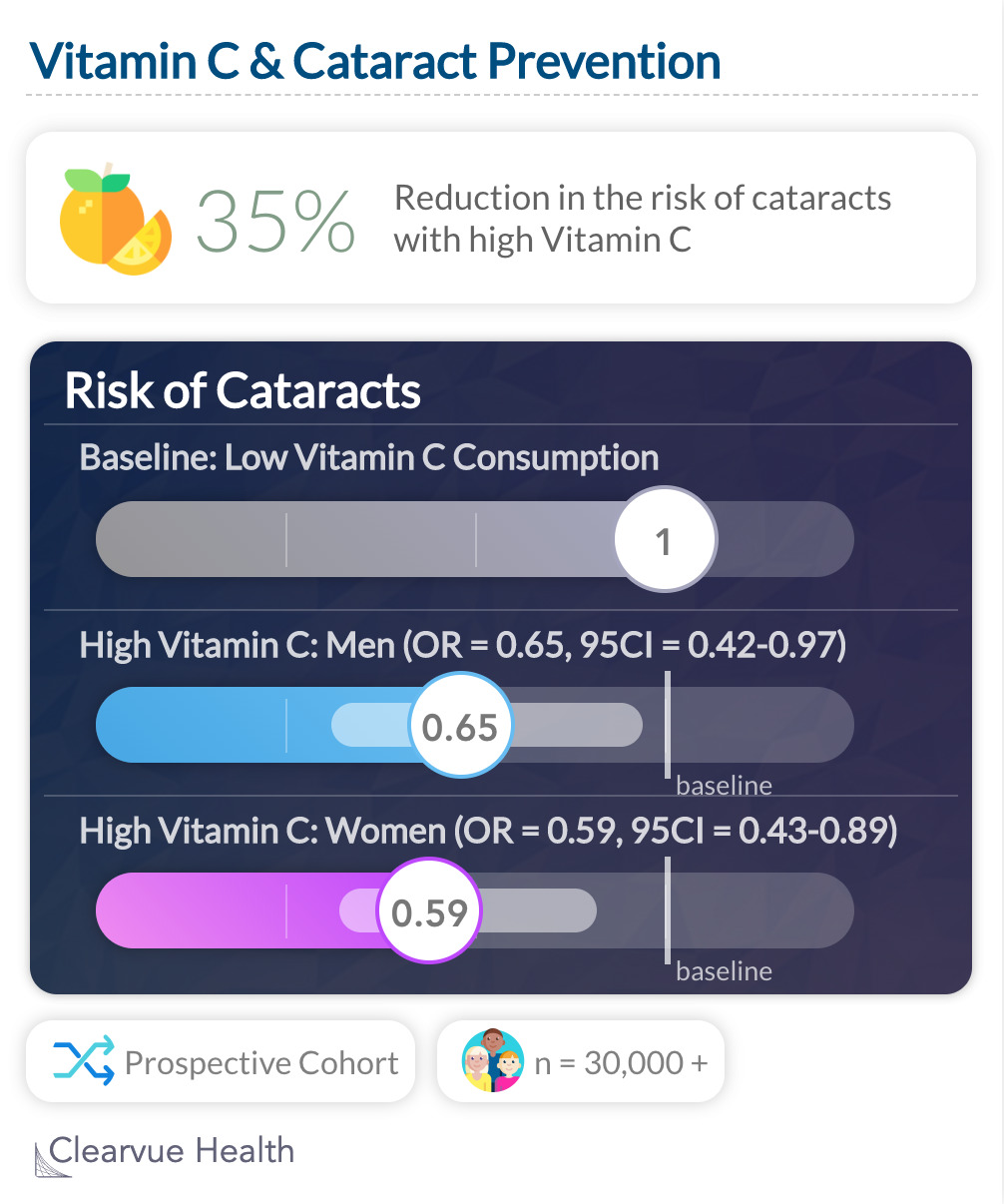
Data Source
""Conclusions: Dietary vitamin C intake might lower the risk of age-related cataracts among middle-aged Japanese." "
More Information:
Top Vitamin C Topics

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#vitaminc
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->