Study 1

Vitamin C reduces risk of cognitive decline
Researchers found that among nearly 1000 elderly in the UK, those who ate the least Vitamin C had the highest risk of cognitive decline.
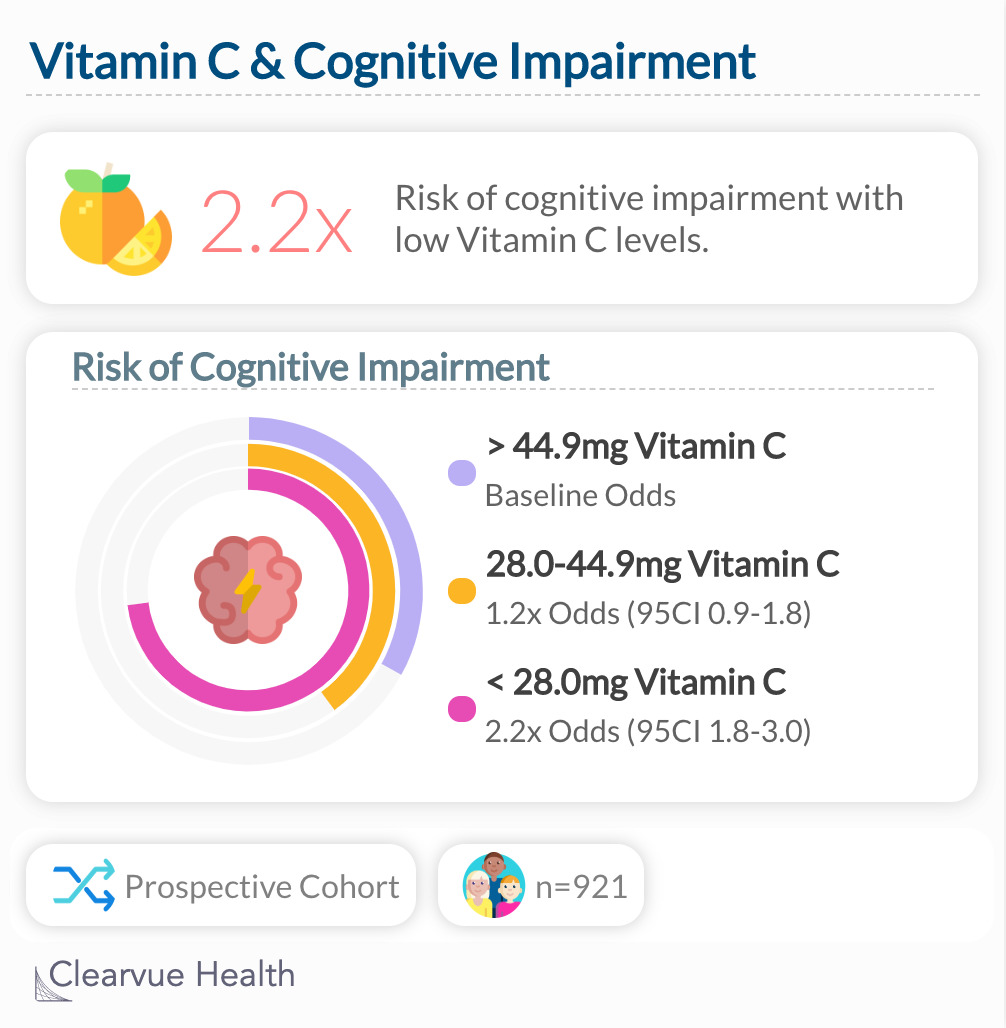
A study out of the UK found that those who consumed the least Vitamin C had the highest risk of cognitive impairment. They had over twice the odds compared to those who consumed the most Vitamin C (2.2x odds, 95CI 1.8-3.0)
Data Source
"Vitamin C status may be a determinant of cognitive function in elderly people through its effect on atherogenesis. A high vitamin C intake may protect against both cognitive impairment and cerebrovascular disease."
Study 2

Vitamin C Supplements May Reduce Risk of cognitive impairment
Another study out of Australia showed that those who took Vitamin C supplements at a retirement community had a significantly lower risk of developing severe cognitive impairment.
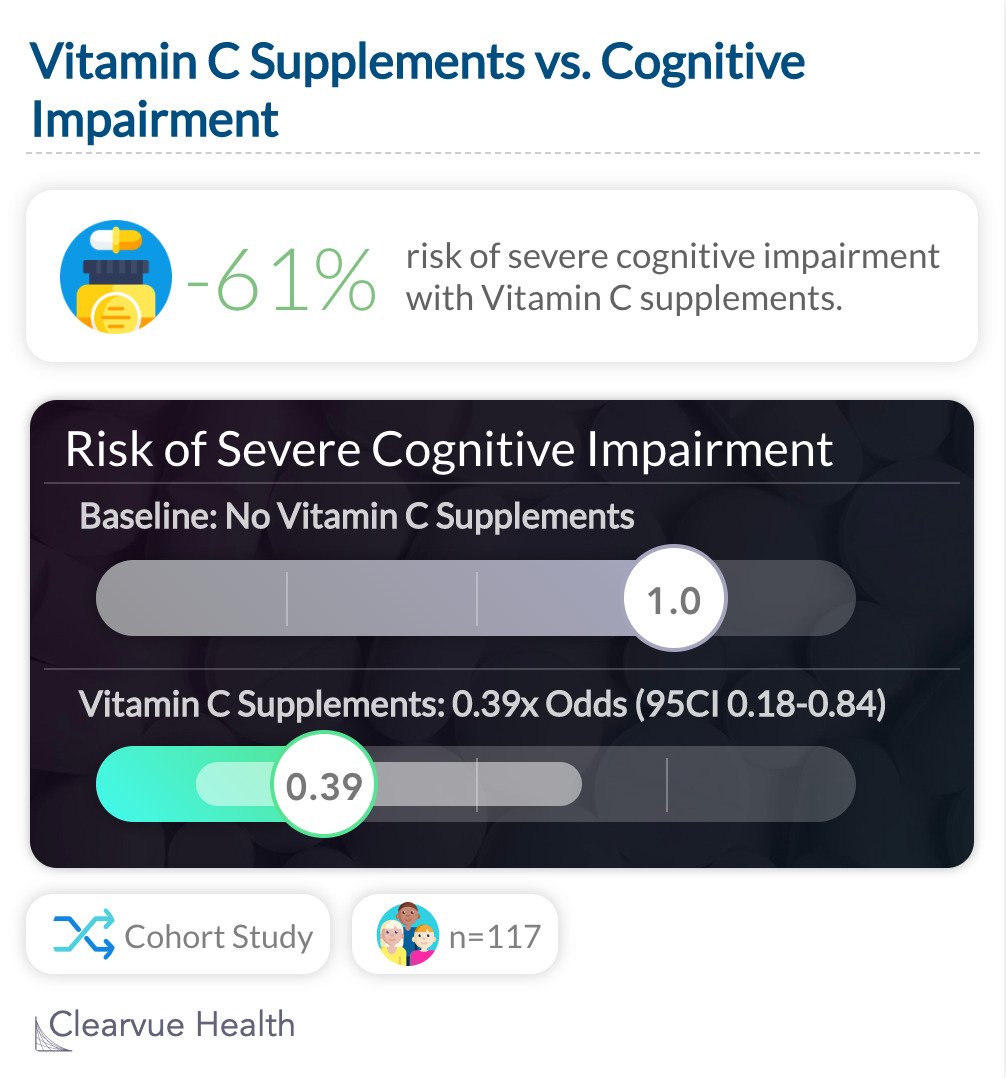
A study from Australia found that those who took Vitamin C supplements within a retirement community had a significantly lower risk of cognitive impairment compared to those who did not, after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, education, total energy intake, and use of psychotropic medications.
Data Source
"After adjustment for age, sex, smoking, education, total energy intake, and use of psychotropic medications, consumption of vitamin C supplements was associated with a lower prevalence of more severe cognitive impairment (based on scores on the Mini-Mental State Examinatio"
Study 3

Vitamin C may reduce risk of Alzheimer's Disease when combined with Vitamin e
A study out of Utah found that elderly individuals who took Vitamin C and Vitamin E in combination had a reduced risk of Alzheimer's Disease.
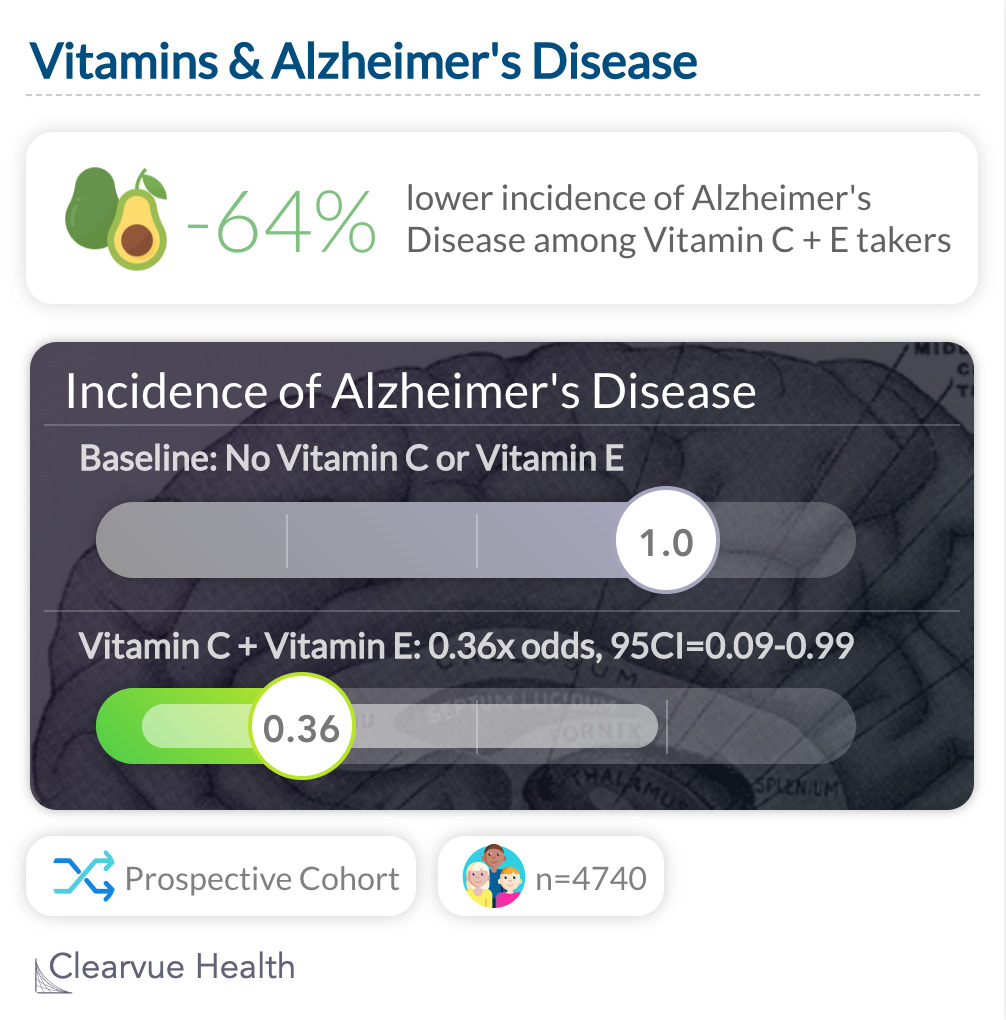
A study out of Utah found that those who took Vitamin C and Vitamin E supplements combined had a significantly lower risk of developing Alzheimer's Disease over 3 years.
Data Source
"Use of vitamin E and vitamin C supplements in combination is associated with reduced prevalence and incidence of AD. Antioxidant supplements merit further study as agents for the primary prevention of AD."
Conclusion

More Information

#neuro
Scroll for more ->



#vitaminc
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->