Key Points

1. Correlation with Heart Disease
Some studies have shown that those who take Vitamin C supplements tend to have a lower risk of heart disease.
2. trials have been inconsistent
However, clinical trials have so far been inconsistent in their results. Some of the best studies have shown negative results.

3. Keep eating fruits and veggies
While the jury is still out on Vitamin C and heart disease, it's never a bad idea to eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables. There are plenty of benefits from these healthy foods.
Background
Key Facts
Key Functions
Key Facts
- TypeEssential, Water soluble
- Other Namesascorbic acid
- Daily AllowanceWomen: 75mg, Men:90mg
Appearance

Key Sources

Fruits

Vegetables

Peas

Collagen
Your body needs Vitamin C to create collagen, a critical component of joints and connective tissue.
Wound Healing
Vitamin C helps your body heal wounds
Immunity
Vitamin C helps your body fight off infection

Study 1
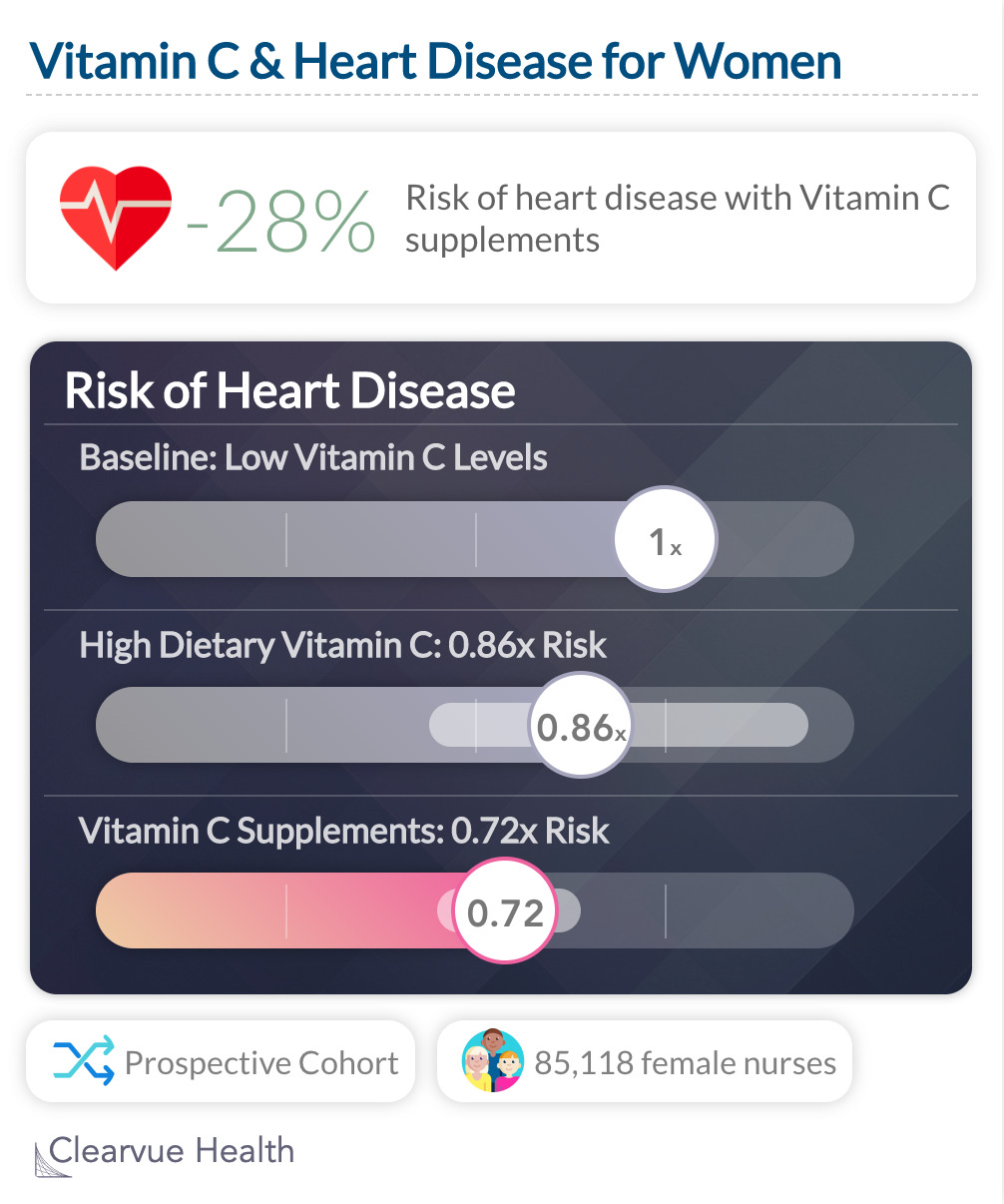
A study looking at 85,118 female nurses found that those who took Vitamin C supplements had a significantly lower risk of heart disease after adjusting for adjusting for age, smoking, and a variety of other coronary risk factors.
Data Source
"In conclusion, our findings suggest that vitamin C supplement users may be at lower risk of CHD. We found no evidence for a gradient in risk across the relatively narrow range of intakes of vitamin C from diet in our study population. "
Study 2
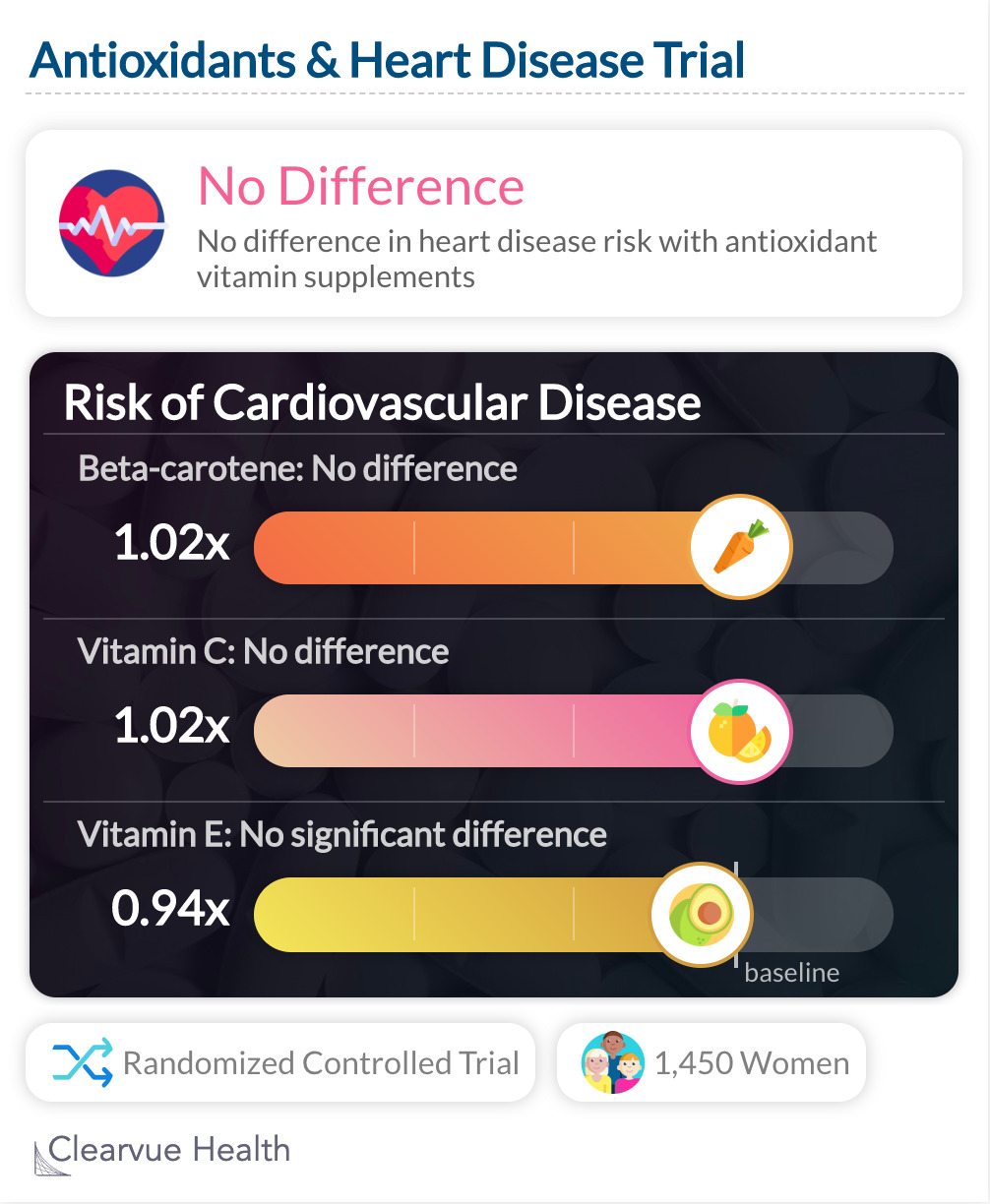
A clinical trial looking at antioxidants and heart disease found that antioxidant vitamin supplements did not reduce the risk of heart disease over 9.4 years. For vitamin C, the relative risk was 1.02; 95% CI, 0.92-1.13. For vitamin E, the relative risk was 0.94; 95% CI, 0.85-1.04. For beta-carotene, the relative risk was 1.02; 95% CI, 0.92-1.13.
Data Source
"There were no overall effects of ascorbic acid, vitamin E, or beta carotene on cardiovascular events among women at high risk for CVD."
Study 3
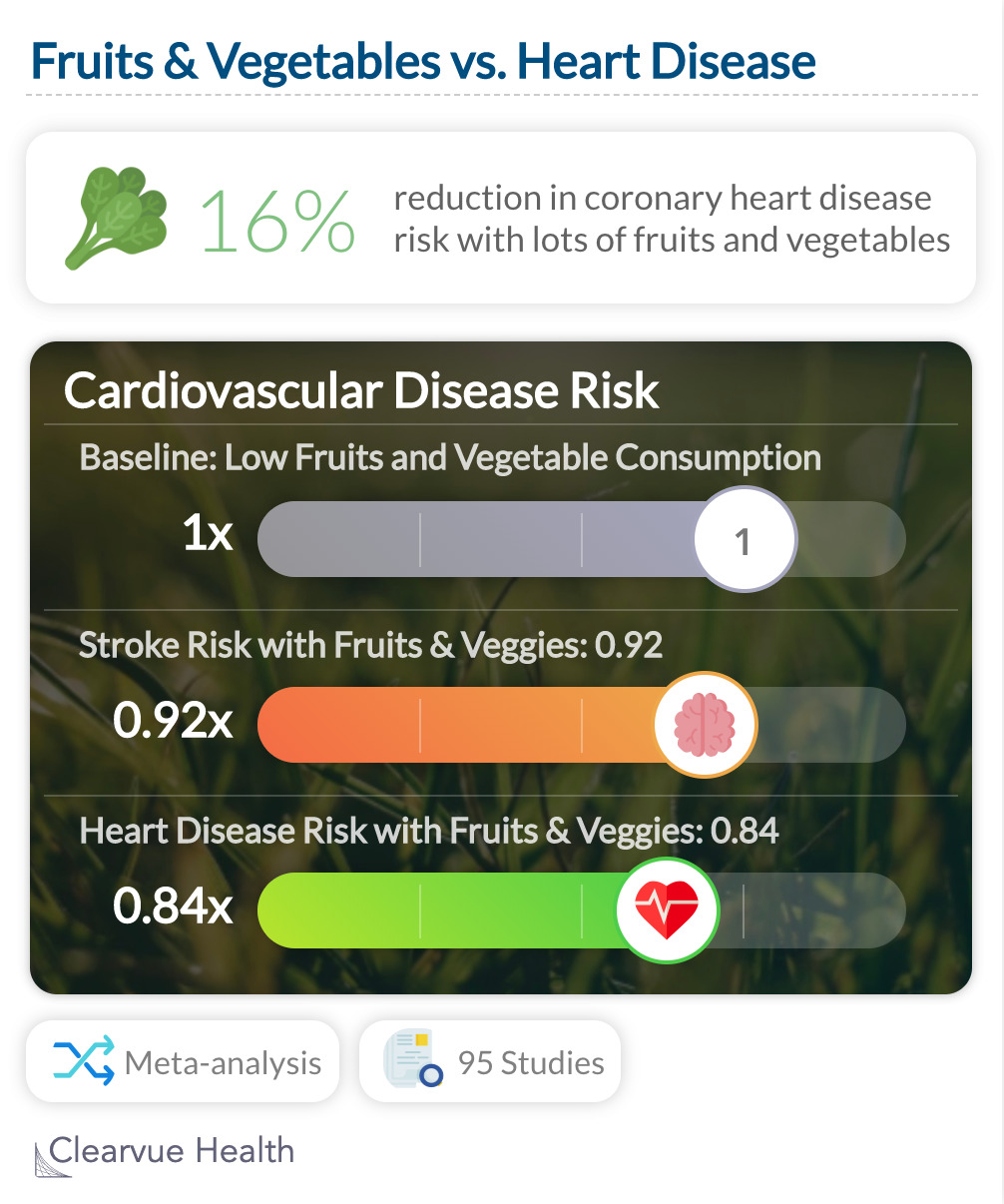
A meta-analysis of 95 studies showed that generally, high fruit and vegetable consumption is correlated with a lower risk of heart disease 0.84 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92) and a lower risk of stroke: 0.92 (95% CI: 0.90–0.95)
Data Source
"Fruit and vegetable intakes were associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer and all-cause mortality. These results support public health recommendations to increase fruit and vegetable intake for the prevention of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and premature mortality."

Key takeaways
As shown by the studies above, there still has not been convincing evidence showing that Vitamin C supplements can prevent heart disease. But, eating lots of fruits and vegetables is likely going to be pretty good for you.
More Info

#hearthealth
Scroll for more ->





#vitaminc
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->