Background
Why Vitamin D Matters
Vitamin D is one of the most important vitamins. It plays an important role across systems throughout your body, not just your bones. Recently, studies have linked Vitamin D levels to cancer risk.
what is it?
where to get it
Key Facts
- typefat soluble
- sourcediet, skin
- other namescalciferol, cholecalciferol
Appearance
Use List

bone growth

calcium

immunity

the sun
your body can create vitamin D with assistance from the sun

diet
some foods such as milk and fish contain vitamin D

supplements
Vitamin D can also be obtained from dietary supplements

Key facts: Vitamin D plays a key role in bone growth, calcium absorption, and your immune system. Unlike some vitamins, your body can produce it with the help of the sun. Sunlight helps catalyze a key reaction in the production of Vitamin D.
Study
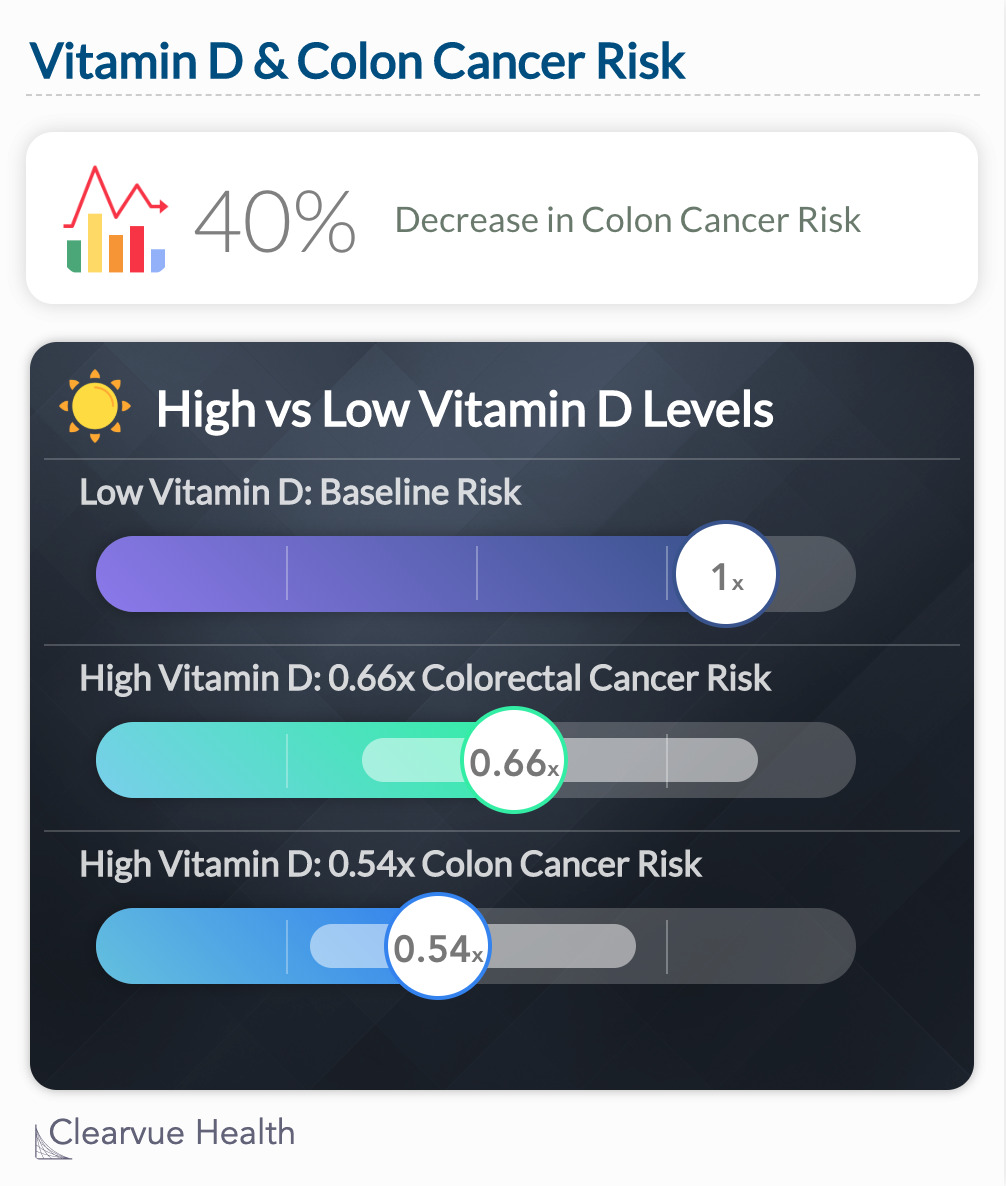
A Case-Control study of 179 colorectal cancer patients and 356 matched controls found that high Vitamin D levels in the blood was associated with a significantly lower risk of developing Colon Cancer and Colorectal Cancer compared to having low levels of Vitamin D in the blood.

What this means
This study showed that vitamin D levels in the blood correlated with a lower risk of developing Colon Cancer and Colorectal cancer. While it doesn’t say whether vitamin D is causing a benefit, it does show that those who have lots of vitamin D tend to have a lower risk.
Author Quote
"We investigated this relationship in a nested case-control study within the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), a large ongoing study of male health professionals living in the United States.......Our data provide additional support for the inverse association between vitamin D and colorectal and, in particular, colon cancer risk."
Study
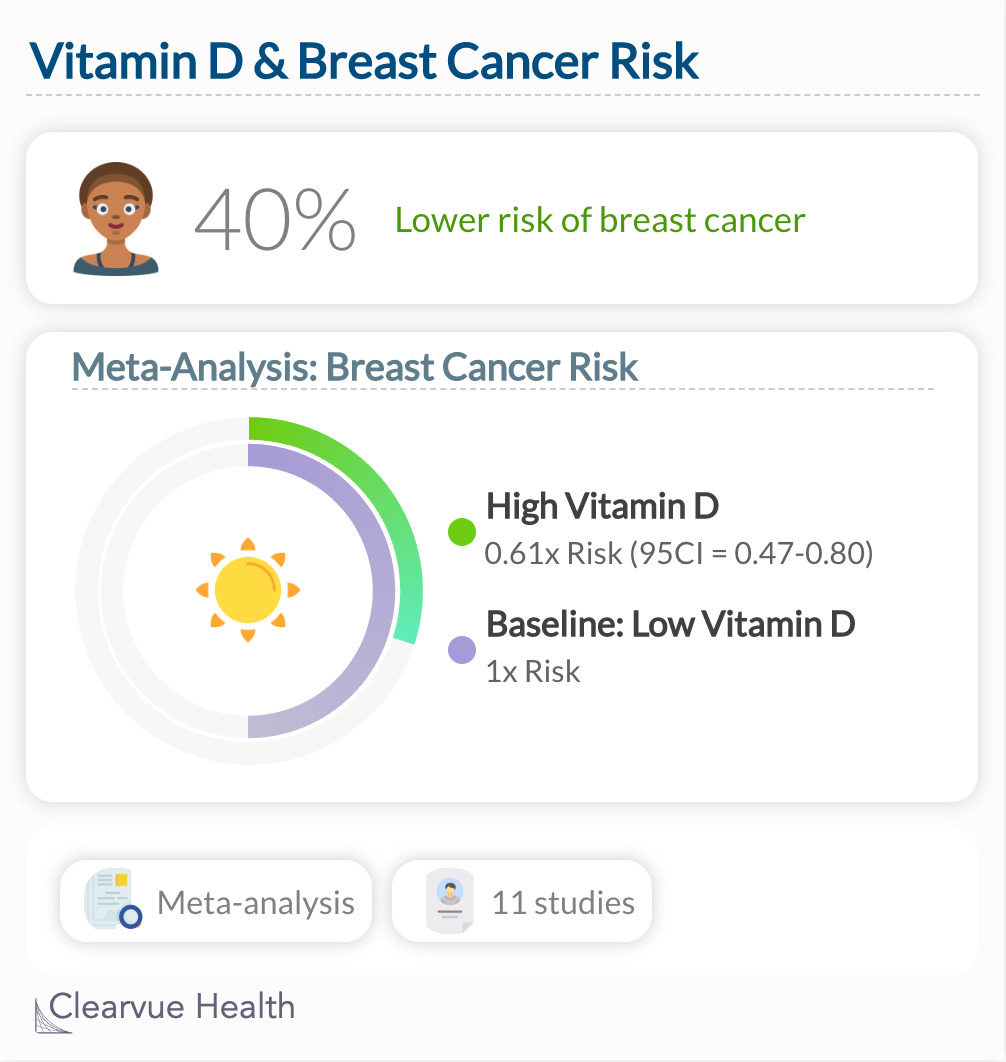
This study found that individuals with high vitamin D levels had a significantly lower risk of breast cancer compared to those with low Vitamin D. This was calculated by combining data from 11 studies, a meta-analysis, and was found to be statistically significant.
From the study
"This study supports the hypothesis that higher serum 25(OH)D levels reduce the risk of breast cancer. According to the review of observational studies, a serum 25(OH)D level of 47 ng/ml was associated with a 50% lower risk of breast cancer."

Why This Matters
Similar to the Colon Cancer data, this research further demonstrates that those who have high vitamin D levels in their blood have a significantly lower risk of developing cancer.
Negative Clinical Trial Results

Supplements may not work
While having high blood levels of Vitamin D shows clear benefits, taking vitamin D supplements may not show benefits for cancer risk as shown by the study below.
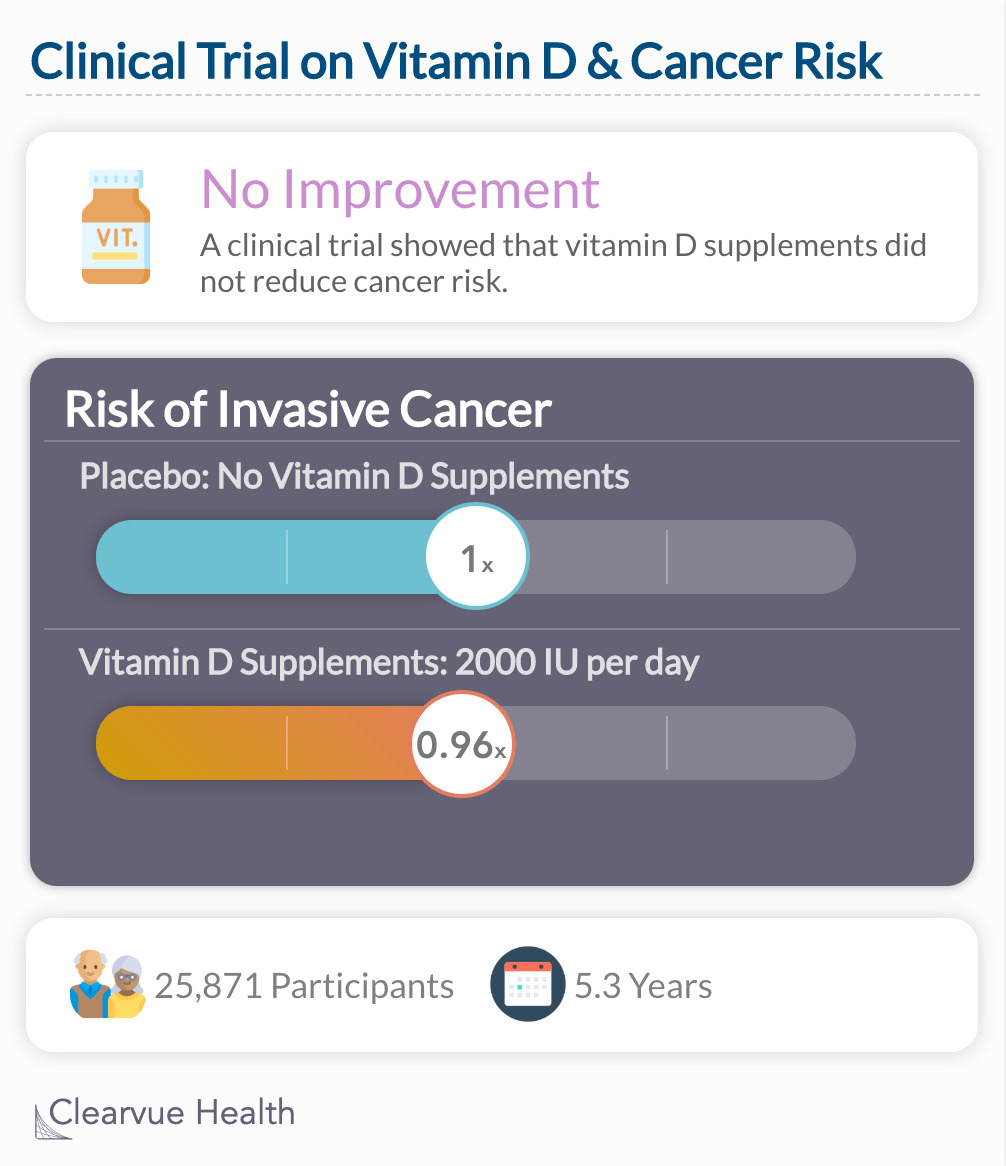
A clinical trial showed that vitamin D supplements did not reduce cancer risk. Researchers studied 25,871 participants over 5.3 years. Participants were randomized to receive either a placebo or a daily vitamin D supplement.
From the study:
"In this large primary-prevention trial, supplementation with vitamin D3 (at a dose of 2000 IU per day) did not lead to a significantly lower incidence of invasive cancer of any type or a composite of major cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, and death from cardiovascular causes) than placebo. The intervention also did not lead to a lower incidence of total deaths from cancer or a lower incidence of breast, prostate, or colorectal cancer than placebo."
Our Take

Key Takeaways
Blood levels of Vitamin D have consistently shown a correlation with a lower risk of developing cancer. However, clinical trials show that taking supplements may not reduce your risk of developing cancer. This suggests that the benefits of vitamin D cannot be obtained by taking supplements. Rather, vitamin D levels may be an indicator of a healthy lifestyle. As always, diet and exercise are a safe bet.
Background
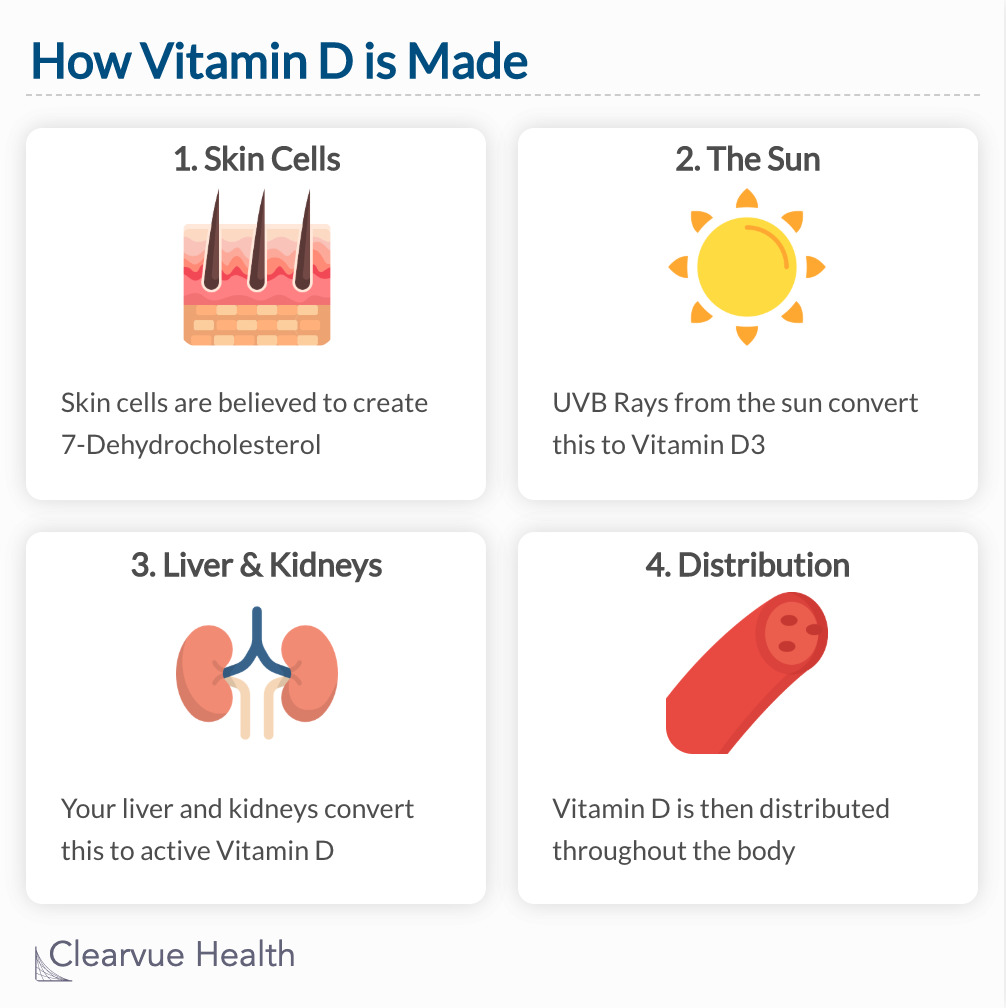
How Vitamin D is Made: Skin cells are believed to create 7-Dehydrocholesterol. UVB Rays from the sun convert this to Vitamin D3. Your liver and kidneys convert this to active Vitamin D. Vitamin D is then distributed throughout the body.
More Information

#vitamind
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->