Key Points
You can make vitamin D
Unlike Vitamin C, your body can create its own vitamin D from the sun. To do so, you need to expose your skin to enough sunlight.

2. It's not very common in food
It's also not very commonly found in food. Some of the best sources of Vitamin D are fortified, which means that it's added by food manufacturers.
3. It's very important
Vitamin D plays important roles across your whole body. Without enough Vitamin D, you can get osteomalacia, a condition characterized by weak bones.
Adults
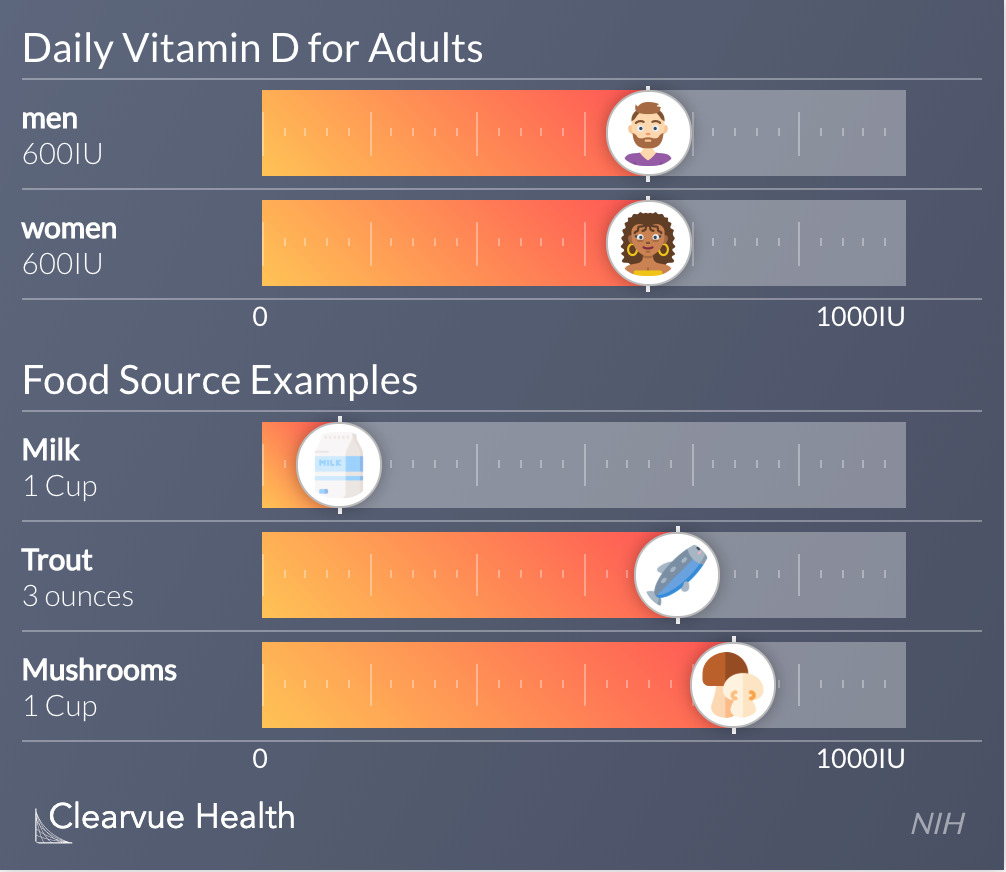
Each day, adults need about 600 IU of Vitamin D. This is the recommended daily allowance given by the NIH. This is set based on minimal sun exposure. You can generate your own Vitamin D with enough sun exposure.
Age Based Requirements
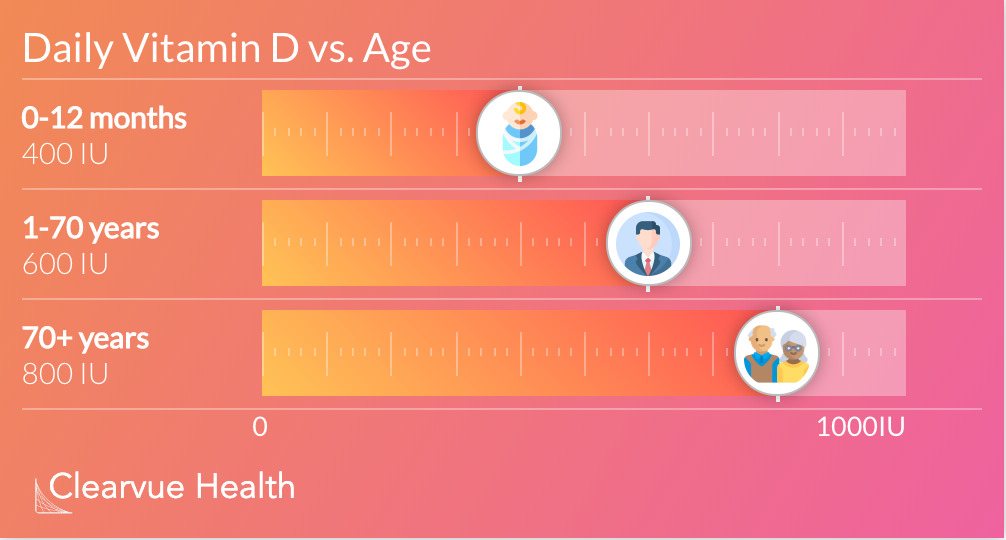
Babies need 400IU of Vitamin D each day. Children and adults ages 1-70 need 600 IU of Vitamin D each day. The elderly need the most Vitamin D, with a recommended daily allowance of 800 IU per day. These figures are calculated based on minimal sunlight.
Background
what is it?
where to get it
Key Facts
- typefat soluble
- sourcediet, skin
- other namescalciferol, cholecalciferol
Appearance
Use List

bone growth

calcium

immunity
the sun
your body can create vitamin D with assistance from the sun

diet
some foods such as milk and fish contain vitamin D

supplements
Vitamin D can also be obtained from dietary supplements

Key facts: Vitamin D plays a key role in bone growth, calcium absorption, and your immune system. Unlike some vitamins, your body can produce it with the help of the sun. Sunlight helps catalyze a key reaction in the production of Vitamin D.
Top Benefits
Benefit #1
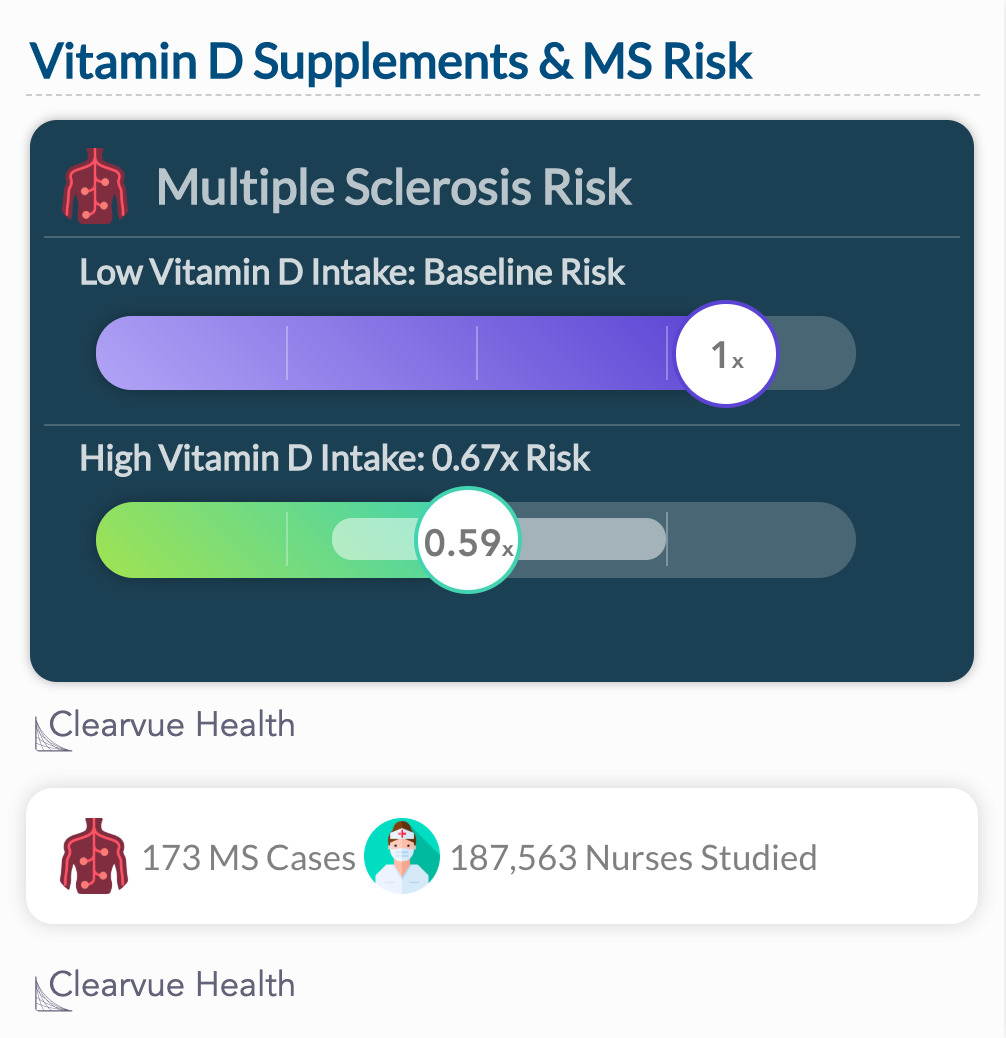
A prospective study found that nurses who took the most Vitamin D supplements had the a significantly lower risk (p=0.006) of developing Multiple Sclerosis compared to those who took the lowest amount of Vitamin D.
Benefit #2
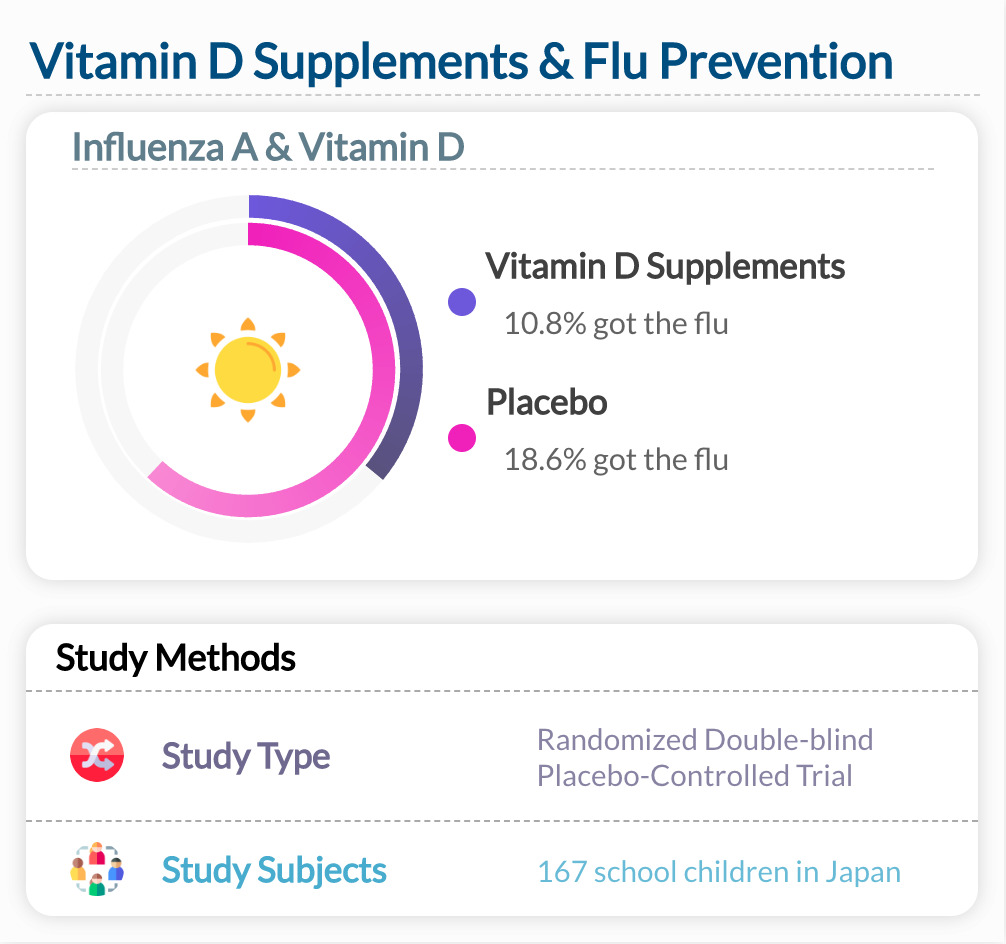
A study found that students were just over half as likely to get Influenza A if they were given vitamin D supplements compared to students who received a placebo. This study was conducted in Japan and was designed to investigate whether Vitamin D supplements could reduce the incidence of the flu among schoolchildren. Only Influenza A was studied.
Data Source
"In conclusion, our study suggests that vitamin D3 supplementation during the winter season may reduce the incidence of influenza A. This effect was prominent in specific subgroups of schoolchildren. Moreover, asthma attacks were also prevented by vitamin D3 supplementation. "
Benefit #3
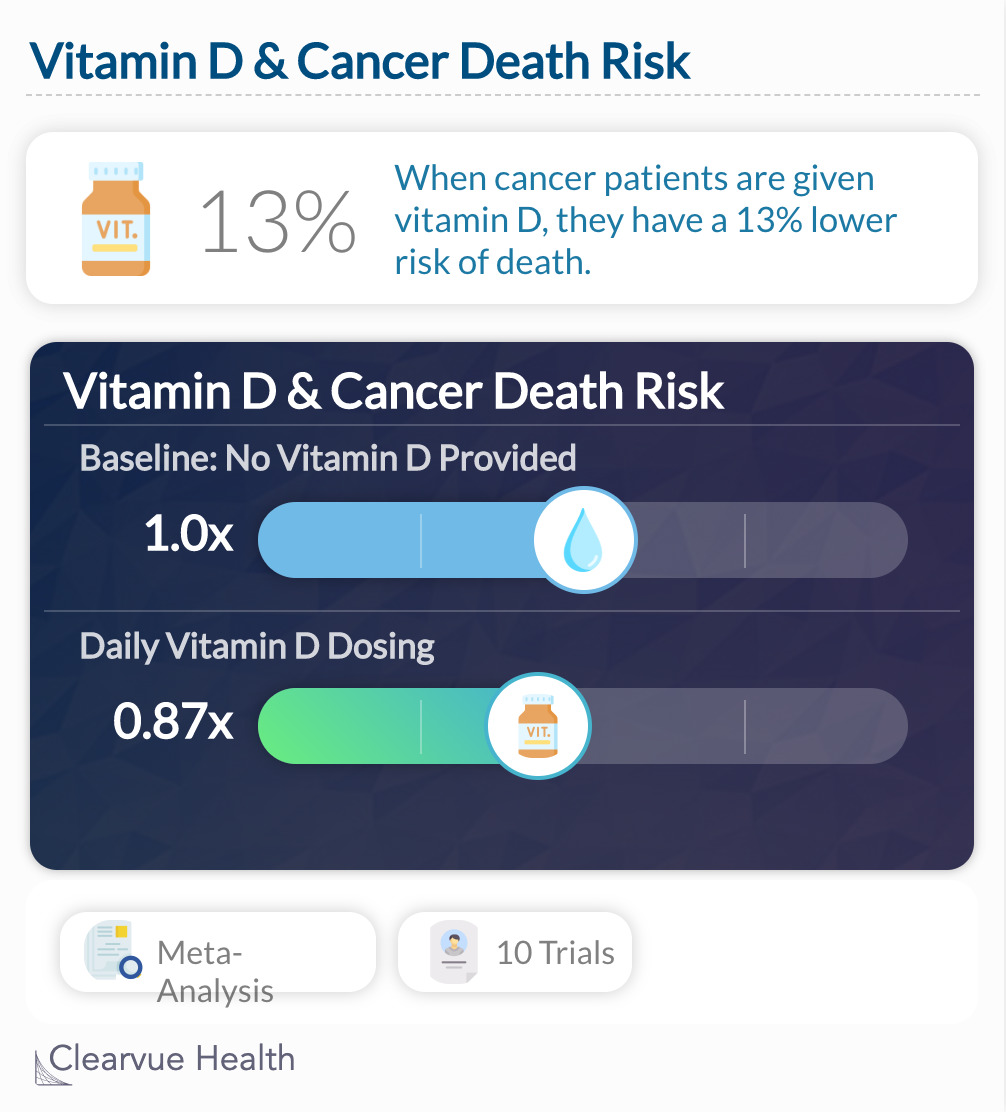
Data Source
"In an updated meta-analysis of RCTs, vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced total cancer mortality but did not reduce total cancer incidence."

#vitamind
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->