Key Points

Why you need Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps your body fight the damaging effects of free radicals. These powerful molecules are believed to play a key role in aging and cell damage.

Where can you get Vitamin E?
Vitamin E can be commonly found in oils and foods with natural plant oils. Nuts and seeds contain lots of Vitamin E.

What are the benefits of Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is believed to play a key role in brain health. Studies have linked a diet rich in Vitamin E with a healthier brain in old age.
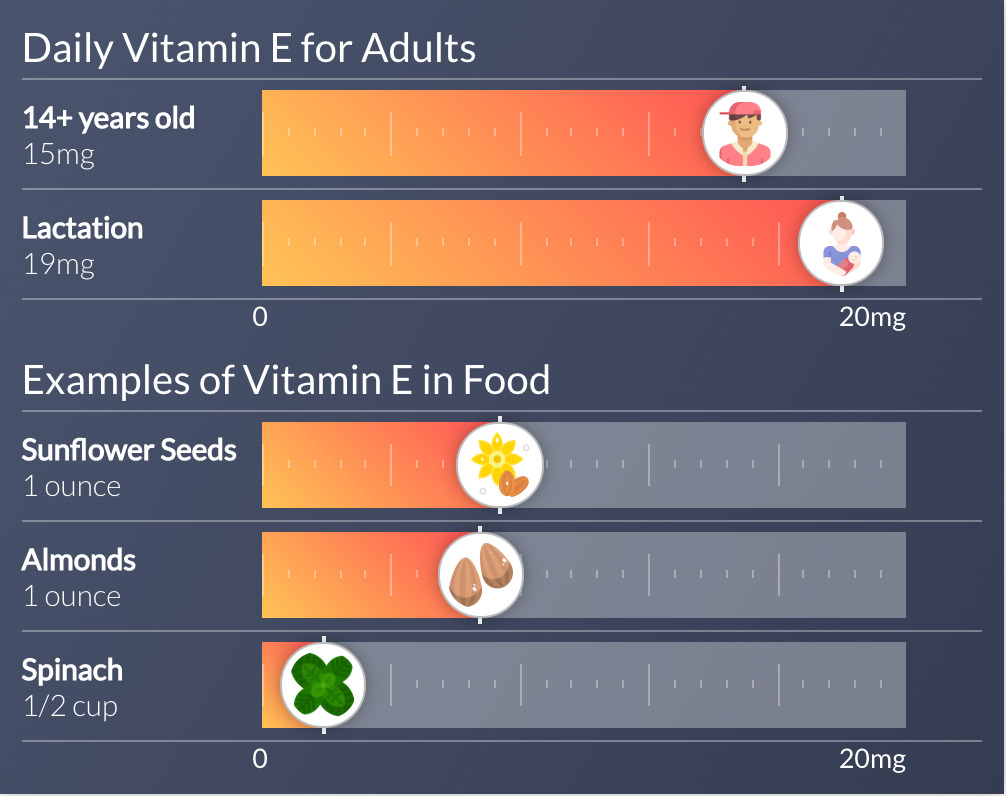
Adults
Vitamin E
Vitamin E
The Basics
Key Facts
Key Facts
- TypeFat Soluble
- Other Namesα-tocopherol
- SourcesDiet, Liver
Appearance

Uses:

Antioxidant

Inflammation

Immunity
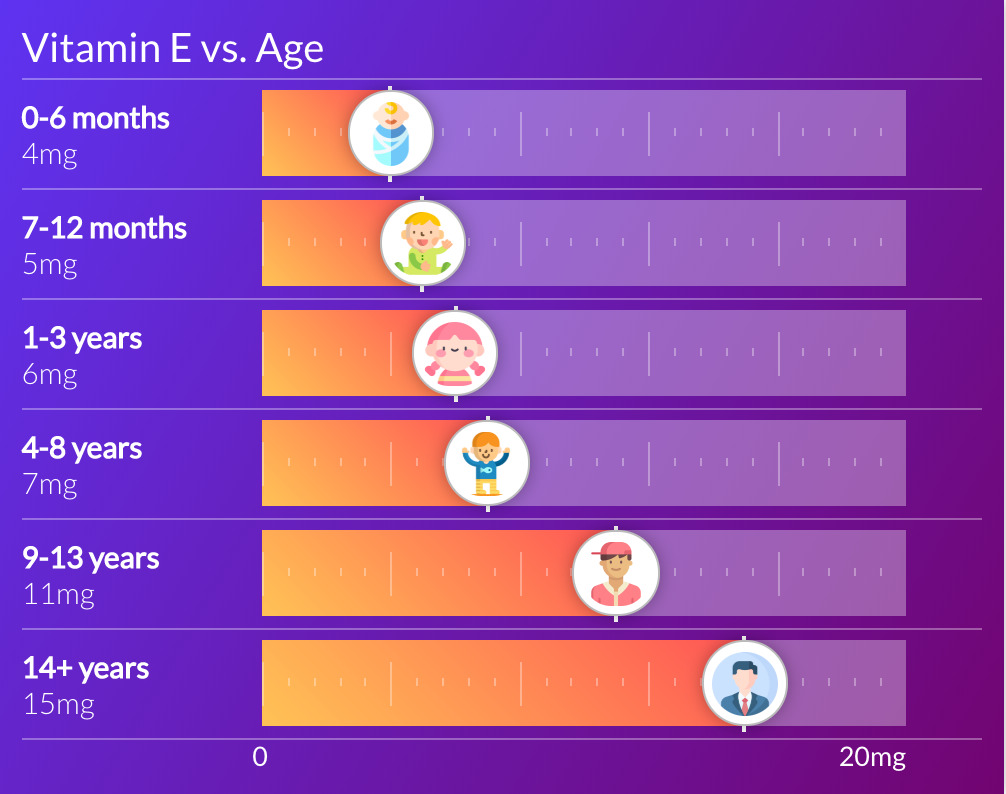
Amount per day
15mg
Source: Institute of Medicine

Types of Foods
Nuts & Seeds
Sunflower seeds, wheat germ, and almonds

Deficiency
Rare in healthy individuals

Key Benefits
Vitamin E Benefit #1
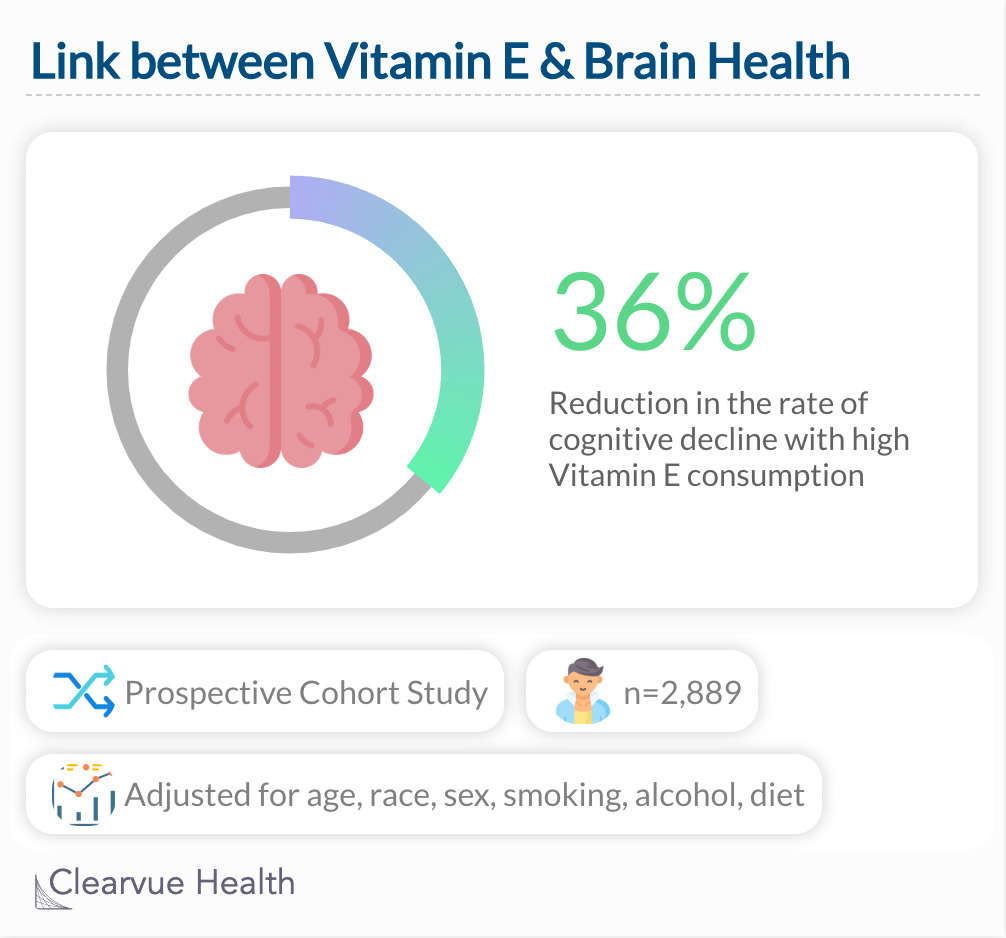
A study looking at the dietary habits of 2,889 individuals found that those who had a lot of Vitamin E in their diet had a lower rate of cognitive decline compared to those who did not.
Data Source
"Vitamin E intake, from foods or supplements, is associated with less cognitive decline with age."
Vitamin E Benefit #2
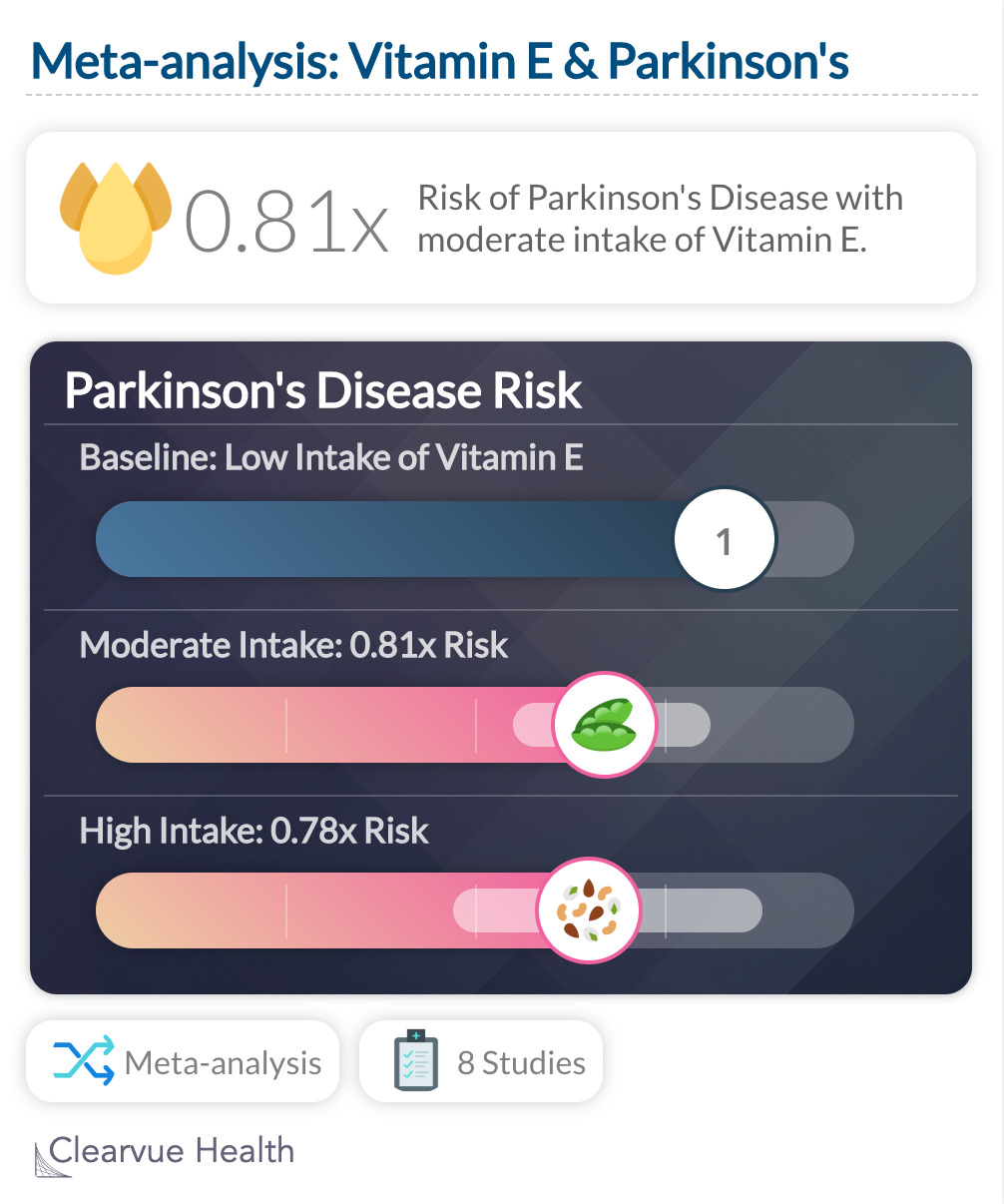
A meta-analysis found that those who ate lots of Vitamin E also had a lower risk of Parkinson's Disease. This was found for both moderate intake, "relative risk 0·81, 95% CI 0·67–0·98", and high intake: 0·78, 0·57–1·06
Data Source
""We found that dietary intake of vitamin E protects against PD. This protective influence was seen with both moderate intake (relative risk 0·81, 95% CI 0·67–0·98) and high intake (0·78, 0·57–1·06) of vitamin E" "
Vitamin E Benefit #3
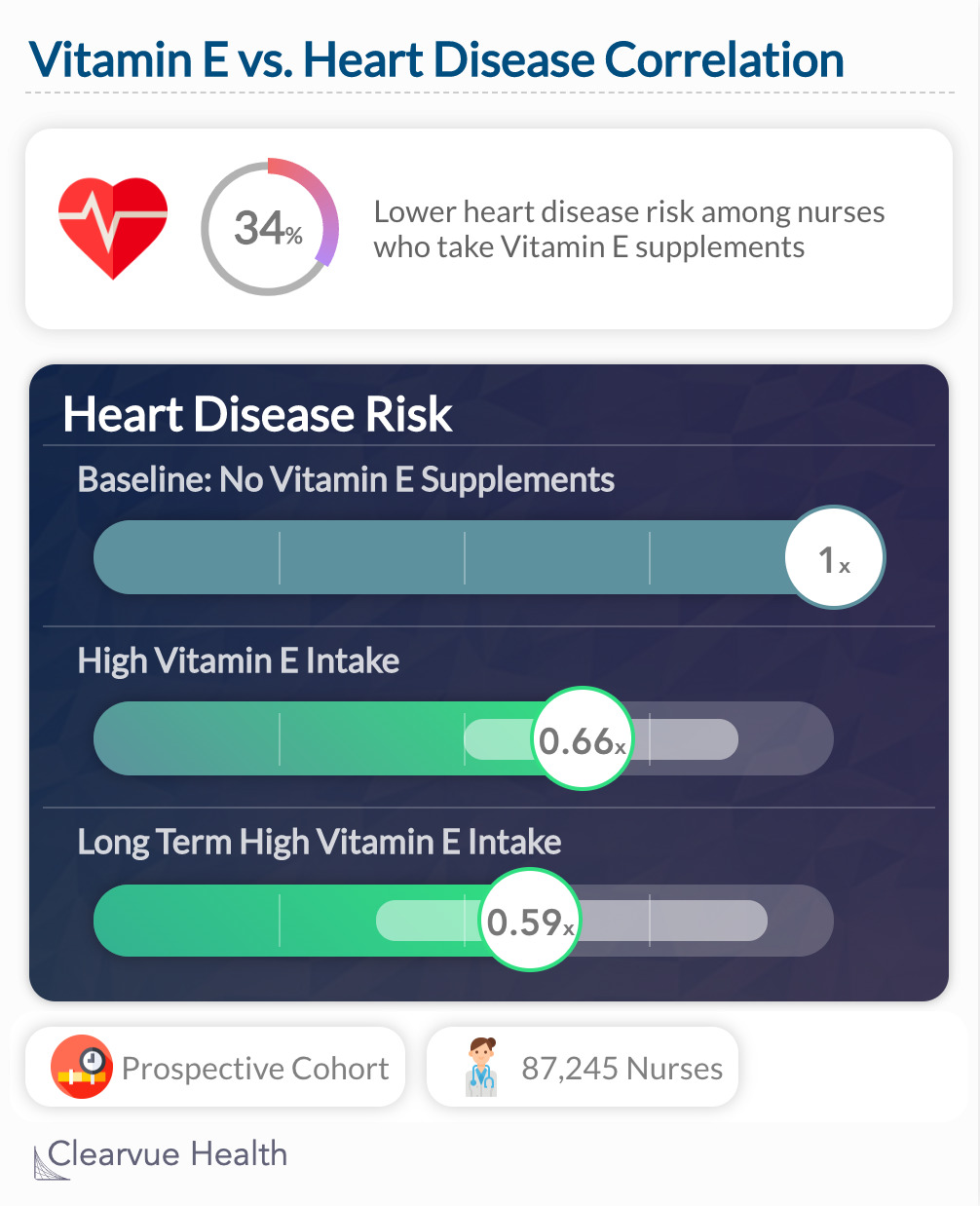
Nurses who chose to take Vitamin E also tended to have a lower risk of heart disease. (0.66 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.50 to 0.87) after adjustment for age and smoking). In the long run, their risk was even lower: RR= "0.59 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.38 to 0.91) after adjustment for age, smoking status, risk factors for coronary disease, and use of other antioxidant nutrients"
Data Source
"As compared with women in the lowest fifth of the cohort with respect to vitamin E intake, those in the top fifth had a relative risk of major coronary disease of 0.66 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.50 to 0.87) after adjustment for age and smoking. "

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#vitamine
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->