TL;DR

1. Vitamin E & Health
Those who take a lot of vitamin E tend to be quite healthy, according to several studies. They have fewer heart attacks and are less likely to die from heart disease.
2. Supplements Might Not Work
However, when people are randomly assigned to take Vitamin E supplements, they may not necessarily have better outcomes when it comes to heart disease and heart attacks.

3. Lifestyle Matters
This difference suggests that Diet and Lifestyle may be the more important factors in this debate. It's likely that those who take a lot of vitamin E also tend to take good care of their health.
The Basics
Key Facts
Key Facts
- TypeFat Soluble
- Other Namesα-tocopherol
- SourcesDiet, Liver
Appearance

Uses:

Antioxidant

Inflammation

Immunity
Amount per day
15mg
Source: Institute of Medicine

Types of Foods
Nuts & Seeds
Sunflower seeds, wheat germ, and almonds

Deficiency
Rare in healthy individuals

Study 1
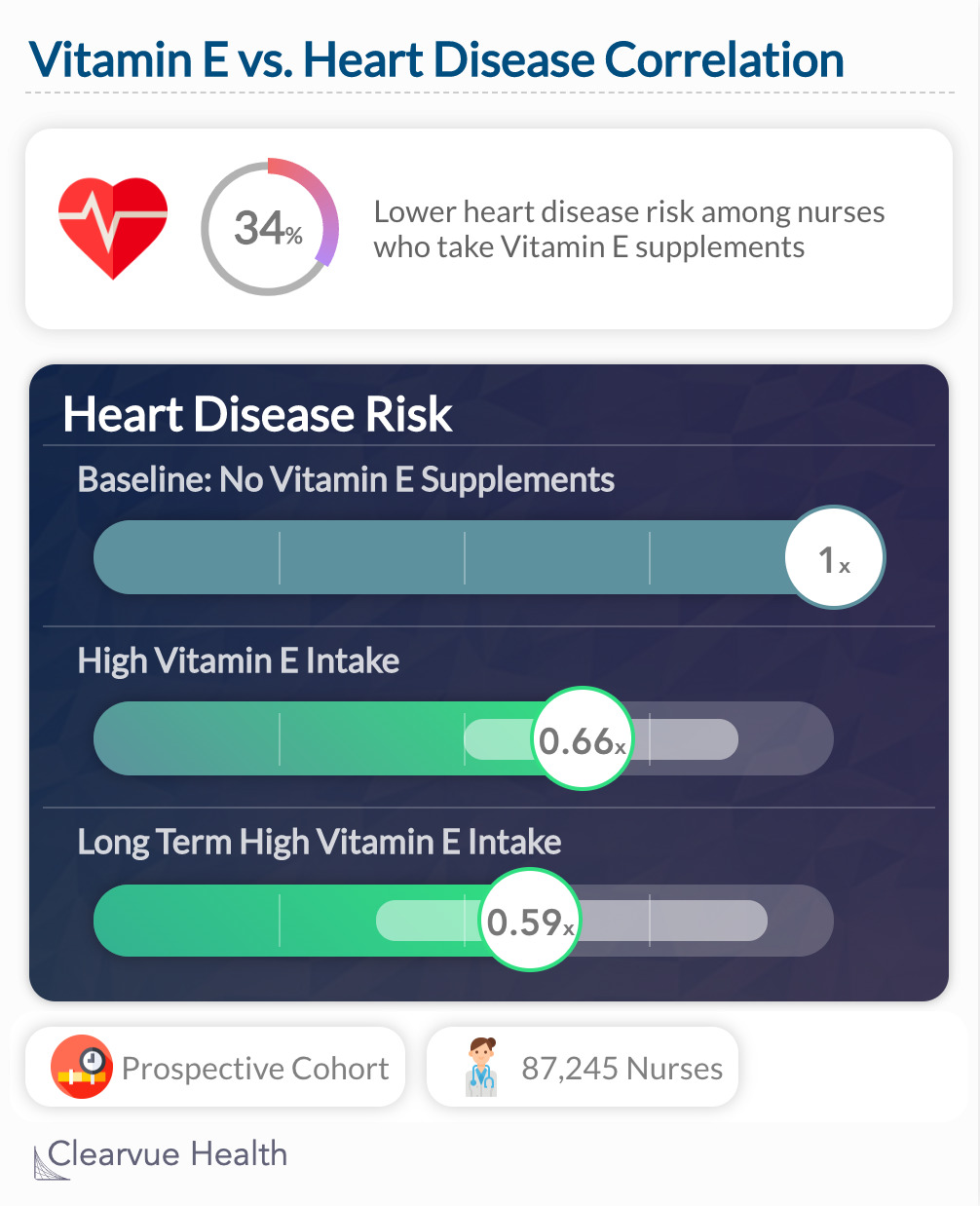
Nurses who chose to take Vitamin E also tended to have a lower risk of heart disease. (0.66 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.50 to 0.87) after adjustment for age and smoking). In the long run, their risk was even lower: RR= "0.59 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.38 to 0.91) after adjustment for age, smoking status, risk factors for coronary disease, and use of other antioxidant nutrients"

Our Take
This study showed an interesting correlation. However, later clinical trials have suggested that Vitamin E may not be necessarily causing the observed benefit.
Data Source
"Although these prospective data do not prove a cause-and-effect relation, they suggest that among middle-aged women the use of vitamin E supplements is associated with a reduced risk of coronary heart disease."
Study 2
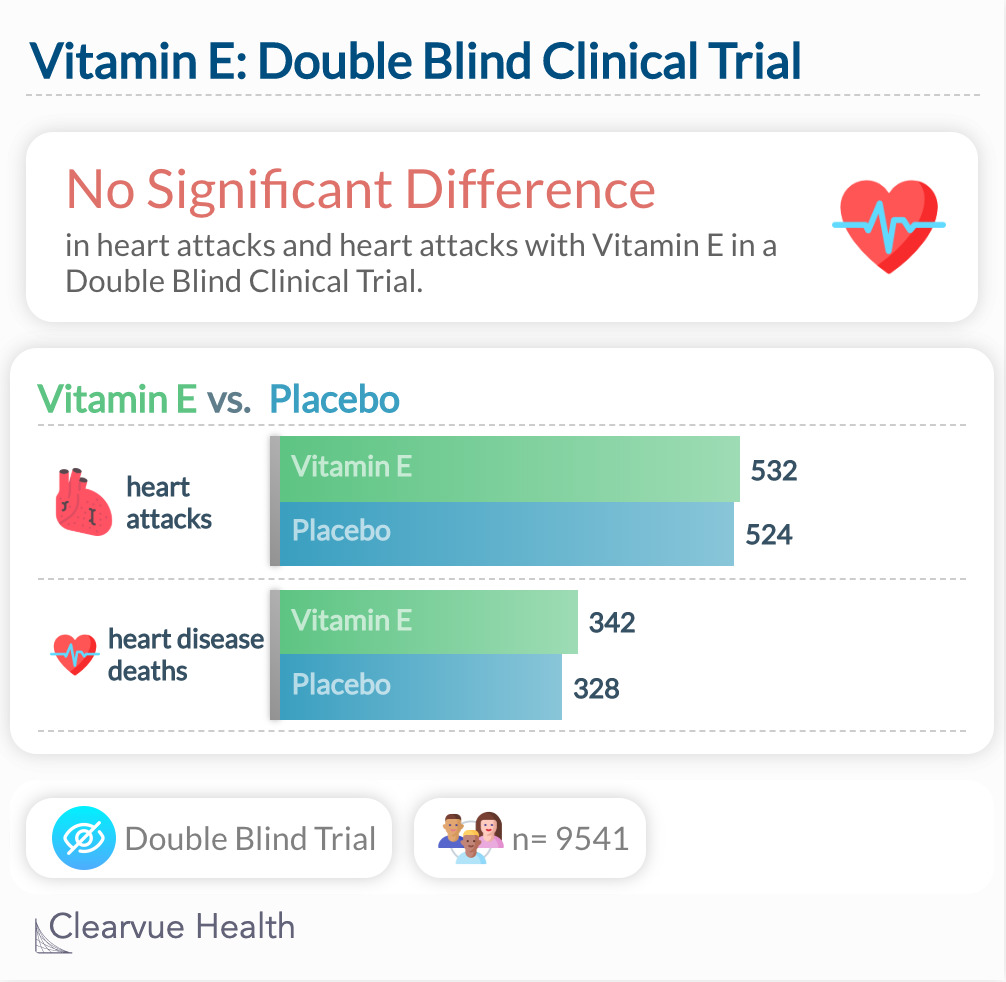
The study above shows that in a randomized double-blind clinical trial, the gold standard of medical research, Vitamin E may not have a benefit for heart disease. Those who were assigned to take Vitamin E had the same number of heart attacks and deaths from heart disease as those who were assigned to take placebo, a control.

Our Take
While this trial doesn't rule out benefits, it does provide strong evidence that much of the benefit seen for Vitamin E may be due to correlation rather than causation. It's likely that those who take Vitamin E tend to have fewer heart attacks because they also choose to live healthier lifestyles.
Data Source
"The data from this large trial indicated that 600 IU of natural-source vitamin E taken every other day provided no overall benefit for major cardiovascular events or cancer, did not affect total mortality, and decreased cardiovascular mortality in healthy women. These data do not support recommending vitamin E supplementation for cardiovascular disease or cancer prevention among healthy women."
Key Takeaways

Final Thoughts
When it comes to vitamin E and heart attacks, the evidence is mixed. Those who take vitamin E regularly tend to have better health. But, when people are randomly assigned to take it, they don't necessarily do better. The key here is to eat healthy, exercise, and focus on lifestyle rather than supplements.
Vitamin E
Key Facts
Examples

How they work
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by counteracting free radicals.

Effect on Disease
Research on Antioxidants and disease prevention has shown mixed results.
Common Sources

Chocolate

Berries & Fruit

Coffee

beta-carotene
Your body makes vitamin A with beta-carotene, commonly found in carrots.

Vitamin C
Found in all sorts of fruits, Vitamin C is a very commonly consumed antioxidant.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in nuts and seeds.

More Information
More Info

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#hearthealth
Scroll for more ->





#vitamine
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->