Key Points

1. High Vitamin E = Less Parkinson's Disease Risk
Those who have a lot of Vitamin E in their diet also have a significantly lower risk of developing Parkinson's Disease.

2. Vitamin E Rich Foods
Legumes, including peas and chickpeas, have a particularly strong protective effect against Parkinson's Diseases

3. Prevention, Not Cure
However, as far as we know, this effect only applies to preventing Parkinson's Disease, not curing it.
Background
What is it?
Key facts
Type

Neurodegenerative Disease
Affects

Dopaminergic neurons in the brain
Key symptoms:

Shaking

Stiffness

Balance issues

# of Americans
900,000+
900,000+ Americans have Parkinson's Disease.

Before Age 50
4%
Only 4% of cases are diagnosed before age 50.
Gender ratio


Background:
The Basics
Key Facts
Key Facts
- TypeFat Soluble
- Other Namesα-tocopherol
- SourcesDiet, Liver
Appearance

Uses:

Antioxidant

Inflammation

Immunity
Amount per day
15mg
Source: Institute of Medicine

Types of Foods
Nuts & Seeds
Sunflower seeds, wheat germ, and almonds

Deficiency
Rare in healthy individuals

Study 1
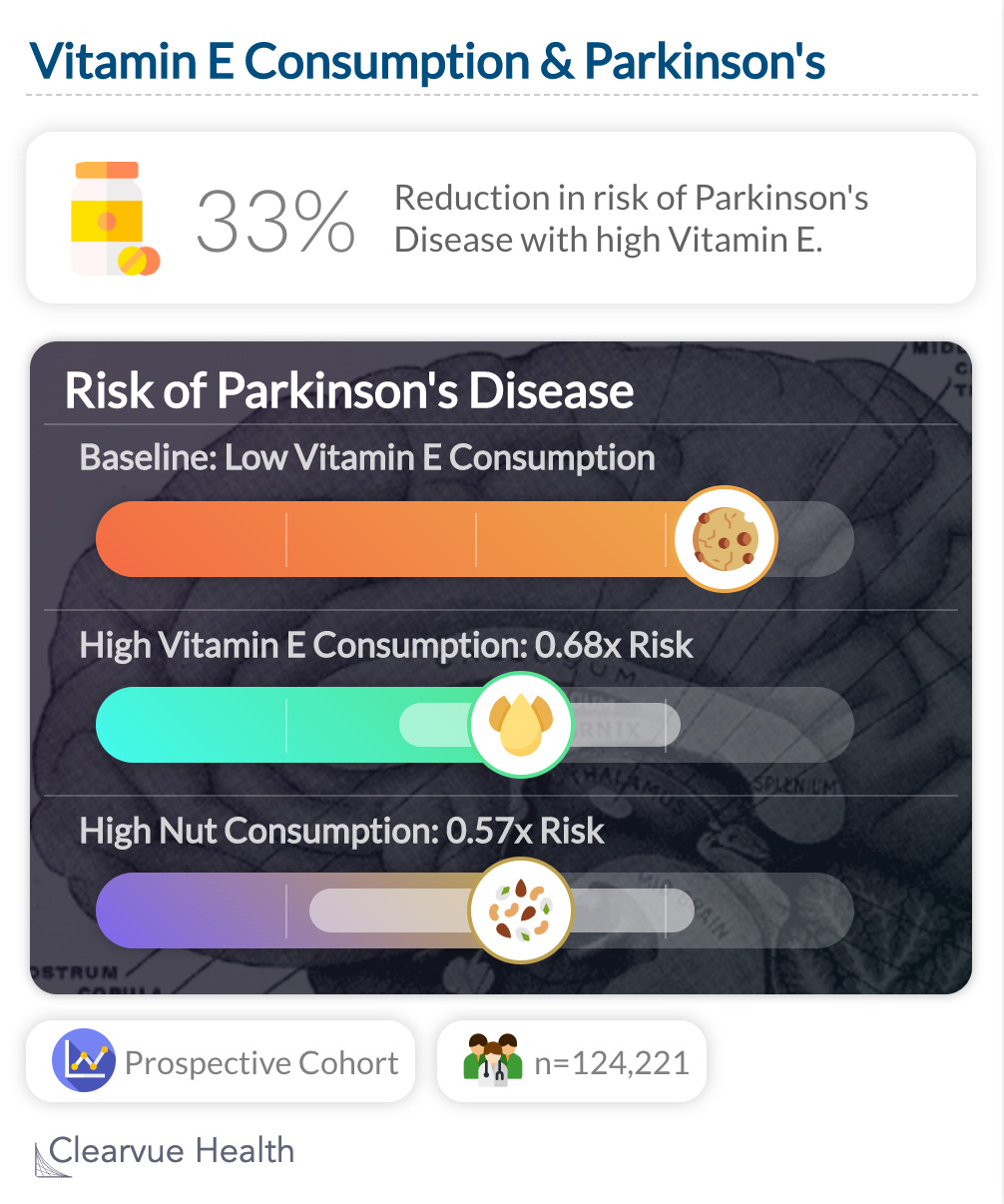
Eating a diet rich in vitamin E was associated with a reduction in Parkinson's Disease risk, 0.68 (95% CI, 0.49 to 0.93), compared to those who ate the least Vitamin E. Supplements did not decrease risk. Similar, nuts, a food high in Vitamin E, also decreased risk of Parkinson's Disease: "for ≥5/week vs <1/month, pooled RR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.34 to 0.95"

Our Take
This study suggests that a diet rich in Vitamin E may protect against Parkinson's Disease. However, taking supplements themselves may not help.
Data Source
"Use of vitamin supplements and high intake of carotenoids do not appear to reduce the risk of PD. The reduction in risk of PD associated with high dietary vitamin E intake suggests that other constituents of foods rich in vitamin E may be protective. "
Study 2
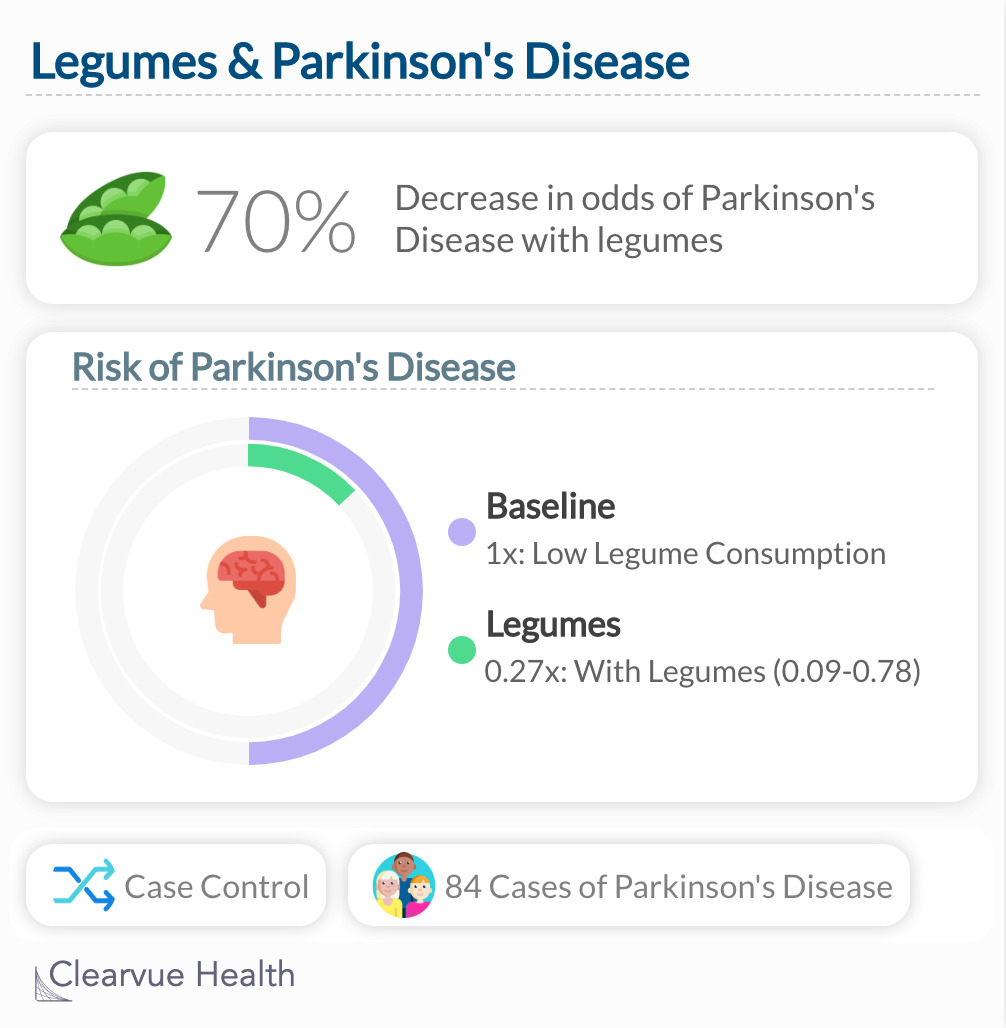
A Case-Control study found that those who ate lots of legumes, including lentils and peas, had a significantly lower risk of developing Parkinson's Disease: adjusted OR = 0.27, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.78.

Our Take
This study suggested that eating lots of Legumes, including peas and lentils, correlated with a significantly lower risk of Parkinson's Disease. While the study doesn't specifically find benefits for Vitamin E, the high Vitamin E content of these foods supports the link between Vitamin E and Parkinson's Disease.
Data Source
"Though consistent with prior reports of PD protection afforded by legumes, and with speculation on the possible benefits of dietary or supplemental vitamin E in preventing PD, these preliminary data do not conclusively document a beneficial effect of dietary vitamin E on PD occurrence."
Study 3
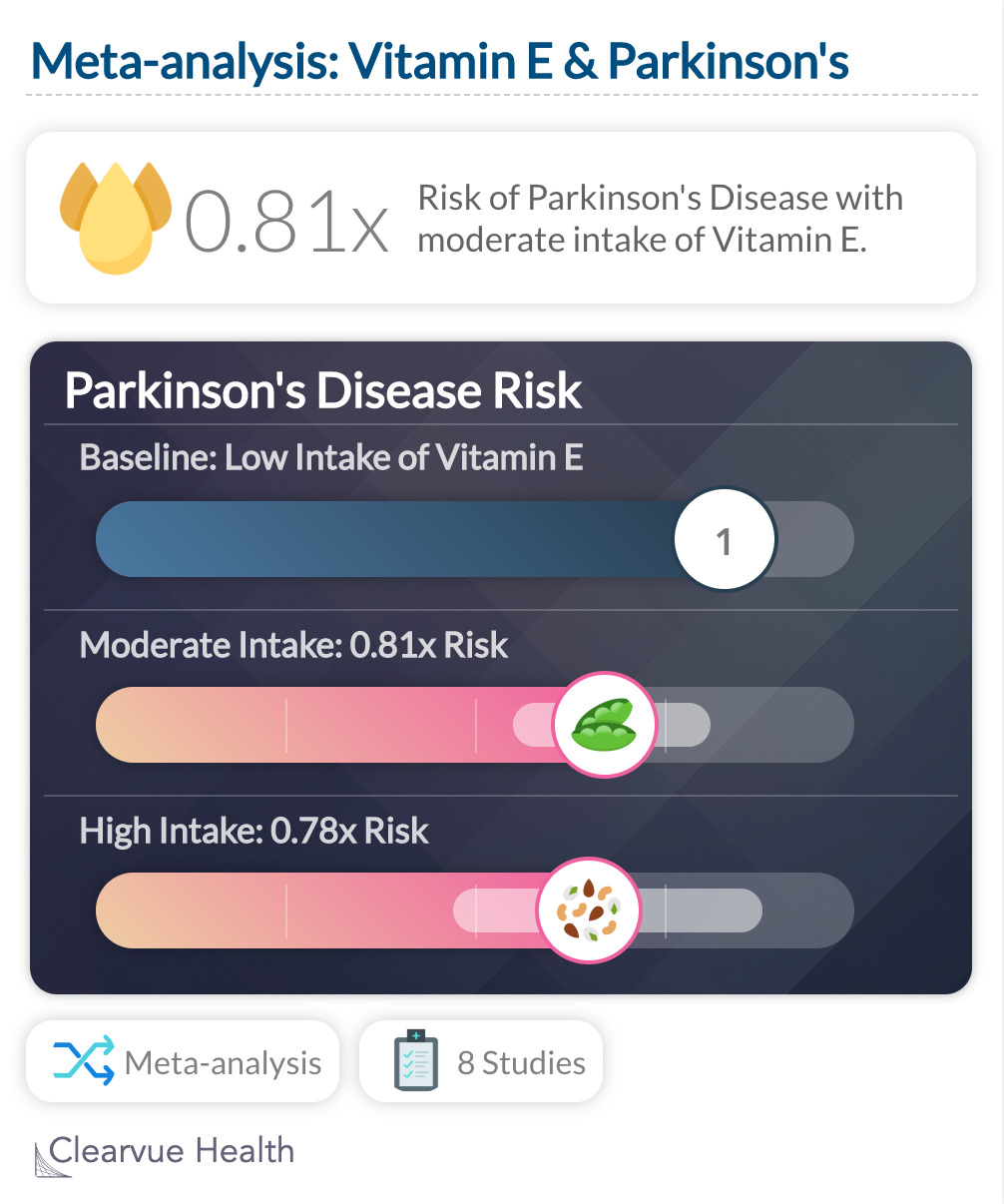
A meta-analysis found that those who ate lots of Vitamin E also had a lower risk of Parkinson's Disease. This was found for both moderate intake, "relative risk 0·81, 95% CI 0·67–0·98", and high intake: 0·78, 0·57–1·06
Data Source
"We conclude that dietary vitamin E may have a neuroprotective effect attenuating the risk of PD. These results require confirmation in randomized controlled trials."
Vitamin E
Key Facts
Examples

How they work
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by counteracting free radicals.

Effect on Disease
Research on Antioxidants and disease prevention has shown mixed results.
Common Sources

Chocolate

Berries & Fruit

Coffee

beta-carotene
Your body makes vitamin A with beta-carotene, commonly found in carrots.

Vitamin C
Found in all sorts of fruits, Vitamin C is a very commonly consumed antioxidant.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in nuts and seeds.

More Info
More Info

#vitamine
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->