Vitamin B12 & The Heart
TL;DR: Vitamin D vs. Depression


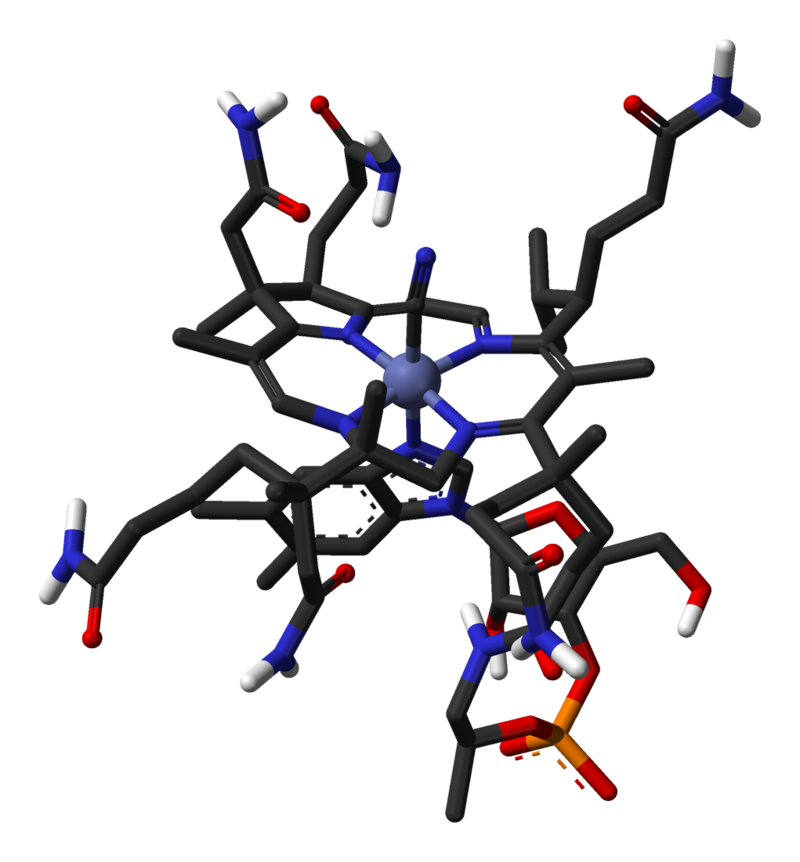
Vitamin B12: Key Facts
Vitamin B12 is a key vitamin for metabolism. It has also been linked to processes that are known to play a role of heart disease.

"Elevated homocysteine promotes atherosclerosis through increased oxidant stress, impaired endothelial function, and induction of thrombosis. Prospective studies have shown that elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations increase risk of cardiovascular disease by twofold and risk of cerebrovascular disease to a lesser degree. "
Trials on Vitamin B12 and Homocysteine




" Typically in Western populations, daily supplementation with both 0.5-5 mg folic acid and about 0.5 mg vitamin B-12 would be expected to reduce blood homocysteine concentrations by about a quarter to a third (for example, from about 12 mumol/l to 8-9 mumol/l)."
Vitamin B12 and Heart Disease





"Supplements combining folic acid and vitamins B6 and B12 did not reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with vascular disease."
At this point, there’s not enough evidence to recommend Vitamin B12 as a way to prevent heart disease. We need to do more studies. However, there’s an overwhelming amount of evidence that eating a balanced diet, in which you will get lots of Vitamin B12 among other nutrients, is a great way of preventing heart disease.

"The American Heart Association has concluded that the available evidence is inadequate to support a role for B vitamins in reducing cardiovascular risk"