Blood pressure changes associated with medication treatment of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
ADHD Medication and Blood Pressure
Timothy E Wilens , Paul G Hammerness, Joseph Biederman, Anne Kwon, Thomas J Spencer, Sarah Clark, Megan Scott, Amy Podolski, Jeffrey W Ditterline, Matthew C Morris, Hadley Moore
Objectives
ADHD is often treated with stimulant medication such as Adderall or Ritalin. While they are highly effective medications, they carry significant side effects and a risk of dependency.
In rare cases, these medications have been linked with heart attacks and sudden deaths. They affect our cardiovascular systems.
This study wanted to examine the effect of ADHD medication on blood pressure and heart rate.
To evaluate the effects of medications used in the treatment of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) on blood pressure and pulse.
Methods
Researchers recruited adults with ADHD who had participated in previous clinical trials. Vitals were obtained before and after the participants were given ADHD medication.
In this study, the authors collected data from 125 participants and combined their data in their analysis.
Subjects were those with DSM-III-R-/DSM-IV-diagnosed ADHD enrolled in placebo-controlled studies of 5 different medications for ADHD. Cardiovascular data from these studies of both stimulants (methylphenidate, amphetamine compounds, pemoline) and nonstimulants (bupropion, desipramine) we...
Results
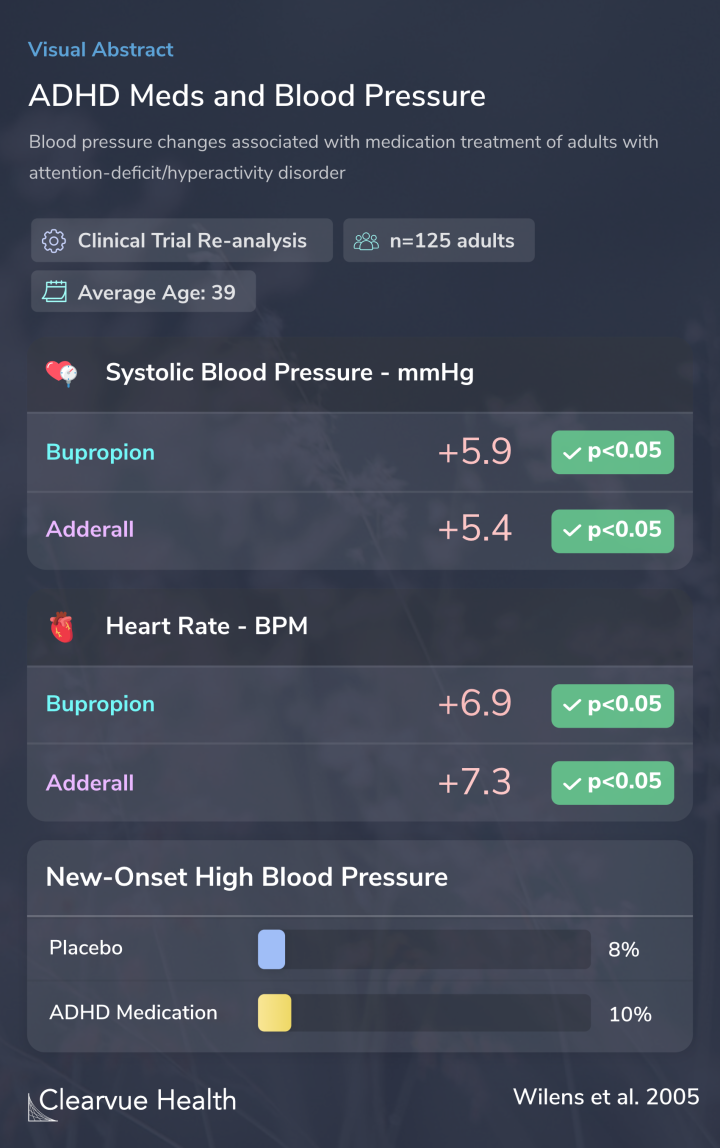
The results showed that participants who were given Adderall and bupropion (Wellbutrin) experienced significantly higher blood pressure after treatment:
Those on Adderall, bupropion (Wellbutrin), and Ritalin (methylphenidate) experienced significant increases in their heart rates:
While some study participants developed high blood pressure after treatment, it was not significantly greater than the new-onset high blood pressure rate in the control group.
There were 125 subjects with a mean +/- SD age of 39 +/- 9 years. In general, active drug treatment for ADHD compared to baseline was associated with several statistically significant changes in systolic blood pressure (bupropion: +5.9 mm Hg, p < .05 by paired t test; amphetamine: +5.4 m...
Conclusions
These results show that some ADHD medications are associated with small but significant increases and heart rate and blood pressure.
ADHD is increasingly recognized as a disorder that commonly extends into adulthood.
As more adults get treated for ADHD, it becomes increasingly important to study the effects of ADHD medication on cardiovascular health.
This particular study was a small study that re-analyzed data from previous trials.
Later studies have further investigated cardiovascular risk in adults taking ADHD and have found that while the medications may increase blood pressure and heart rate, the overall risk of sudden death is likely low:
Both stimulant and nonstimulant catecholaminergic medications used in adults with ADHD are associated with minor, but statistically significant, changes in heart rate and blood pressure that were often observed in those receiving placebo. Given the minor pressor and chronotropic effect o...