College students with and without ADHD: comparison of self-report of medication usage, study habits, and academic achievement
ADHD Medication's Impact on College Students' Academics
Advokat C, Lane SM, Luo C
Objectives
The study looked into how ADHD medications like Ritalin affect college students' study habits and their success in school. Students with ADHD often struggle more than their peers with things like staying organized, remembering stuff, and finishing schoolwork.
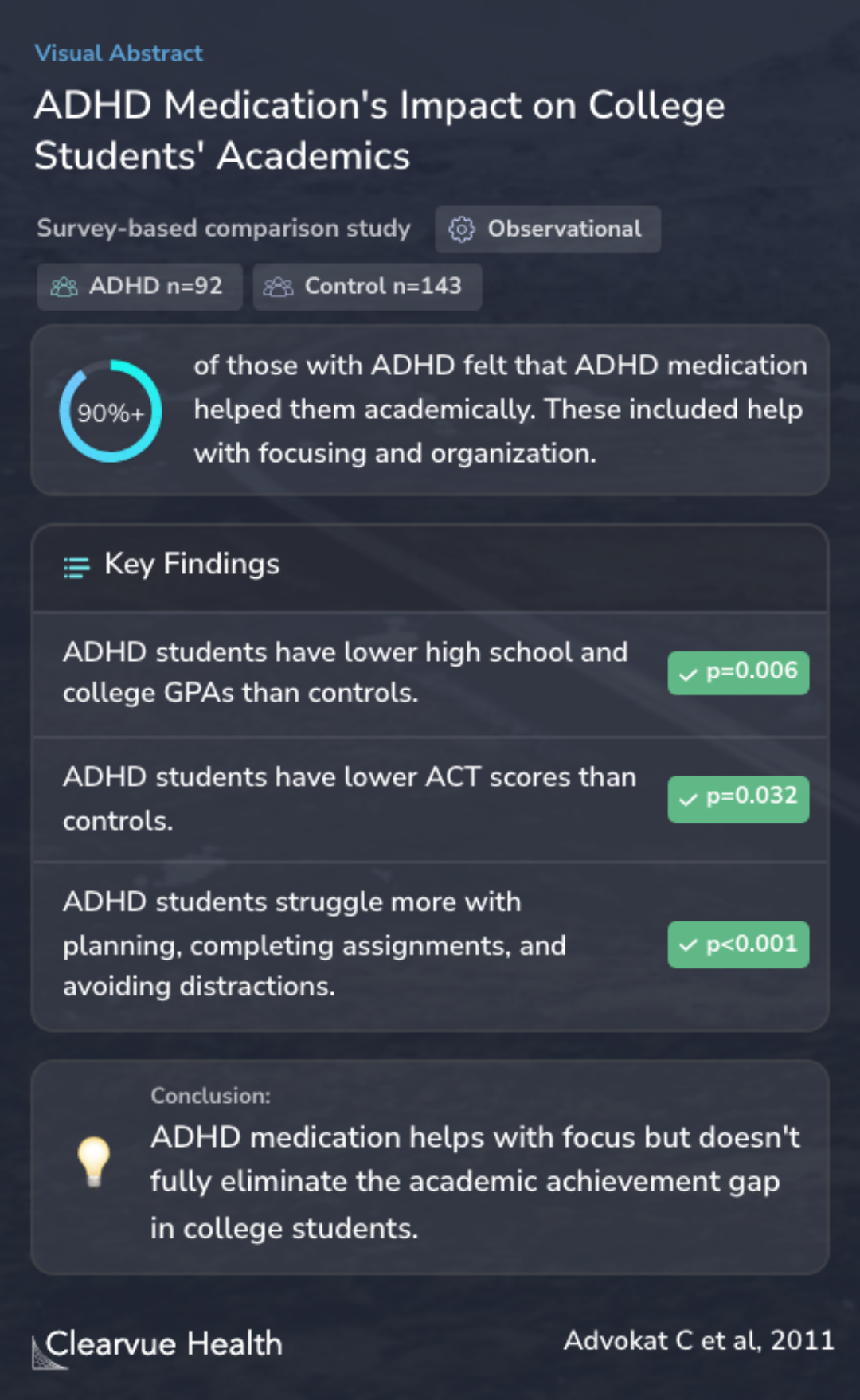
To examine the relationship between ADHD medications, study habits, and academic achievement of ADHD-diagnosed undergraduates.
Methods
In this study, 92 college students who said they have ADHD and take medicine for it were compared with 143 students who don't have ADHD. They all answered questions about how they did in school.
A total of 92 students with a self-reported ADHD diagnosis and a current prescription for ADHD medication were compared with 143 control students in a survey of academic performance.
Results
The students with ADHD mentioned that their medicine helps them focus and be more organized when studying. However, even with medication, they still had lower grades in high school and college, lower ACT scores, and withdrew from more classes than students without ADHD. Interestingly, students with ADHD who had good study habits, even without medication, did better in school. This shows that while medication can help, it doesn't solve all the problems students with ADHD face in school.
Most ADHD students took stimulant medication and said the drugs helped them, yet believed they were worse than other students at planning and completing assignments and avoiding distractions. Although most study habits of ADHD students did not differ from controls, their high school and ...
Conclusions
Just like with younger kids, the study found that medication alone doesn't fully fix the lower school performance seen in college students with ADHD. This means that while ADHD medications can help with focusing, they aren't the only answer to the challenges students with ADHD face in school.
As previously shown for children and adolescents, stimulant medications alone did not eliminate the academic achievement deficit of ADHD undergraduates.
Key Takeaways
Context
This study adds to other research on ADHD treatments. For example, a 2009 study by Abikoff and others looked at how Ritalin affects organizational skills in kids with ADHD. They found that the medication helped, but some kids still needed more help.
Another study in 2022 by Hartung and others explored a new program to help college students with ADHD. They found that this program really helped improve things like attention, ADHD symptoms, self-concept, and organizational skills. These studies all suggest that treatments for ADHD might need to include more than just medication.