Acute administration of d-amphetamine decreases impulsivity in healthy volunteers
Amphetamine Reduces Impulsivity in Healthy Volunteers
Harriet de Wit, Justin L Enggasser, Jerry B Richards
Objectives
Impulsivity, defined as the tendency to act hastily without considering potential consequences, is a significant aspect of ADHD. This study hoped to determine whether Adderall, a known treatment for impulsivity in ADHD, could improve impulsivity in healthy individuals by investigating the acute behavioral effects of d-amphetamine, the active ingredient in Adderall, on various behavioral indices of impulsivity.
This study investigated the acute behavioral effects of d-amphetamine on several behavioral indices of impulsivity.
Methods
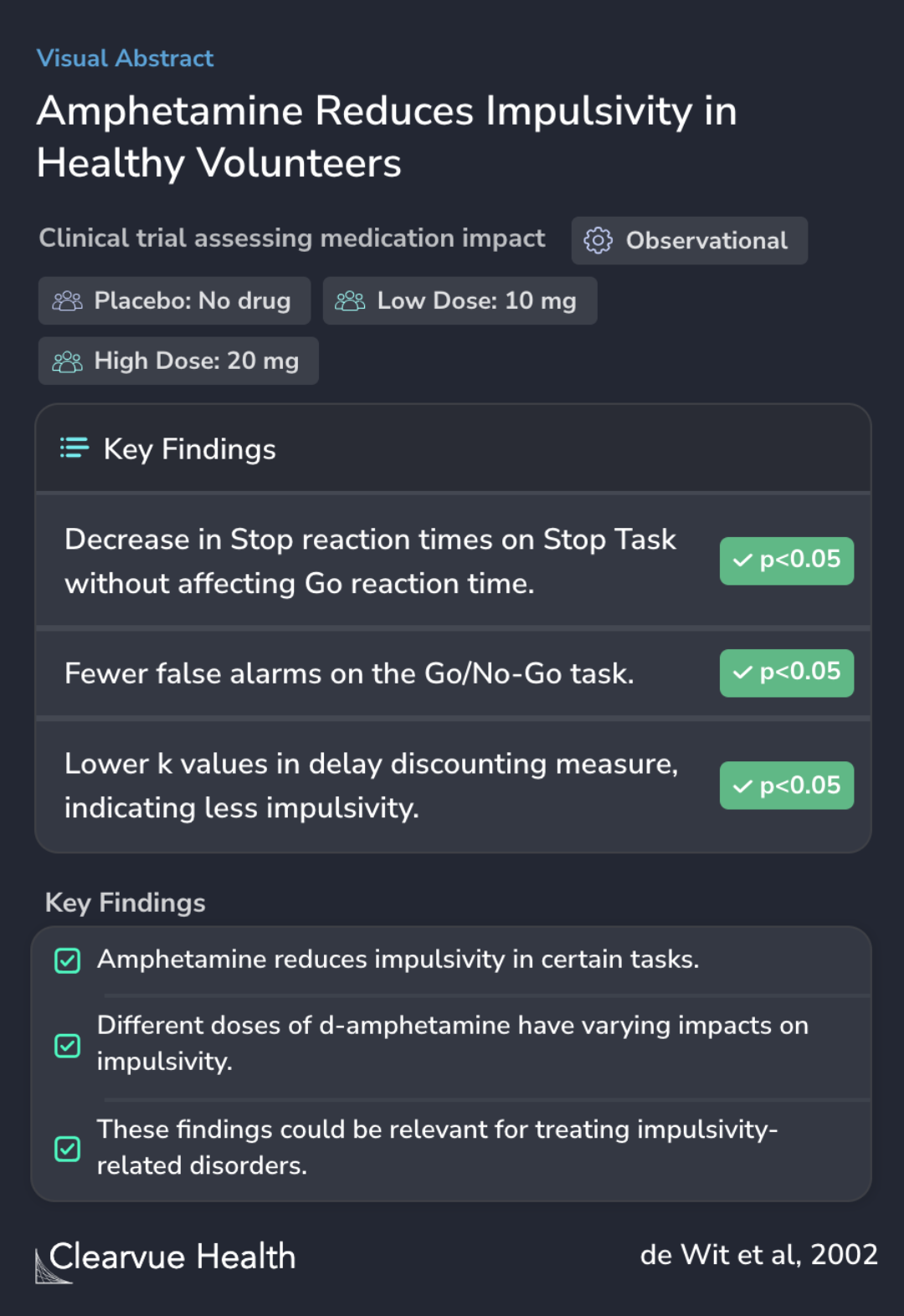
In this clinical trial, 36 healthy men and women participated in a study receiving different doses of d-amphetamine (placebo, 10 mg, or 20 mg) in randomized order over three sessions. They were then asked to complete five tasks designed to measure various aspects of impulsivity. Additionally, mood questionnaires were completed by the participants to assess any emotional changes.
36 healthy men and women participated in three sessions, in which they received placebo, 10 mg, or 20 mg d-amphetamine in randomized order. They performed five tasks to measure impulsivity and also completed mood questionnaires.
Results
The study's findings indicated that healthy individuals showed improved control over impulsivity when administered Adderall. This was evidenced by decreased stop reaction times in a key impulsivity test, fewer false alarms in a Go/No-Go task, and better performance in the delay discounting task, which assesses the ability to wait for greater rewards.
These results suggest that Adderall can positively impact multiple aspects of impulse control.
Amphetamine decreased impulsive responding on three of the tasks: on the Stop Task it decreased Stop reaction times without affecting Go reaction time, on the Go/No-Go task, it decreased the number of false alarms, and on the delay discounting measure, amphetamine (20 mg) decreased k val...
Conclusions
The study's conclusions highlight that amphetamines, such as d-amphetamine, can reduce impulsivity in specific tasks. This finding aligns with other research showing that Adderall can alleviate ADHD symptoms, which include impulsivity.
Impulsivity is linked to negative consequences, including addiction, which underscores the potential significance of these findings in addressing impulsivity-related disorders.
Impulsivity's complex nature and its association with addiction behaviors are further elucidated by noting its multidimensional psychological domains and shared neurobiological mechanisms.
This research adds to the body of evidence indicating that Adderall can be an effective treatment for impulsivity, a factor in both the risk and consequence of drug and alcohol consumption.
Additionally, the study's results are consistent with findings from a comprehensive systematic review and network meta-analysis by Cortese et al. in 2018, which determined the efficacy and tolerability of ADHD medications and highlighted the effectiveness of Adderall in treating ADHD:
These results suggest that acute doses of amphetamine decrease several forms of impulsive behavior. These findings extend and confirm previous findings in humans and laboratory animals.