The risk of treatment-emergent mania with methylphenidate in bipolar disorder
Does Ritalin increase the risk of mania in those with Bipolar Disorder?
Alexander Viktorin, Ph.D., Eleonore Rydén, M.D., Ph.D., Michael E. Thase, M.D., Zheng Chang, Ph.D., Cecilia Lundholm, M.Sc., Brian M. D’Onofrio, Ph.D., Catarina Almqvist, M.D., Ph.D., Patrik K.E. Magnusson, Ph.D., Paul Lichtenstein, Ph.D., Henrik Larsson, Ph.D., Mikael Landén, M.D., Ph.D.
Objective
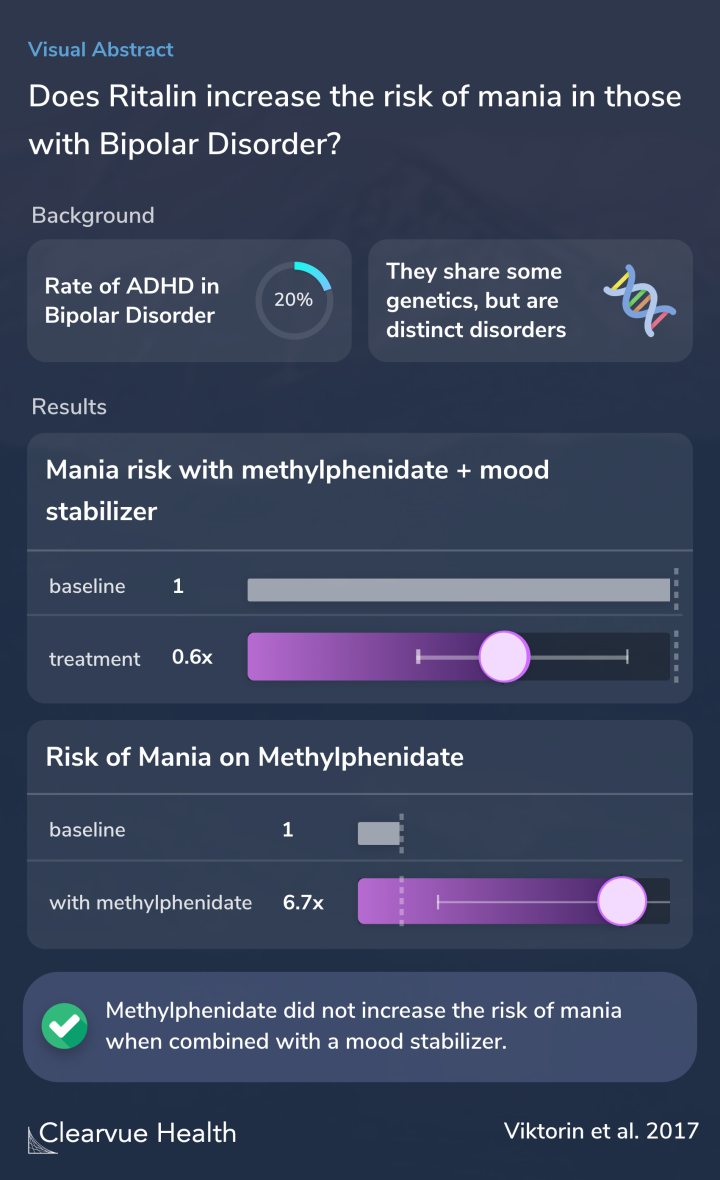
Bipolar disorder and ADHD often occur together. Some studies show that up to 20% of those with bipolar disorder may also have ADHD. ADHD has also been linked to strong mood swings in general:
Having both disorders together is also associated with more severe symptoms overall
Given how common this combination is, researchers wanted to determine whether treating ADHD with Ritalin in individuals with bipolar disorder can cause mania.
To determine the risk of treatment-emergent mania associated with methylphenidate, used in monotherapy or with a concomitant mood-stabilizing medication, in patients with bipolar disorder.
Methods
To conduct the study, researchers combed through medical records in Sweden to identify patients who had bipolar disorder and were taking Ritalin or methylphenidate.
They divided the patients into two groups based on whether they were also taking a mood stabilizer in addition to methylphenidate.
They analyzed the records to see whether the individuals had more episodes of mania before or after starting treatment with Ritalin.
Linking Swedish national registries, we identified 2,307 adults with bipolar disorder who initiated therapy with methylphenidate between 2006 and 2014. The cohort was divided into two groups: with or without concomitant mood-stabilizing treatment. To adjust for individual-specific confou...
Results
Researchers found that patients who were given Ritalin without a mood stabilizer were more likely to experience mania after starting Ritalin.
In this particular study, patients were 6.7 times more likely to experience mania after taking Ritalin alone. This increased risk continued for months.
However, when paired with a mood stabilizer, researchers found that combining the two medications decreased the risk of mania.
This suggests that extra caution should be taken when treating ADHD in patients who also have bipolar disorder.
However, as long as a mood stabilizer medication accompanies it, stimulant medications can be used without increasing the risk of mania in individuals with bipolar disorder.
Patients on methylphenidate monotherapy displayed an increased rate of manic episodes within three months of medication initiation (hazard ratio 6.7, 95% confidence interval: 2.0–22.4), with similar results for the subsequent three months. By contrast, in those taking mood-stabilizers, t...
Conclusions
One of the most critical findings in the study is that patients who are given Ritalin and a mood stabilizer do not have a higher risk of mania. This provides evidence that those with ADHD and bipolar disorder can be safely treated with Ritalin if accompanied by a mood stabilizer.
However, researchers do recommend that bipolar disorder should be ruled out before someone is started on a stimulant.
Not everyone with bipolar disorder knows that they have it, so it’s important to test for it before starting a medication that could worsen bipolar disorder symptoms.
It is important to note that this study has significant limitations.
The study was observational, not a clinical trial, and therefore can’t say for sure that Ritalin was causing mania. There is a possibility that these two factors are correlated rather than causal.
However, it does offer useful insights into a potential risk when treating ADHD in individuals with bipolar disorder.
No evidence was found for a positive association between of methylphenidate and treatment-emergent mania among bipolar disorder patients who were concomitantly receiving a mood-stabilizing medication. This is clinically important given that up to 20% of people with bipolar disorder suffe...