Comparison of On-Road Driving Between Young Adults With and Without ADHD
Driving with ADHD in young adults
Richard L Merkel Jr , J Quyen Nichols , Jonathan C Fellers , Priscilla Hidalgo , Lady A Martinez , Ivan Putziger , Roger C Burket , Daniel J Cox
Objective
Previous studies have shown that young adults with ADHD have more challenges with safe driving. ADHD has been linked to the higher accident and infraction rates.
Since driving is the leading cause of death in teenagers, researchers wanted to understand how young adults with ADHD drive and what potentially dangerous behaviors they might engage in.
This study compared video recordings from routine driving of ADHD and non-ADHD young adults to identify differences in driving behaviors.
Method
Researchers recorded events where a driver rapidly accelerated, turned, or braked with a special video recording device.
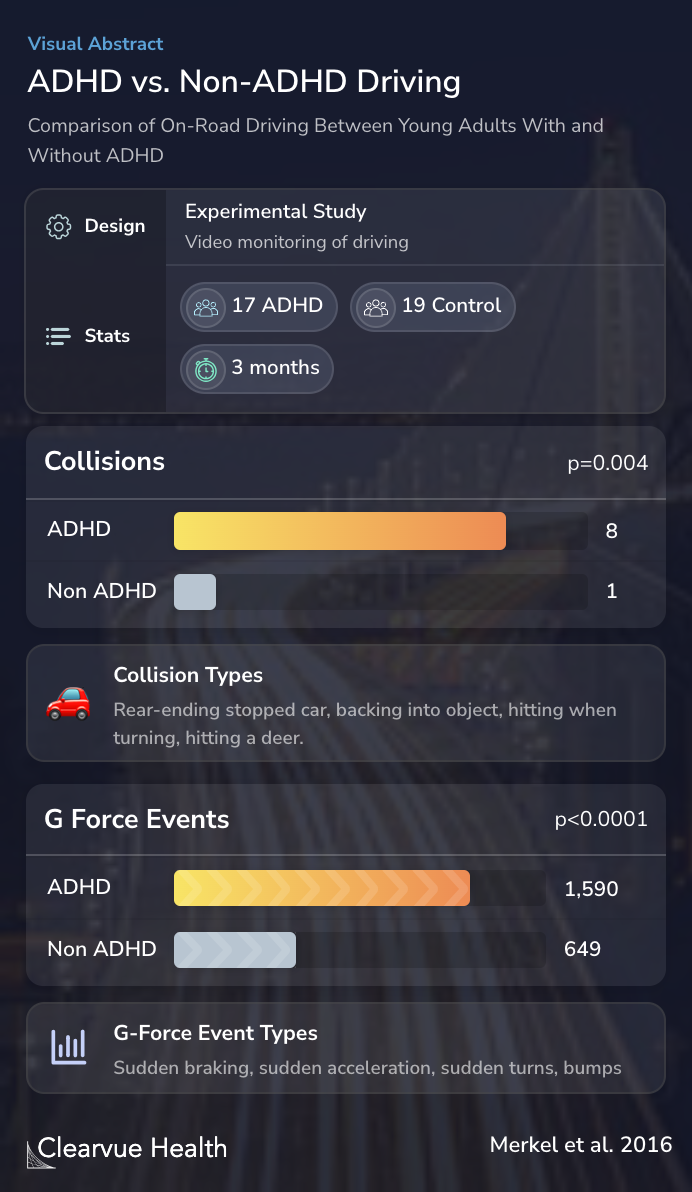
The participants were a group of individuals with ADHD and a closely matched group without ADHD for comparison.
They monitored participants and gathered data for three months.
A matched sample of young adult drivers with and without ADHD are compared via blinded ratings of videoed g-force events recorded by DriveCam technology over 3 months of on-road driving.
Results
Those with ADHD were far more likely to get into car accidents than those without ADHD. In this study, the accidents typically involve hitting stationary objects, an accident where the driver is at fault.
They also had more “g-force” incidents. These include sudden acceleration, braking, and turning. While these aren’t necessarily accidents, they can indicate careless driving.
The researchers also found that the g-force events for drivers with ADHD were noticeably different than for drivers without ADHD.
They were more likely to swerve or brake because of a lack of attention or because of impulsiveness, which are known symptoms of ADHD.
Those without ADHD typically were practicing responsible defensive driving when they swerved or braked.
ADHD drivers were significantly more likely to have more crashes, minor events, and g-force events. G-force events for the ADHD drivers involved significantly more risky and illegal, hyperactive/impulsive, and distracted behaviors. The g-force events of non-ADHD drivers were due to evas...
Conclusion
Based on the study's results, the authors concluded that those with ADHD were more likely to engage in risky or distracted driving and were prone to impulsivity when driving.
These results show some reasons behind the higher accident rates in those with ADHD.
These accident types are also avoidable with good training and awareness. If you or your loved one has ADHD, it can be important to understand how ADHD changes driving so they can be more aware and safer on the road.
Increased risk for ADHD drivers may be the result of increased risk taking, increased hyperactivity/impulsivity or distraction behavior, and increased vulnerability to factors that interfere with driving in general, whereas the consequences of faulty driving were either higher or potenti...