The impact of ADHD symptoms on intelligence test achievement and speed of performance
How ADHD and Test Taking Speed Affect Intelligence Testing
Emily Goodwin, Gisli H. Gudjonsson, Jon Fridrik Sigurdsson, Susan Young

Objectives
Most evaluations of intelligence and cognitive function involve a paper or computerized test, similar to a test you may take at school.
Beyond intelligence, these tests also require some focus and sustained attention, skills that those with ADHD can struggle with.
Researchers wanted to see whether ADHD is linked with underperformance in cognitive testing. If so, many intelligence tests may underestimate those with ADHD because their symptoms are getting in the way.
There is evidence of an association between Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and impaired performance on neuropsychological tests. Nevertheless, there is a dearth of research on this topic, particularly among forensic populations where rates of ADHD are notably high. This ...
Methods
Researchers conducted a small study on 73 Icelandic male prisoners. They evaluated the prisoners for ADHD symptoms and conducted cognitive testing. This way, they can correlate ADHD with IQ test performance.
Forty three Icelandic male prisoners were screened for childhood ADHD using the Wender Utah Rating Scale (WURS), and for adult ADHD using the DSM-IV checklist of symptoms. IQ was measured using the Ravens Standard Progressive Matrices (RSPM) total score, and test completion time was also...
Results
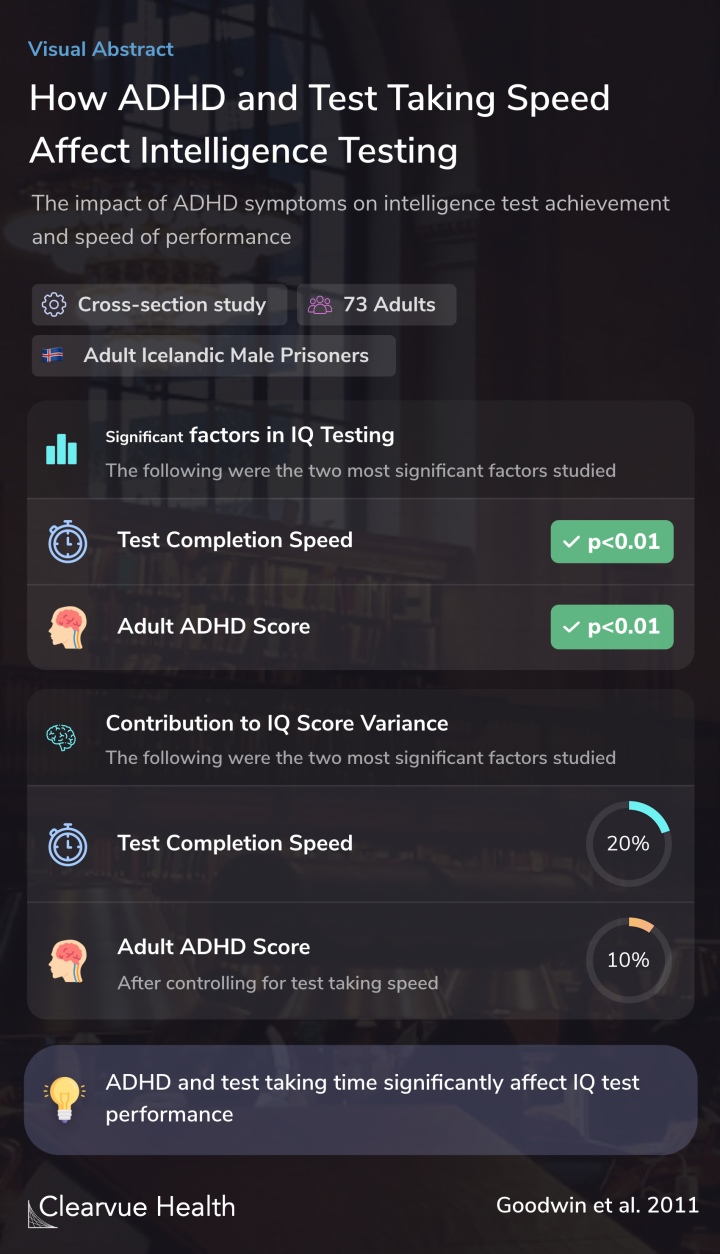
Researchers found strong links between IQ scores, test completion speed, and ADHD symptoms.
Those who took longer to think throughtheir answers tended to score lower on intelligence testing. Those who had stronger ADHD symptoms also did worse.
Around 20% of the differences in IQ test score was explained by the speed at which someone completes the test.
Since those with ADHD tend to take longer to finish tests, this result suggests that we may be underestimating the intelligence of those with ADHD based on IQ testing.
Through statistical analysis, researchers found that an additional 10% of the test score variance was linked with ADHD symptoms beyond just slow test-taking speed.
Multiple regression analysis indicated that intellectual performance was significantly negatively affected by fast test completion time (medium effect size), but even after controlling for this, performance was further impaired by adult ADHD symptoms (large effect size).
Conclusions
There is a complicated relationship between ADHD and IQ. While we know that ADHD can affect individuals with all levels of intellect, there’s also been evidence linking ADHD with underperformance on IQ tests.
ADHD symptoms may explain some of this link. Those with ADHD take longer to finish tests and answer questions. ADHD symptoms themselves significantly contribute to IQ underperformance, according to these data.
These results suggest that a low IQ test score for someone with ADHD doesn’t necessarily reflect their intellect. At least for some with ADHD, it may be due to their ADHD symptoms.
The results indicate that ADHD symptoms in adulthood adversely affect intellectual test performance above the speed of performance alone.