Predictors of Response and Mechanisms of Change in an Organizational Skills Intervention for Students with ADHD
Improving ADHD Students' Organization Skills with HOPS
Langberg JM, Becker SP, Epstein JN, Vaughn AJ, Girio-Herrera E
Objectives
This study aimed to assess how effective the Homework, Organization, and Planning Skills (HOPS) intervention is for middle school students diagnosed with ADHD. Specifically, it looked at what factors contribute to the success of this program in improving organizational skills in these students.
The purpose of the study was to evaluate predictors of response and mechanisms of change for the Homework, Organization, and Planning Skills (HOPS) intervention for middle school students with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Methods
Twenty-three middle schoolers with ADHD participated in the HOPS program. They worked with school mental health professionals to enhance their ability to organize and plan. The study considered various factors, including the students' backgrounds, the severity of their ADHD symptoms, and whether they were taking ADHD medication. It also examined how well the students adopted the organizational strategies taught in the HOPS program and the quality of their relationship with their therapists.
The intervention program used 16 sessions to help students improve their skills in organizing and planning.
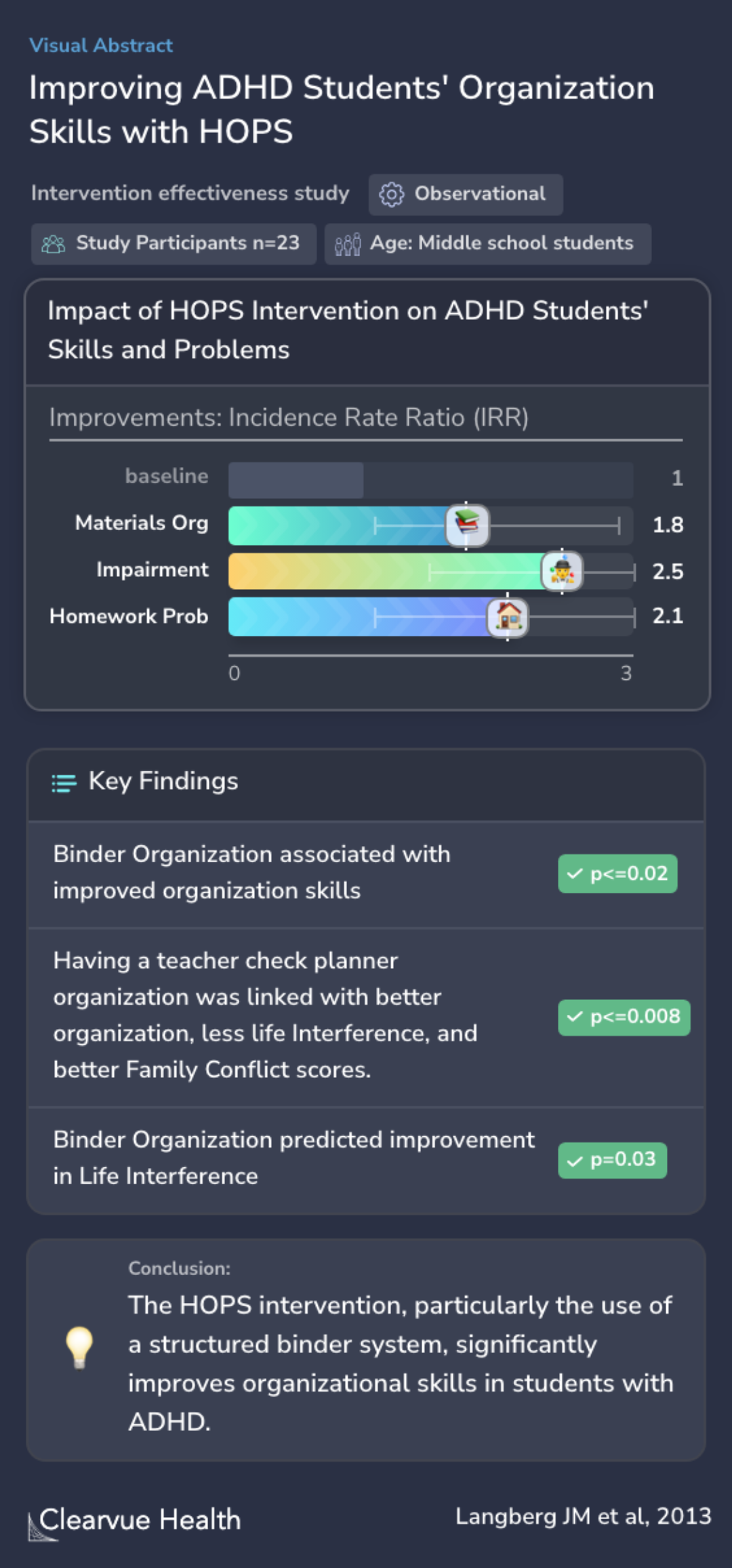
Twenty-three middle school students with ADHD (grades 6-8) received the HOPS intervention implemented by school mental health providers and made significant improvements in parent-rated materials organization and planning skills, impairment due to organizational skills problems, and home...
Results
The students showed notable improvements in organizing their school materials and managing their homework, based on feedback from their parents. Those who actively used the HOPS binder system for organizing schoolwork saw the most significant progress.
Twenty-three middle school students with ADHD (grades 6-8) received the HOPS intervention and made significant improvements in parent-rated materials organization and planning skills (IRR = 1.8, 95% CI [1.1,2.9]), impairment due to organizational skills problems (IRR = 2.5, 95% CI [1.5,4...
Conclusions
The findings highlight the effectiveness of structured organizational systems, like the HOPS binder, in improving organizational skills among students with ADHD. This underscores the importance of tailored organizational strategies in enhancing academic performance for students facing ADHD challenges.
These findings demonstrate the importance of teaching students with ADHD to use a structured binder organization system for organizing and filing homework and classwork materials and for transferring work to and from school.
Key Takeaways
Context
This study's insights are part of a larger body of research on ADHD and organizational skills. Similar studies have shown beneficial results in various age groups. For instance, a 2022 study by Hartung et al. revealed that an intervention significantly improved organizational and study skills in college students with ADHD.
Additionally, research by Abikoff et al. in 2009 found that ADHD medications like Ritalin also contributed to improved organizational skills in children with ADHD. Together, these studies emphasize the value of both skill-building interventions and medication in managing ADHD effectively.