Association between Internet gaming disorder and adult attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder and their correlates: Impulsivity and hostility
Link Between Online Gaming Disorder, Adult ADHD, and Behavioral Traits
Yen JY, Liu TL, Wang PW, Chen CS, Yen CF, Ko CH
Objectives
The study aims to explore the connection between Internet gaming disorder (IGD), attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), impulsivity, and hostility. It specifically looks at how ADHD, impulsivity, and hostility are related to IGD.
Internet gaming disorder (IGD) and attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are associated with impulsivity and hostility. This study evaluated the associations among ADHD, impulsivity, hostility, and IGD.
Methods
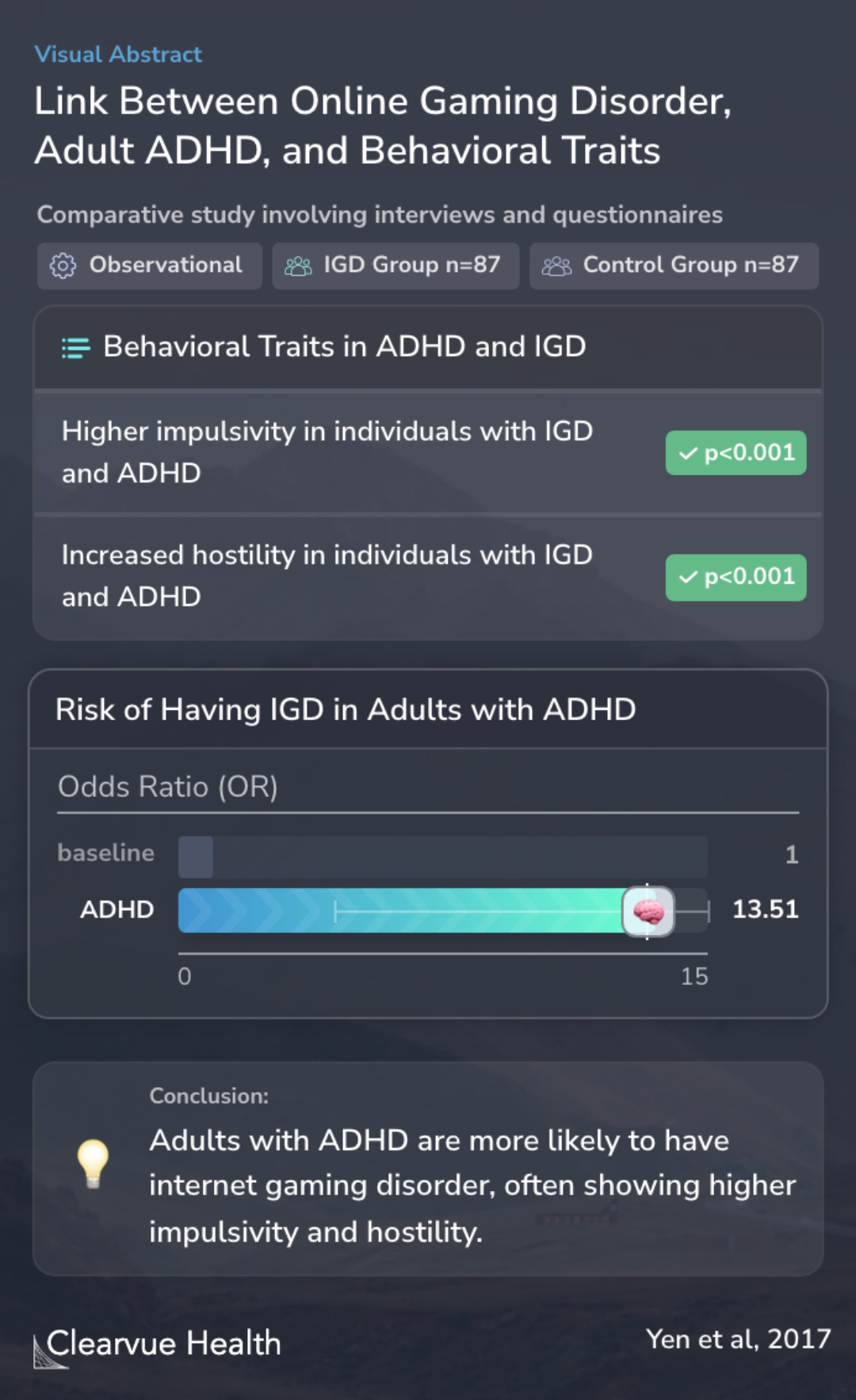
To understand these connections, the study involved 174 participants, split into two groups: 87 individuals with IGD and 87 without a history of IGD. All participants were evaluated through interviews and questionnaires based on specific criteria for IGD and ADHD. They also answered questions about their impulsivity and hostility levels.
We recruited 87 individuals with IGD and 87 controls without a history of IGD. All participants underwent a diagnostic interview based on the DSM-5 IGD criteria and DSM-IV-TR ADHD criteria and completed a questionnaire regarding impulsivity and hostility. The information from the diagnos...
Results
The findings of the study revealed significant links between IGD and ADHD. Particularly, young adults with both IGD and ADHD showed higher levels of impulsivity and hostility compared to others. This suggests that these behavioral traits might play a role in the relationship between ADHD and IGD.
The study also highlighted that adults with ADHD are much more likely to experience IGD. This points to a strong relationship between these two conditions.
The results suggested that IGD is associated with ADHD among young adults and that young adults with both IGD and ADHD have higher impulsivity and hostility. Furthermore, impulsivity and hostility mediate the association between ADHD and IGD.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study underscores ADHD as a common factor in IGD among young adults. Importantly, impulsivity and hostility are critical elements in this relationship. This finding emphasizes the need for thorough assessment and intervention strategies for young adults with ADHD, focusing on these behavioral traits to effectively address IGD.
Thus, ADHD is a common comorbidity of IGD among young adults, and impulsivity and hostility are major factors involved in comorbid ADHD and IGD. Young adults with ADHD should be thoroughly assessed, particularly for their impulsivity and hostility, and interventions for IGD should be dev...
Key Takeaways
Context
Impulsivity, a vital focus of this study, is often linked with negative consequences. It can lead to intrusive behaviors in social interactions, addictions, and reckless decisions without considering the outcomes. This is especially significant in the context of ADHD, where impulsivity is a central symptom, leading to hasty conclusions and impatience. The study’s findings on impulsivity's role in IGD among adults with ADHD resonate with these broader observations, highlighting the multidimensional impact of impulsivity on both psychological and physical health.
Additionally, the causes of impulsivity, such as brain structure damages, play a critical role in various disorders: