Risk of Irritability With Psychostimulant Treatment in Children With ADHD: A Meta-Analysis
Zachary D Stuckelman , Jilian M Mulqueen , Eduardo Ferracioli-Oda , Stephanie C Cohen , Catherine G Coughlin , James F Leckman , Michael H Bloch
Many children and adults with ADHD experience irritability. In certain cases, medication for ADHD can make this worse. Some patients and parents are so concerned about irritability that they avoid taking medication for ADHD.
Objective
ADHD medication can cause irritability in some people. It can also reduce irritability for others if irritability is one of their ADHD symptoms.
This apparent contradiction can make it difficult when deciding which ADHD treatment to take.
The researchers of this study wanted to measure the risk of irritability as a side effect of ADHD medication.
Irritability is listed as a common side effect of psychostimulant medications. However, psychostimulants have been demonstrated as an effective treatment in reducing irritability and aggression in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The goal of this study was t...
Data sources and study selection
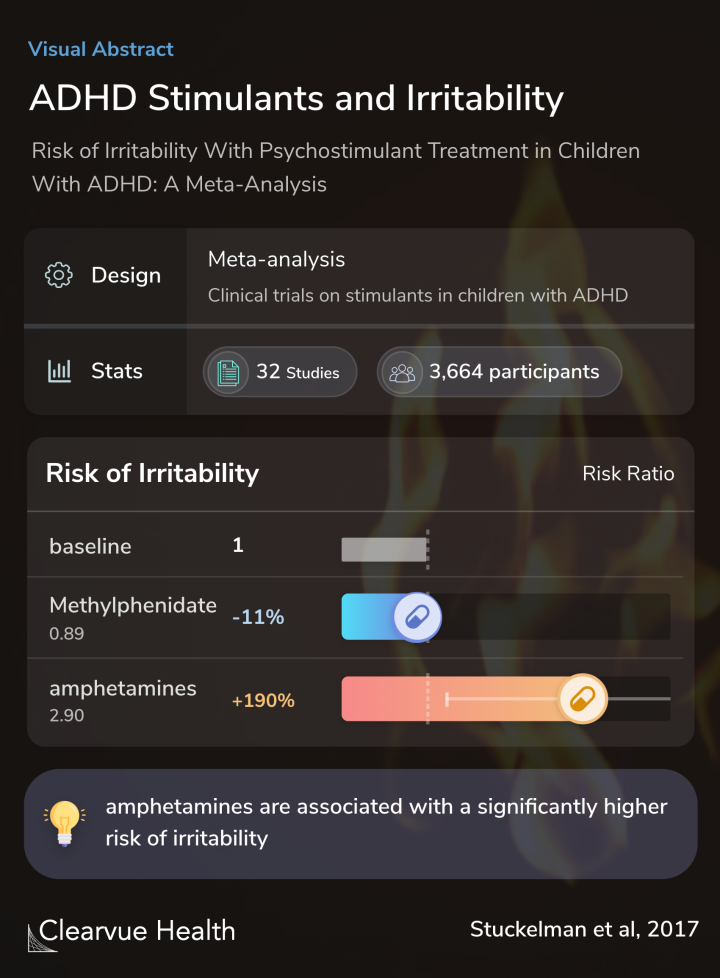
Researchers collected 32 studies that measured irritability among kids given stimulant medication for their ADHD.
Researchers conducted a meta-analysis to measure the effect of medication on irritability.
A PubMed search was conducted on August 18, 2013, to identify all double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials published in English examining the efficacy of psychostimulant medications in the treatment of children with ADHD. Trials were excluded if (1) they required additional ps...
Results
The data in the study confirmed that there might be a risk of irritability with stimulant treatments for ADHD. However, surprisingly, this risk is only significant with amphetamines, otherwise known as Adderall
Children who were given Ritalin, also known as methylphenidate, actually experienced less irritability with treatment. In these cases, it is possible that irritability is an ADHD symptom that can be improved with the right medication.
Children who were given amphetamines, on the other hand, had nearly triple the risk of irritability compared to those who did not receive amphetamines.
This provides strong evidence that amphetamines can cause irritability as a side effect.
From 92 potentially eligible trials, the meta-analysis identified 32 trials involving 3,664 children with ADHD that reported data on irritability as a side effect. The relative risk of irritability significantly differed between psychostimulant classes (test for subgroup differences χ21 ...
Conclusions
This study provides evidence that amphetamines increase the risk of irritability—Methylphenidate, or Ritalin, may be a better option when irritability is a concern.
However, because of the design of this study, we will need more research before we know for sure. Ideally, clinical trials measuring irritability risk between the two medications will provide the highest quality evidence.
This meta-analysis suggests an increased risk of irritability may be confined to amphetamine-derived psychostimulants. Future meta-analyses examining the effects of amphetamine and methylphenidate derivatives on irritability as a continuous measure, as well as head-to-head trials between...
