Academic Motivation Deficits in Adolescents with ADHD and Associations with Academic Functioning
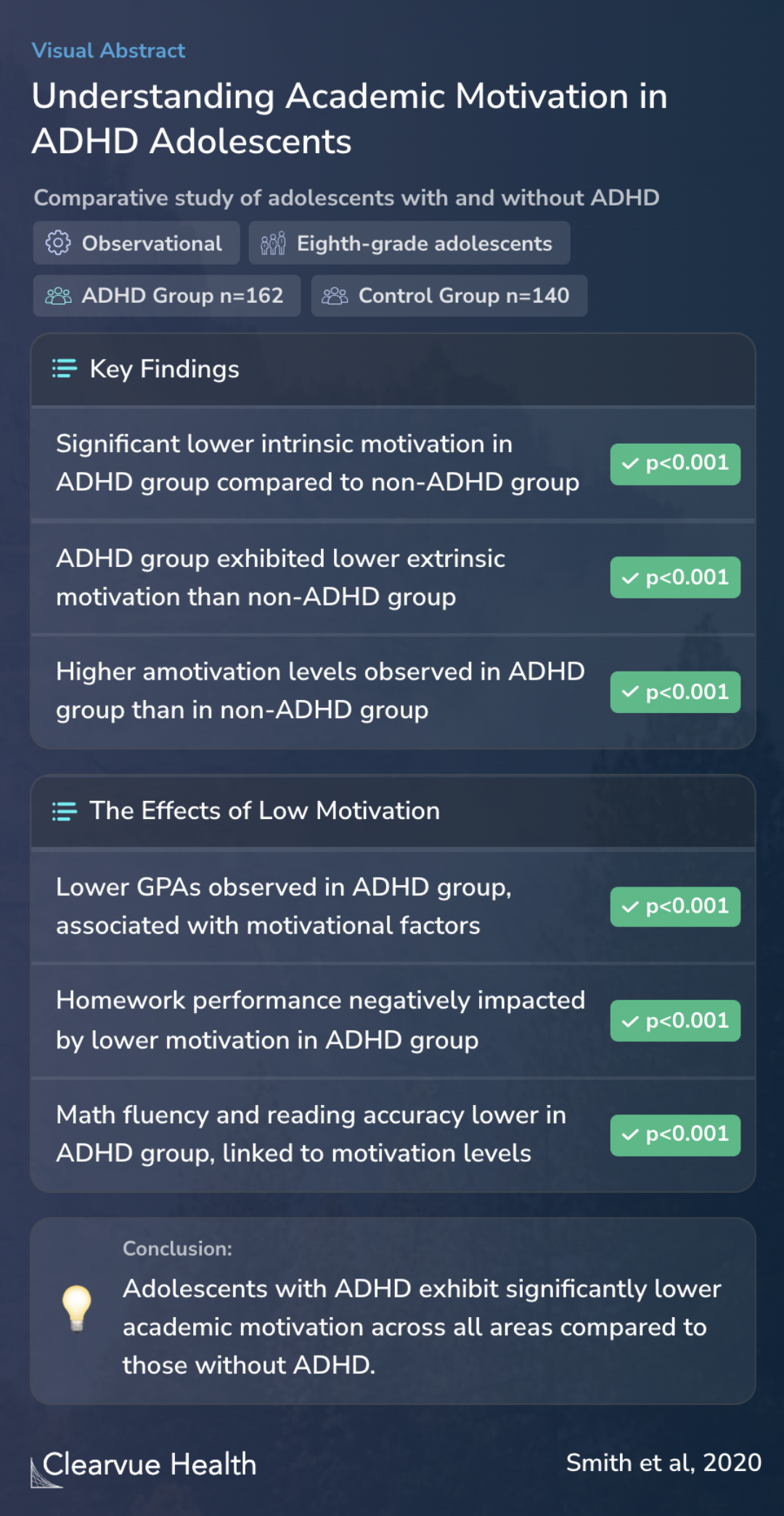
Understanding Academic Motivation in ADHD Adolescents
Zoe R Smith, Joshua M Langberg, Caroline N Cusick, Cathrin D Green, Stephen P Becker
Objectives
The present study delves into the academic motivation of eighth-grade students, specifically contrasting those with ADHD against their peers without this condition.
The present study evaluates differences in self-reported intrinsic and extrinsic academic motivation and amotivation between eighth-grade adolescents with (n = 162) and without (n = 140) ADHD.
Methods
In this comparative study, researchers utilized multivariate analysis of variance. This approach was critical to account for variables such as sex, intelligence, and medication status, ensuring a more accurate assessment of motivation differences between adolescents with and without ADHD.
Multivariate analysis of variance controlling for sex, intelligence, and medication status.
Results
The findings showed that adolescents with ADHD demonstrated significantly lower intrinsic motivation compared to their non-ADHD counterparts. This was evident across all areas of academic motivation, including extrinsic motivation and amotivation. This suggests a broad motivational deficit in students with ADHD, impacting various aspects of their academic life.
Adolescents with ADHD exhibited a significant motivational deficit compared to adolescents without ADHD across all areas of academic motivation, including intrinsic motivation (d = 0.49), extrinsic motivation (d = 0.43), and amotivation (d = 0.42).
Conclusions
The study found evidence that adolescents with ADHD face substantial challenges in maintaining academic motivation. This insight builds upon existing research, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to boost academic drive and success in this group. Understanding the longitudinal effects of motivation on academic performance in ADHD is vital for developing effective strategies.
This study builds upon previous research in demonstrating that adolescents with ADHD have academic motivational deficits when compared to their peers without ADHD. Research is needed to understand the longitudinal interplay of academic motivation and academic functioning, with an eye tow...
Context
The current study fits into a broader research context that examines the link between motivation and ADHD. For instance, a study by Volkow et al. in 2011 revealed that ADHD is associated with dysfunction in the brain’s dopamine reward pathway, affecting motivation. This aligns with the recent findings that ADHD impacts academic motivation.
Additionally, research by Dovis et al. in 2012 showed that while incentives like money and gaming improve task persistence in children with ADHD, they do not normalize working memory. This suggests that while motivation can be externally influenced, underlying cognitive challenges remain. These studies collectively shed light on the complex interplay between motivation, reward pathways, and cognitive functions in ADHD.